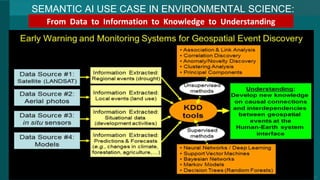
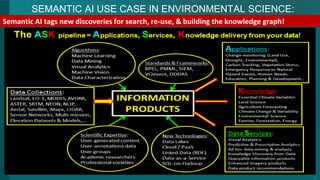
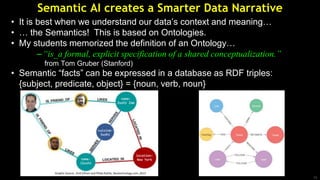
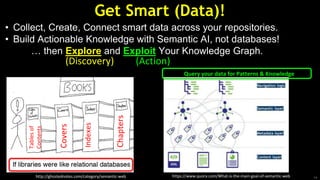
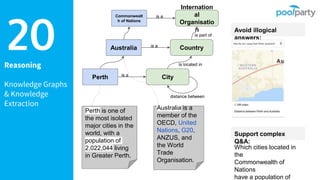
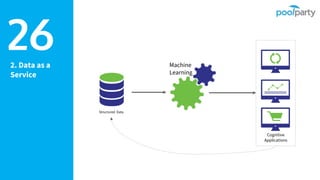
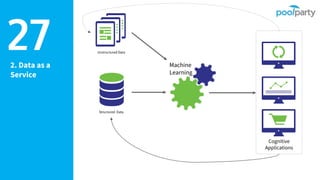
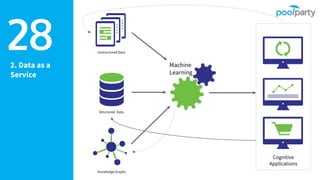
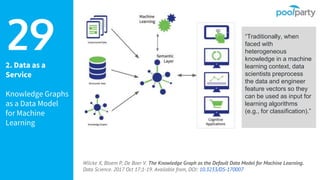
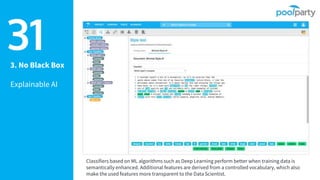
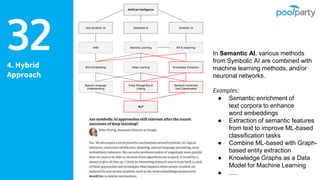
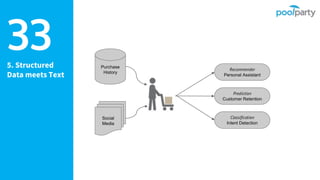
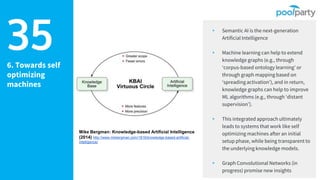
The document discusses Semantic AI and its six core aspects, emphasizing the importance of data quality, the hybrid approach of integrating symbolic and statistical AI, and the need for transparency in AI systems. It highlights the role of Semantic AI in enhancing machine learning through ontologies, taxonomies, and linked data, contributing to smarter and actionable intelligence in contexts like environmental science and the Internet of Things. The ultimate aim is to evolve towards self-optimizing machines that leverage knowledge graphs for improved AI governance and operational efficiency.






![1) Class Discovery: Find the categories of objects
(population segments), events, and behaviors in your
data. + Learn the rules that constrain the class
boundaries (that uniquely distinguish them).
2) Correlation (Predictive and Prescriptive Power)
Discovery: Finding trends, patterns, dependencies in
data, which reveal the governing principles or behavioral
patterns (the object’s “DNA”).
3) Novelty (Surprise!) Discovery:
Finding new, rare, one-in-a-[million / billion / trillion]
objects, events, or behaviors.
4) Association (or Link) Discovery: (Graph and Network
Analytics) – Find the unusual (interesting) co-occurring
Make your data smarter with Machine Learning =
= generate semantic tags that describe discoveries
10
(Graphic by S. G. Djorgovski, Caltech)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/brighttalksemanticai-180523122111/85/BrightTALK-Semantic-AI-10-320.jpg)