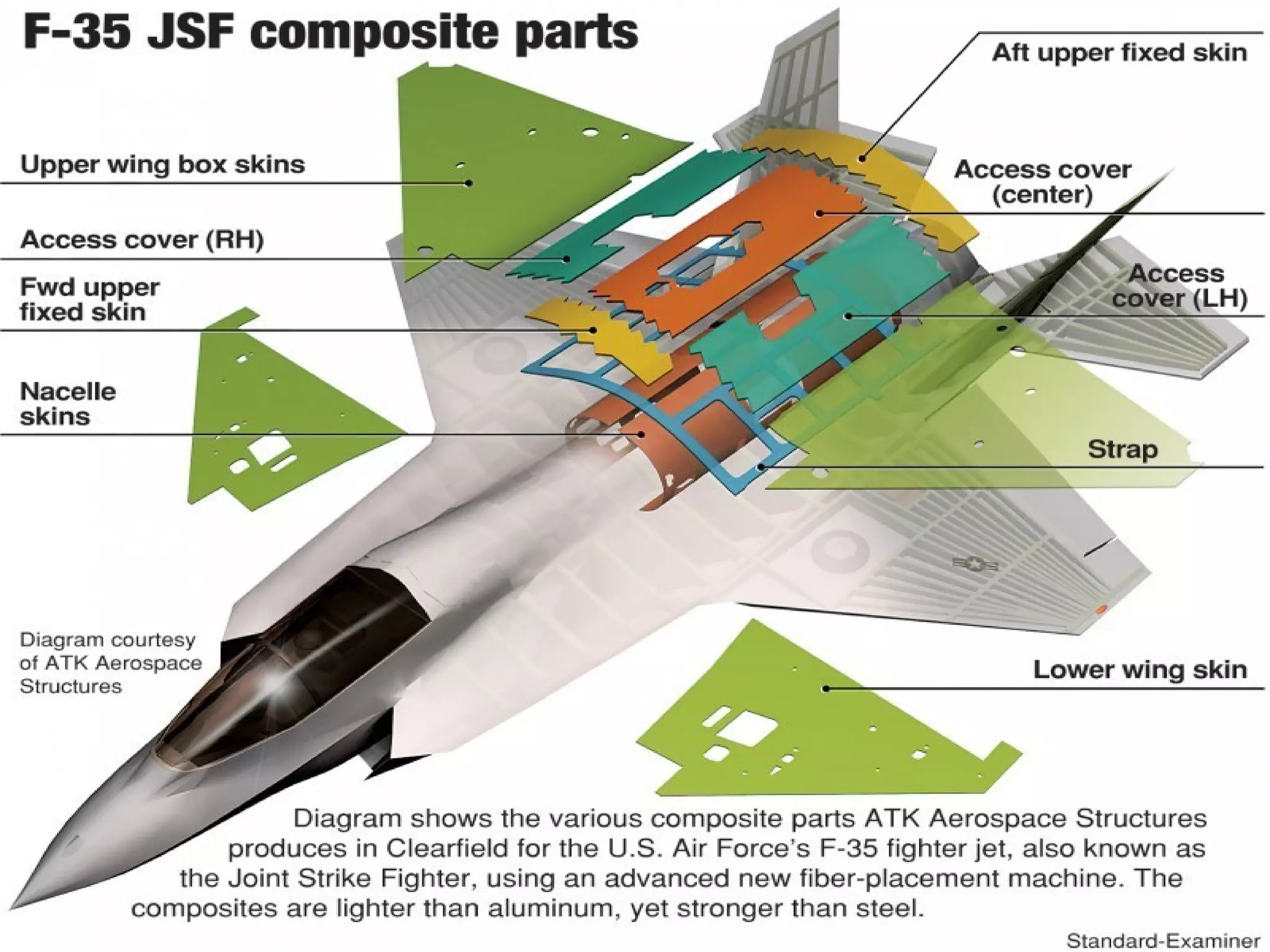
This document provides an overview of advanced composites. It begins with early forms of composites like mud bricks and plywood. It then defines advanced composites as consisting of fiber cloth and resin. Some advantages are listed as low weight and high strength, while disadvantages include high costs and difficulty detecting hidden damage. The document outlines different types of composites like carbon fiber, Kevlar, and boron, and discusses proper storage, handling and safety procedures when working with composites.