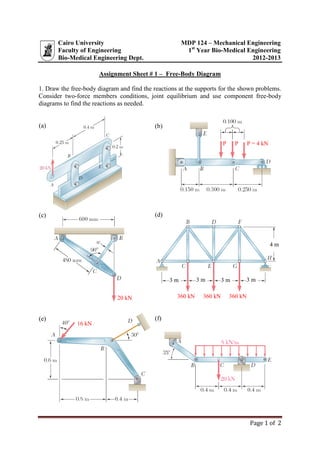
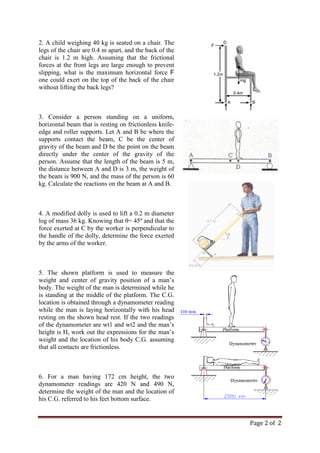
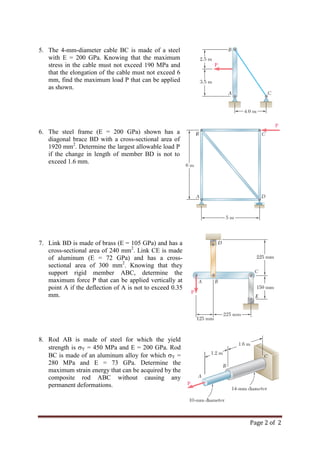
This document contains 8 assignment sheets related to mechanical engineering concepts including:
1. Free body diagrams and reactions at supports
2. Internal reaction diagrams for beams
3. Axially loaded bars including stresses and deflections
4. Bending of bars including stresses, deflections, and internal reaction diagrams
5. Torsion of bars including shear stresses and angles of twist
6. Thin walled pressure containers including stress components and allowable pressures
7. Stress transformation including Mohr's circle and principal stresses
8. A problem involving stresses in a thin walled steel pressure container
The assignments cover a range of load cases and ask students to calculate stresses, deflections, reactions and other mechanical properties.