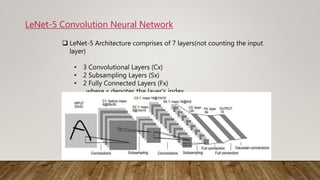
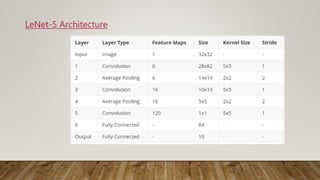
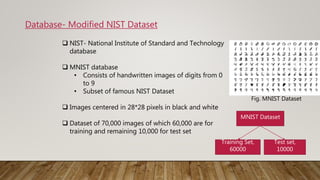
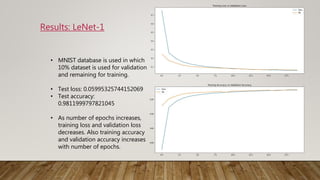
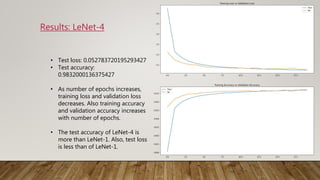
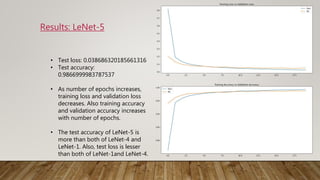
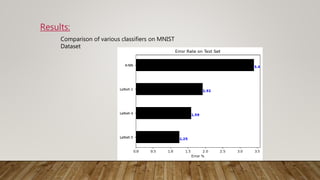
The document discusses the application of gradient-based learning for document recognition, highlighting the Lenet-5 architecture introduced by Yann LeCun and others in 1998. It details the structure and functioning of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and compares different versions of the Lenet architecture (Lenet-1, Lenet-4, and Lenet-5) using the MNIST handwritten digit dataset. Results show that as model complexity increases, test accuracy improves while test loss decreases.