This document provides an overview of big data, including:
- A brief history of big data from the 1920s to the coining of the term in 1989.
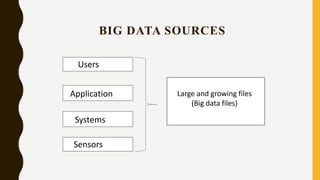
- An introduction explaining that big data requires different techniques and tools than traditional "small data" due to its larger size.
- A definition of big data as the storage and analysis of very large digital datasets that cannot be processed with traditional methods.
- The three key characteristics (3Vs) of big data: volume, velocity, and variety.