The document summarizes the structure of an atom in 3 paragraphs:
1) It describes the three main subatomic particles - electrons, protons, and neutrons - and their relative masses and charges.
2) It outlines the historical discoveries of these particles, including Thomson discovering electrons in 1900, discoveries of positively charged particles (protons) in the late 1800s, and Chadwick discovering neutrons in 1932.
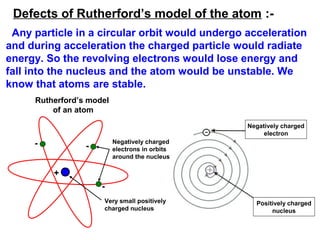
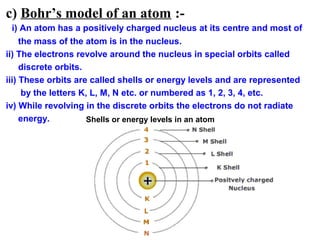
3) It discusses several historical models of the atom, including Thomson's "plum pudding" model, Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus from alpha scattering experiments, and Bohr's improvement adding discrete electron orbits that explained atomic stability.