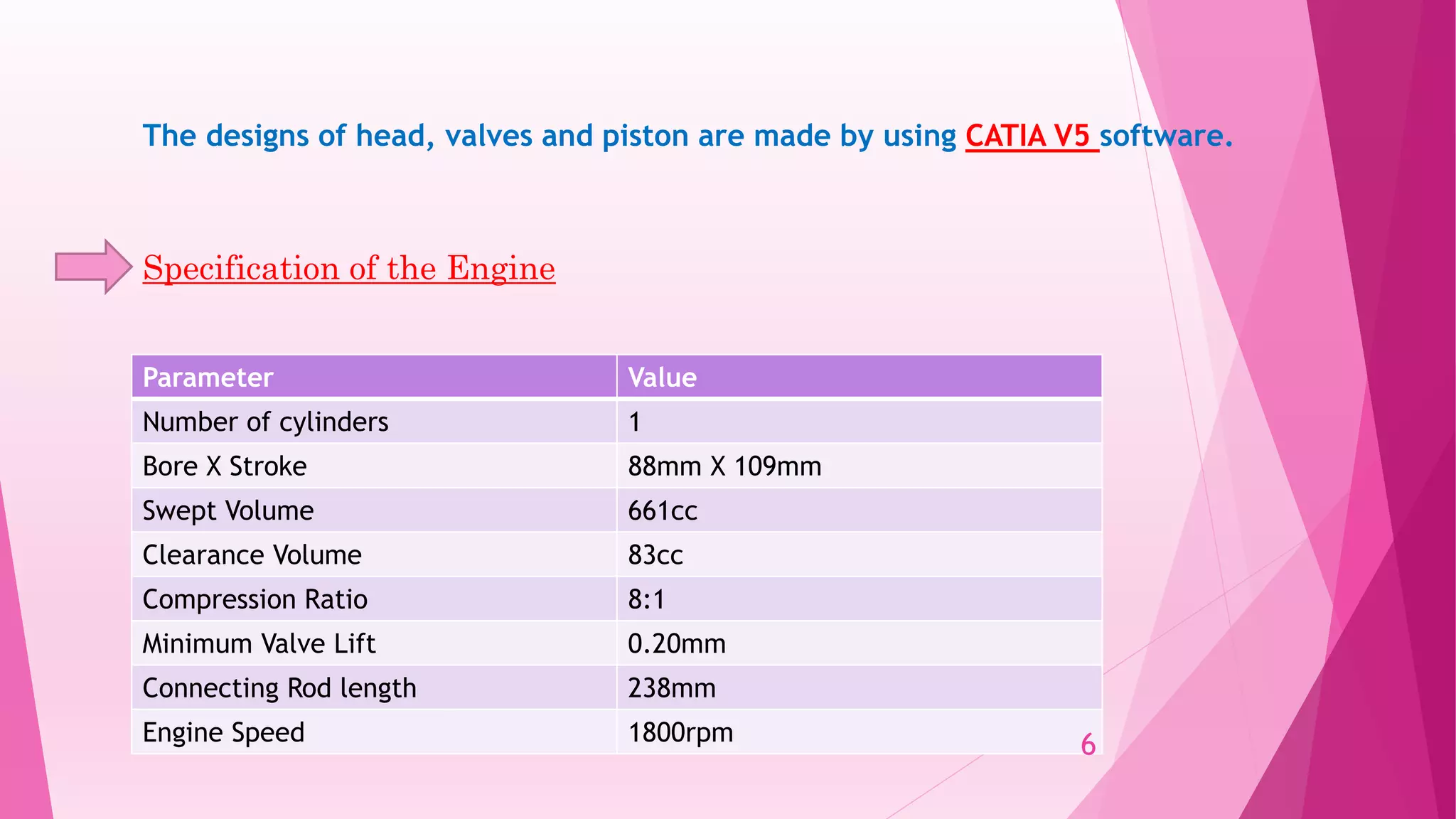
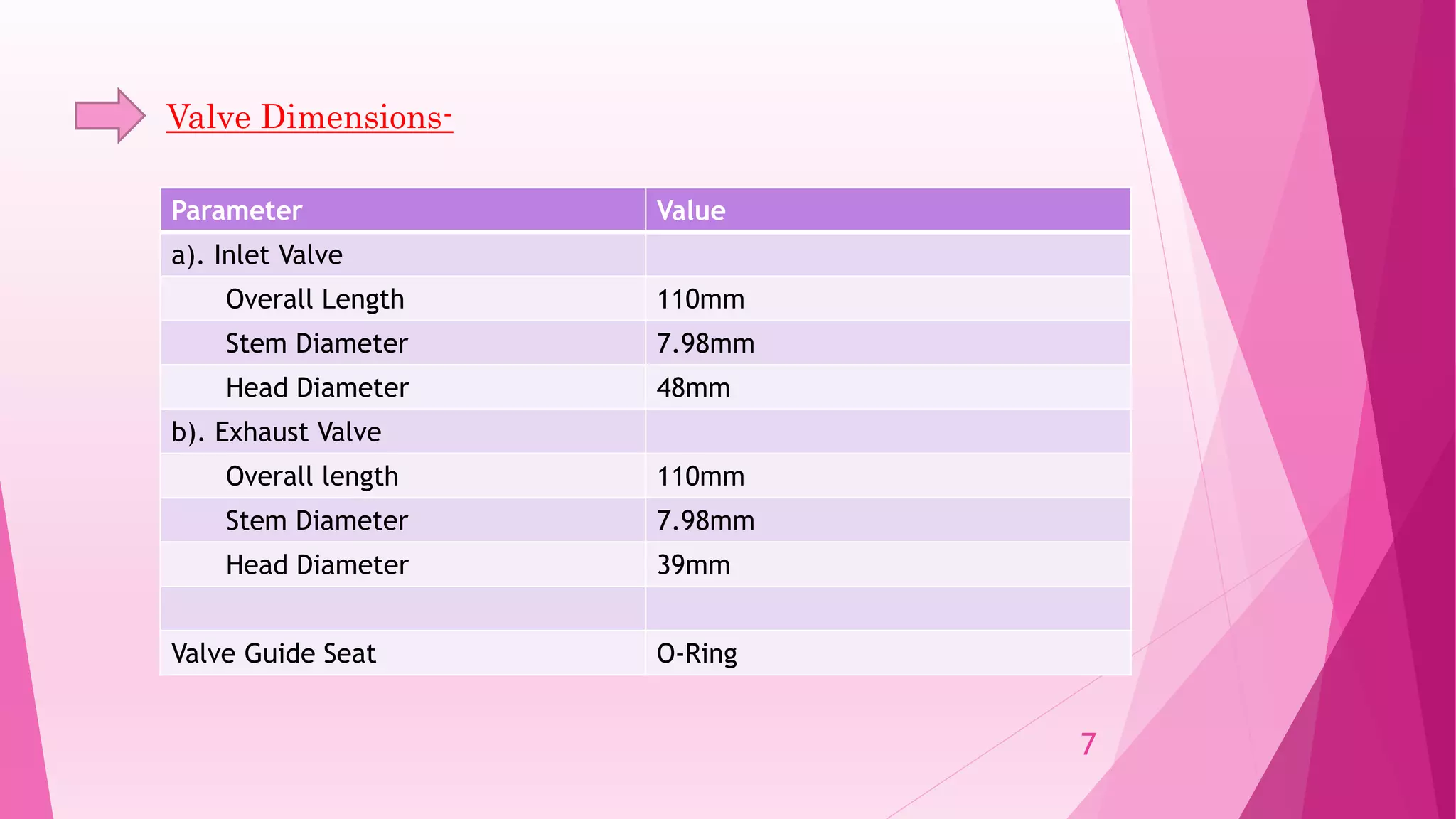
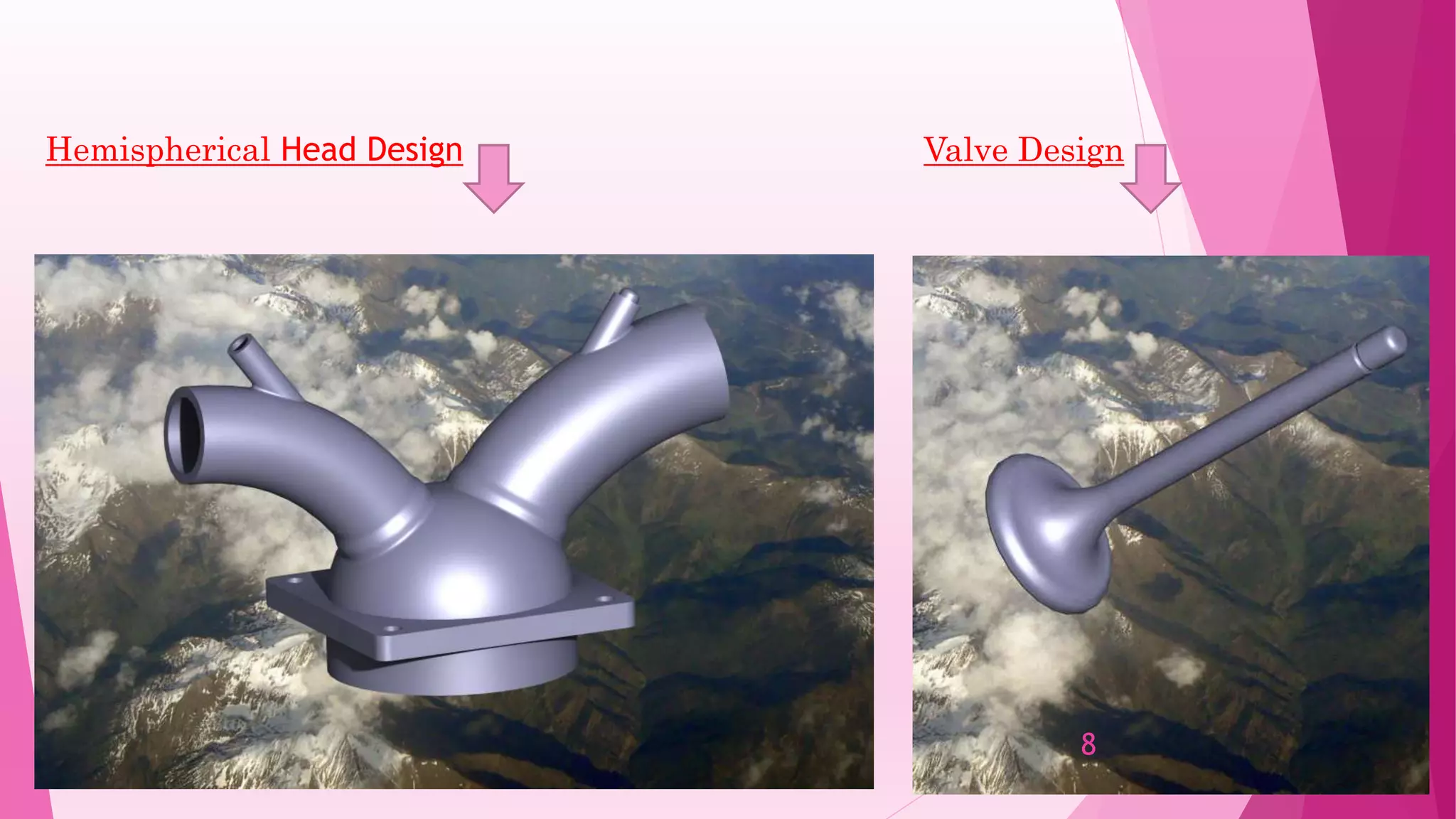
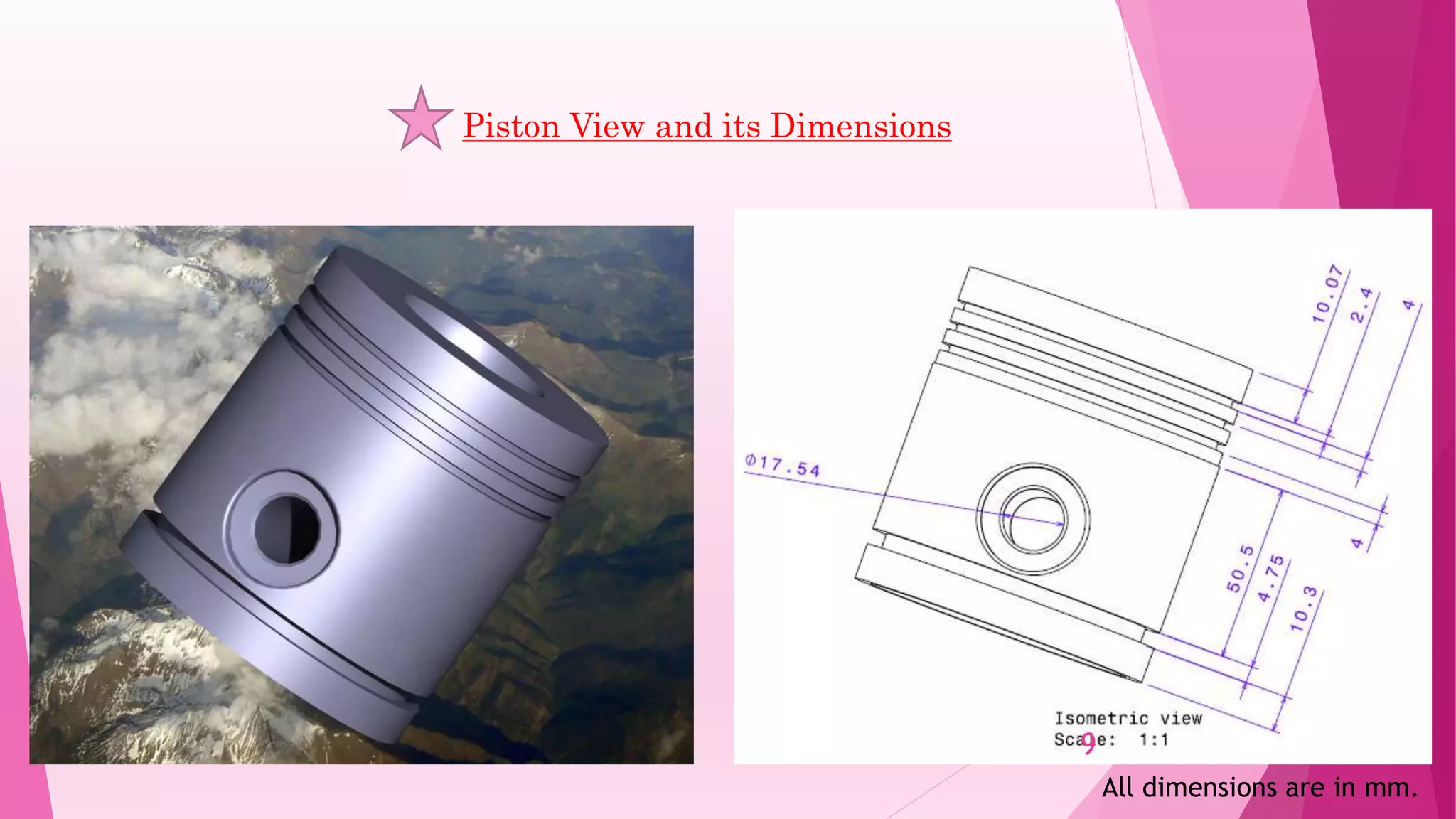
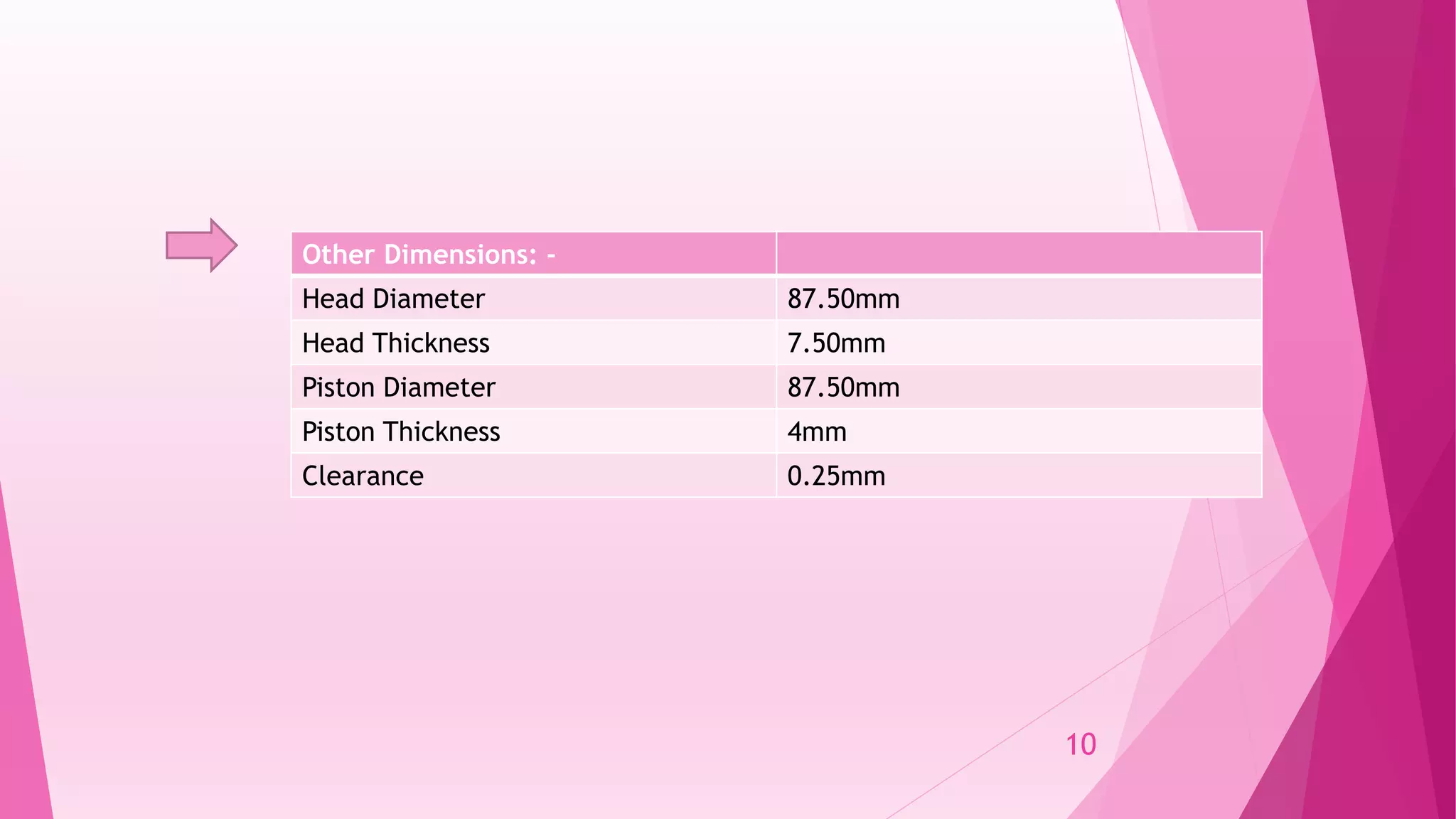
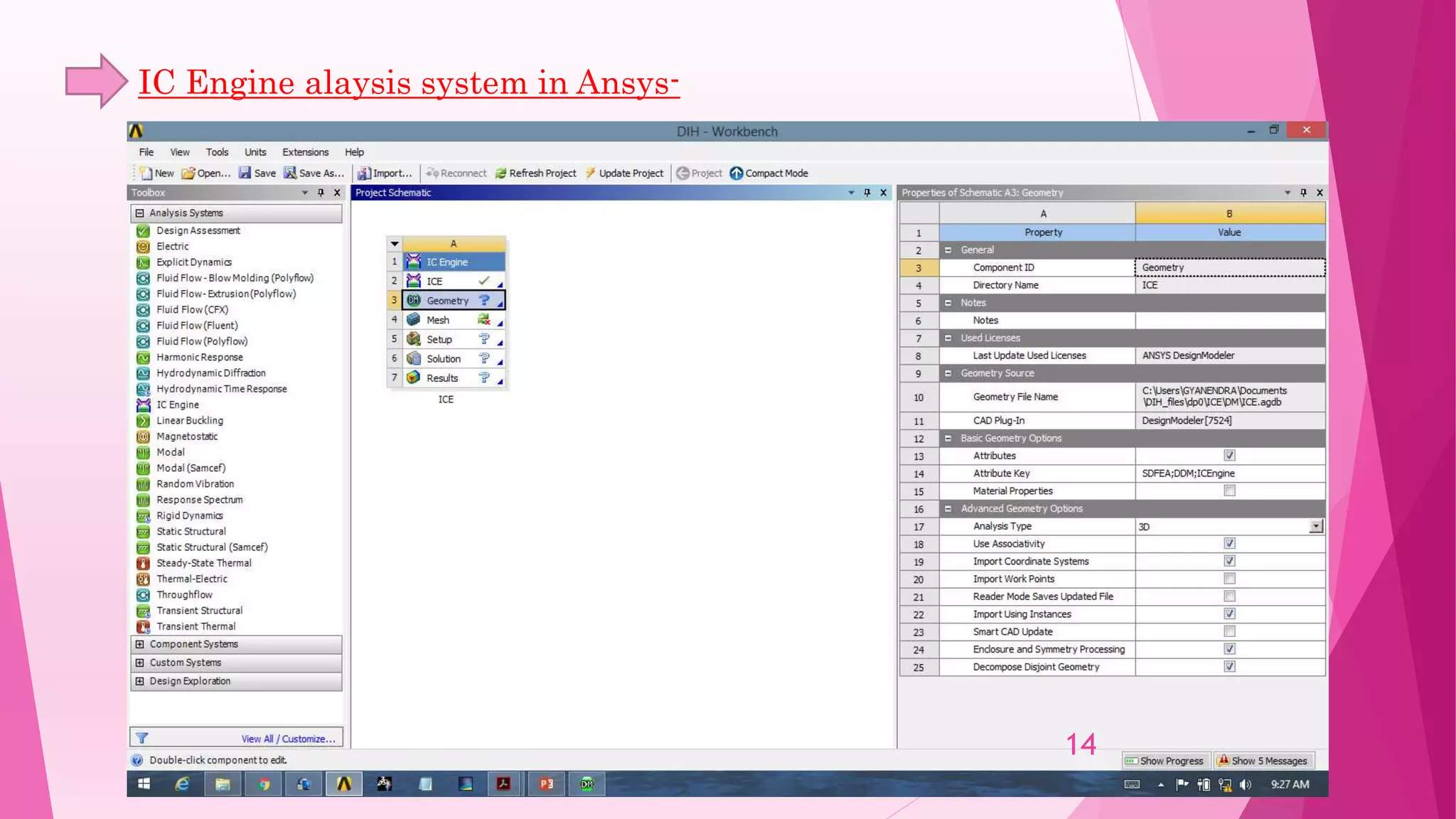
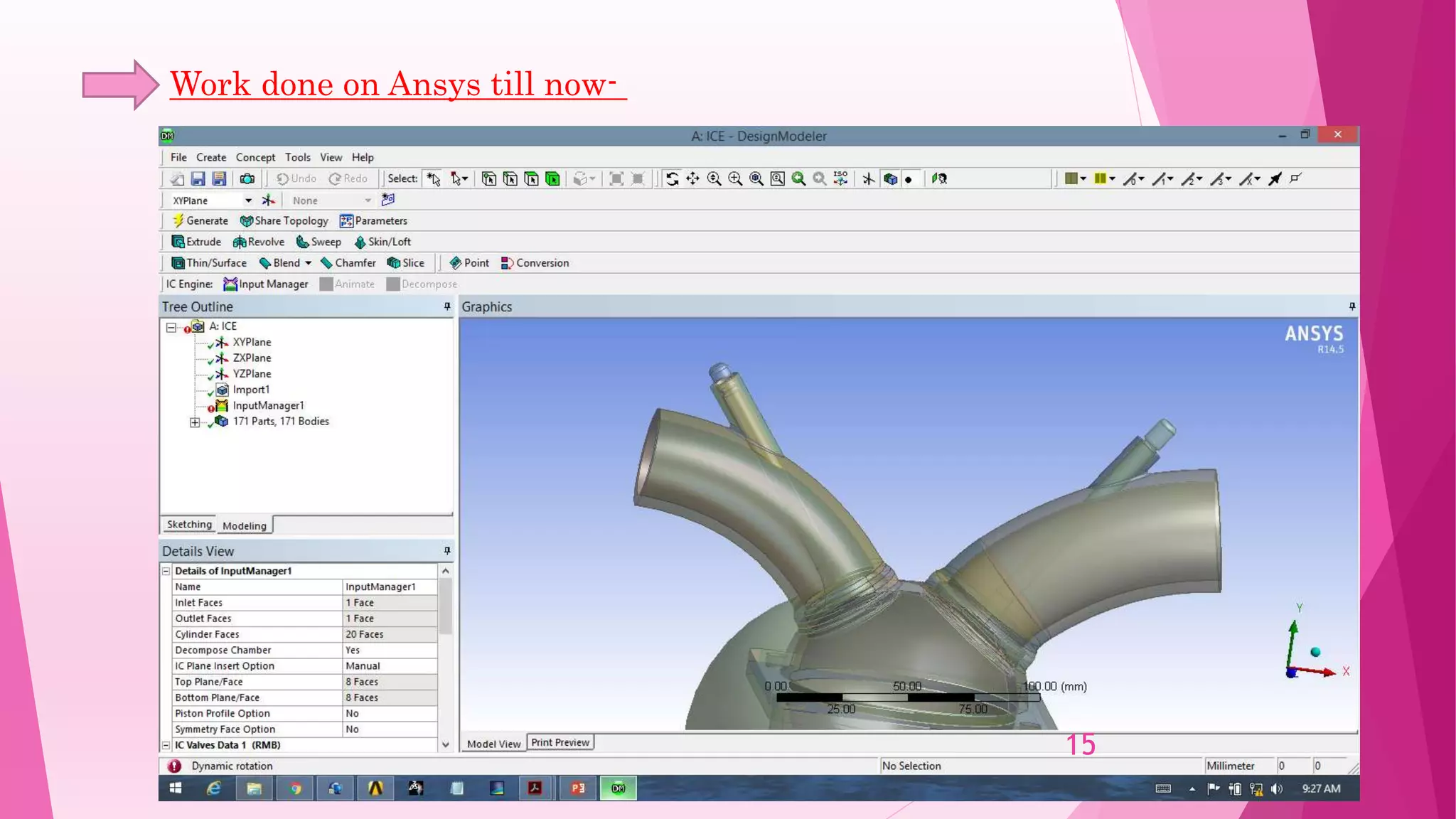
This document summarizes the design and analysis of a single cylinder hemispherical combustion chamber engine using ANSYS. It outlines the primary design decisions for an engine, describes the different types of combustion chambers and why a hemispherical chamber was chosen. It provides the specifications and dimensions of the engine components modeled in CATIA and analyzed in ANSYS including the valves, piston, combustion chamber geometry. The document discusses the different types of analyses that can be done in ANSYS including cold flow, combustion and emissions and summarizes the objectives and references for the study.