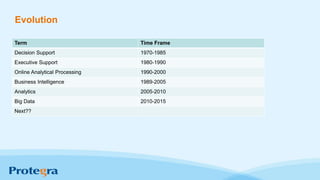
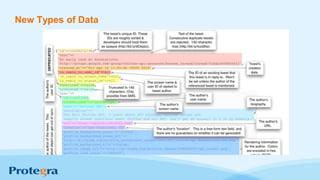
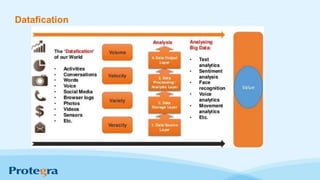
The document explores the significance and evolution of big data, debunking common myths and highlighting its rapid growth in recent years. It emphasizes the technology enabling big data analytics, such as Hadoop, and discusses various applications ranging from predictive policing to healthcare cost savings. Additionally, it outlines important strategies for businesses to effectively leverage big data for better decision-making and innovation.