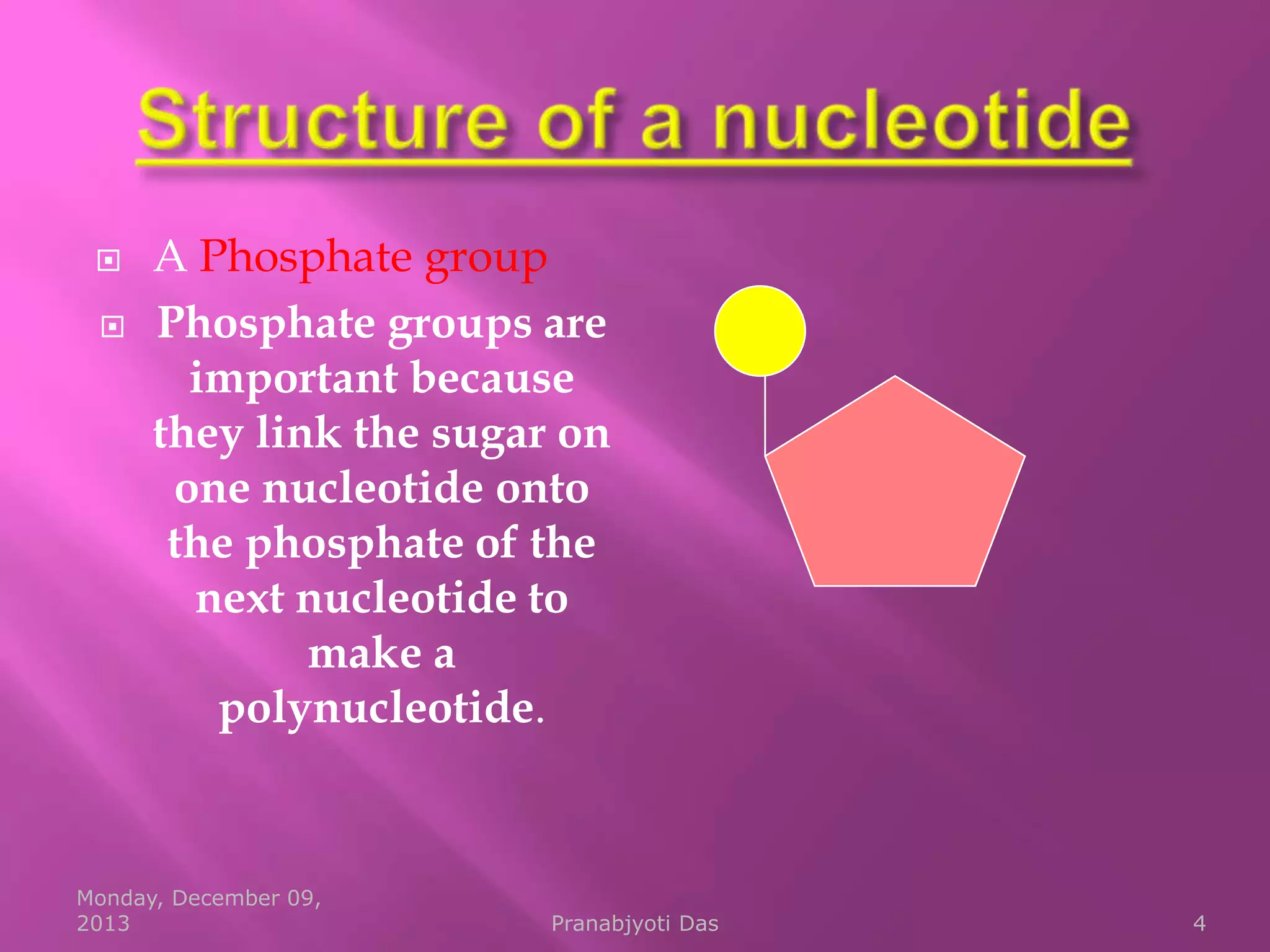
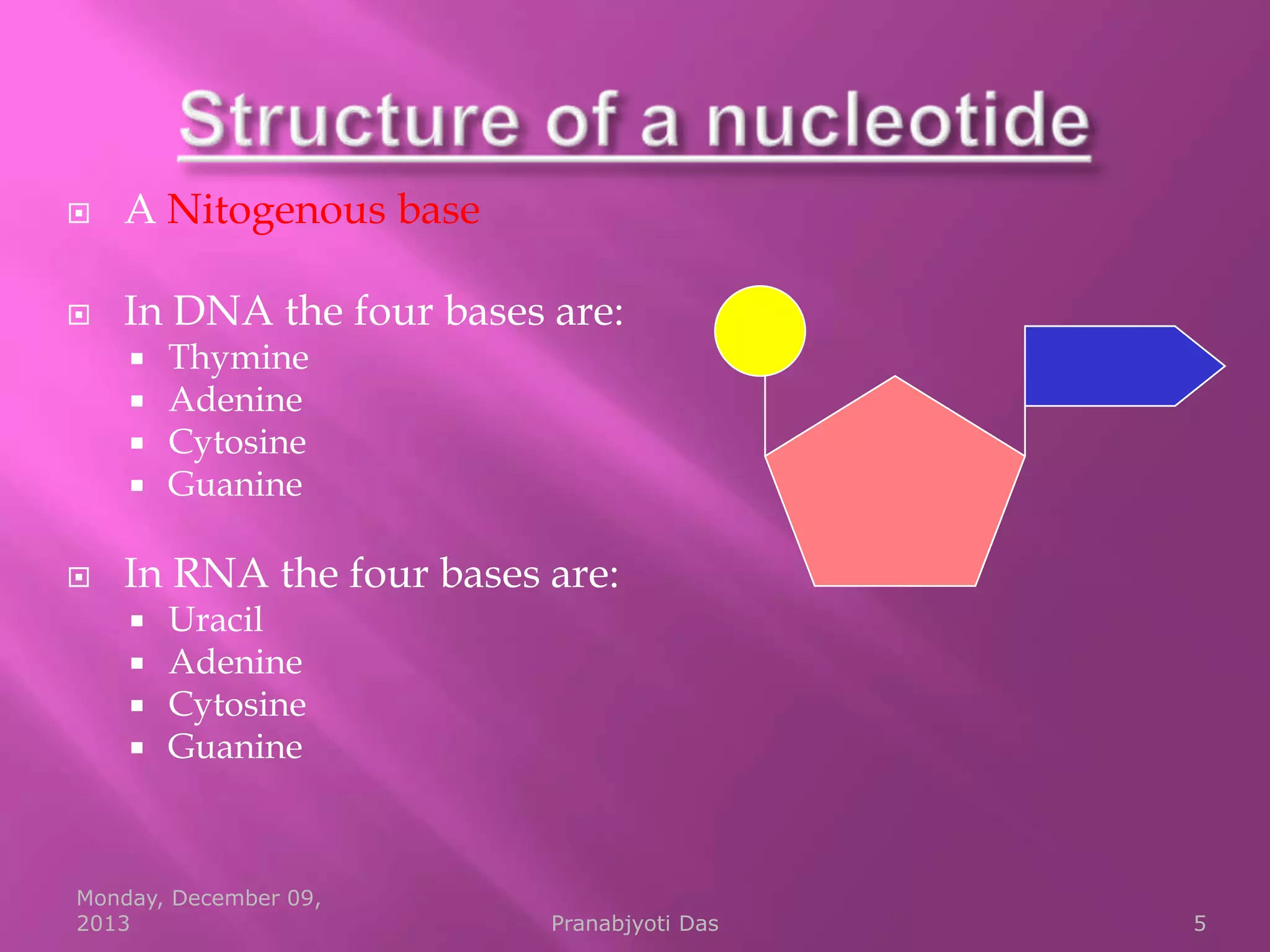
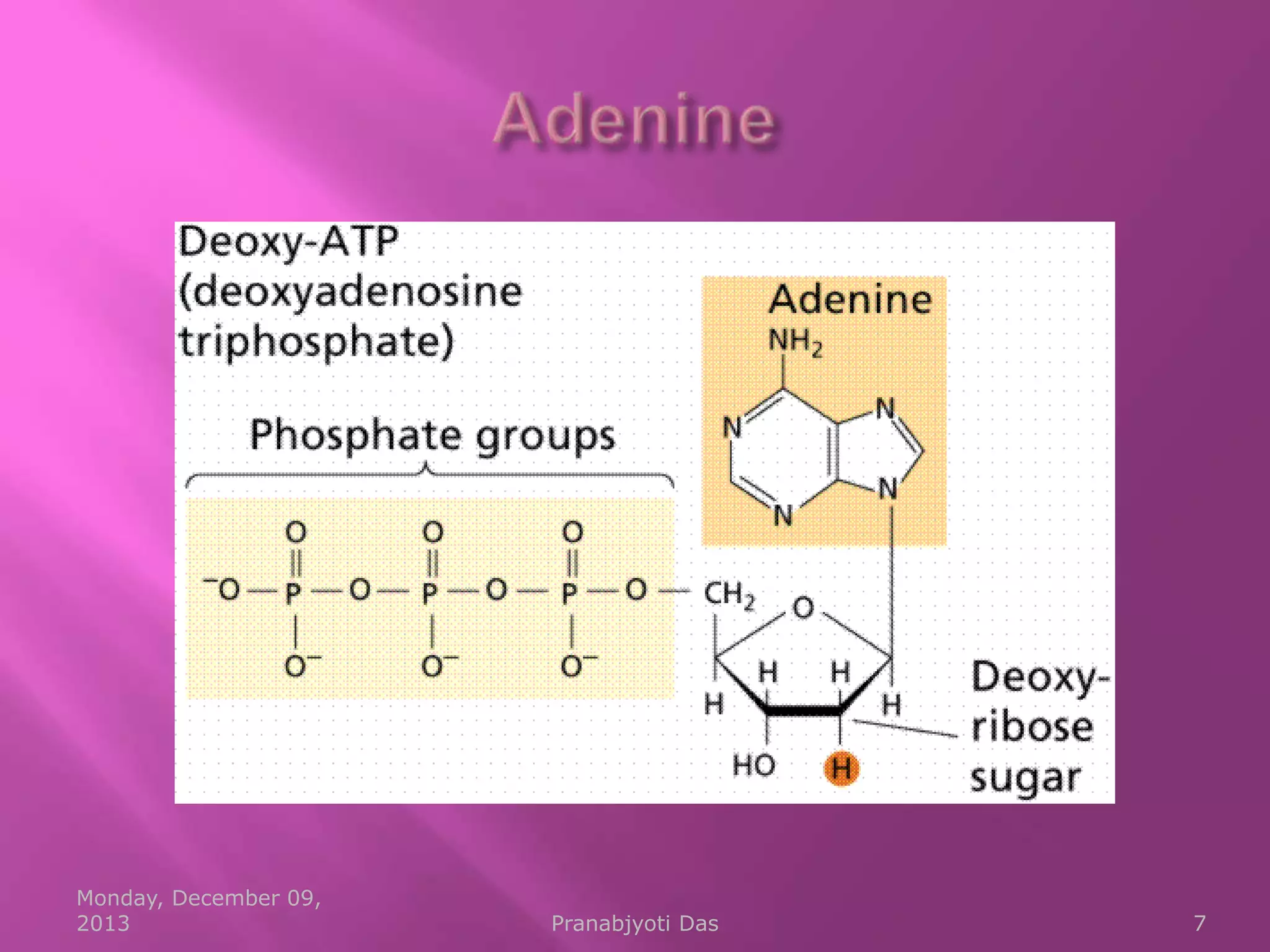
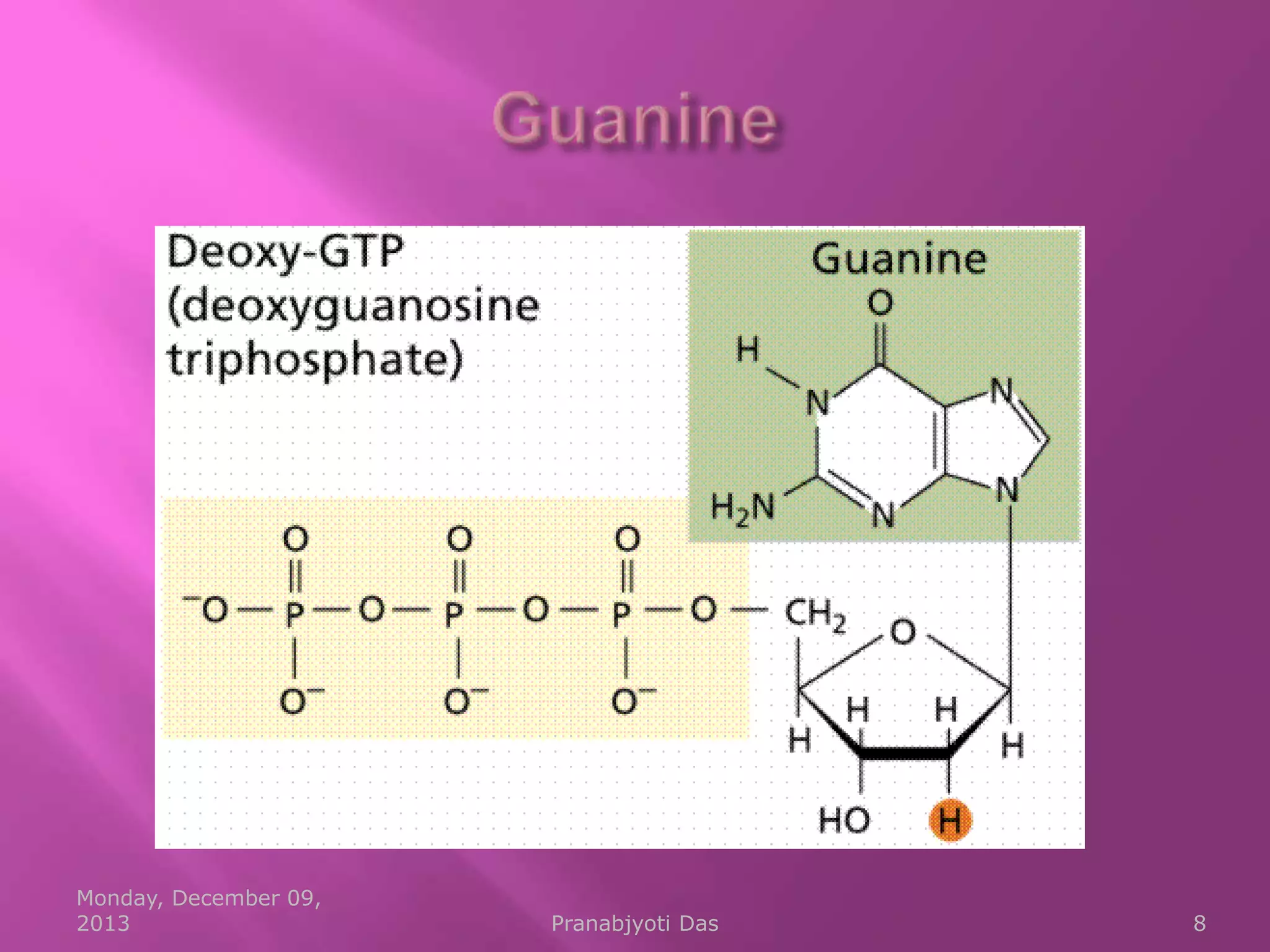
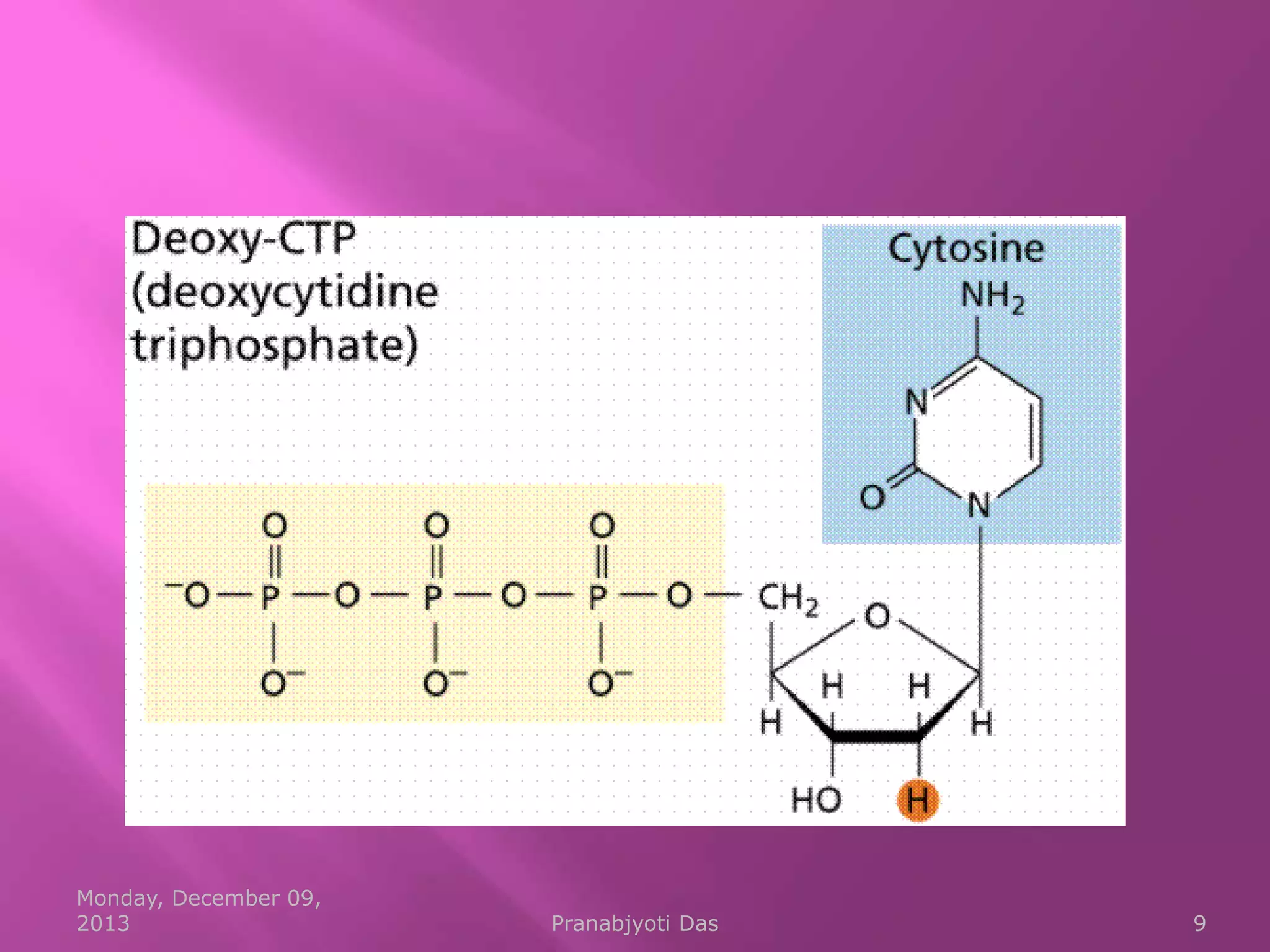
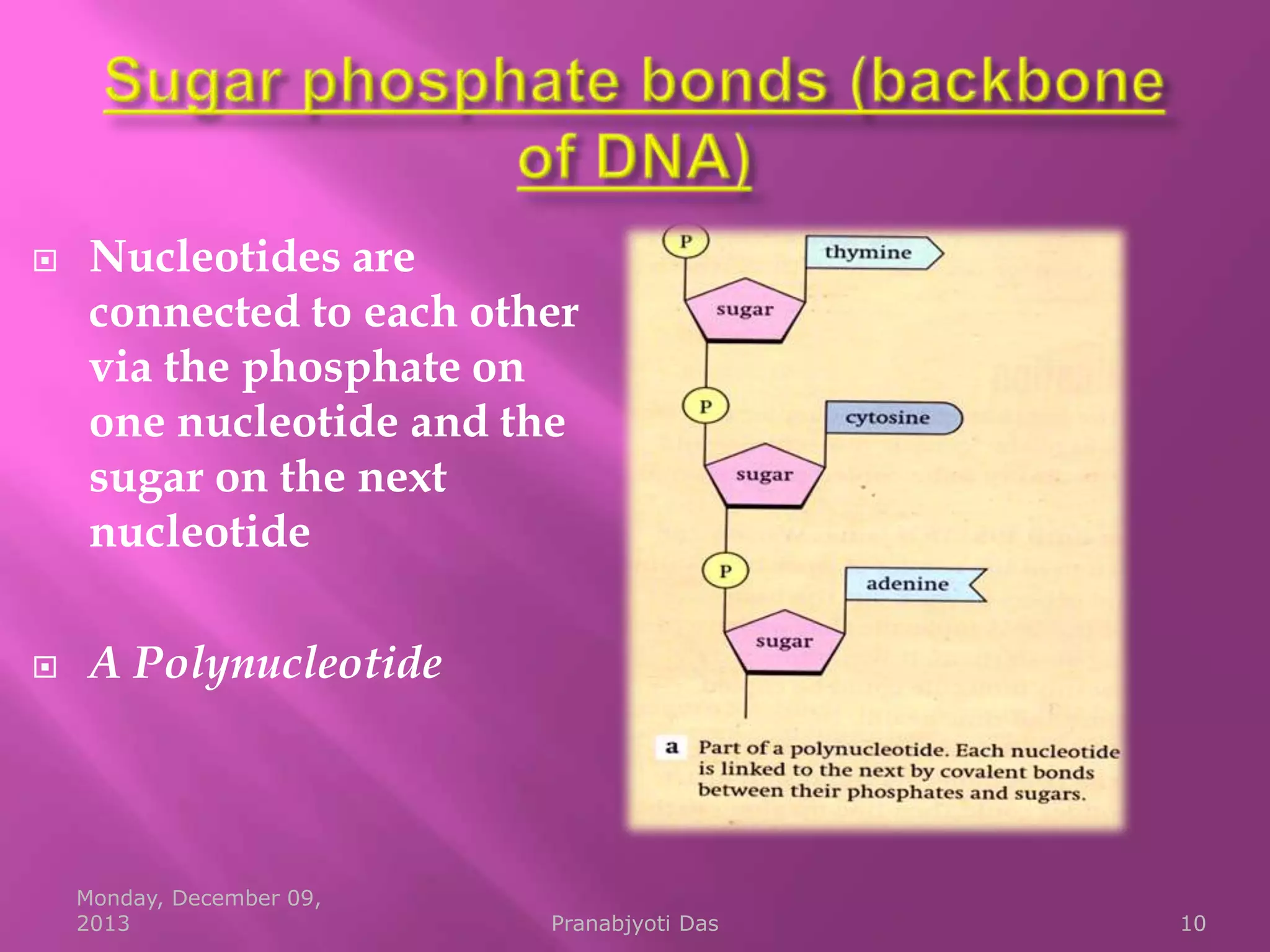
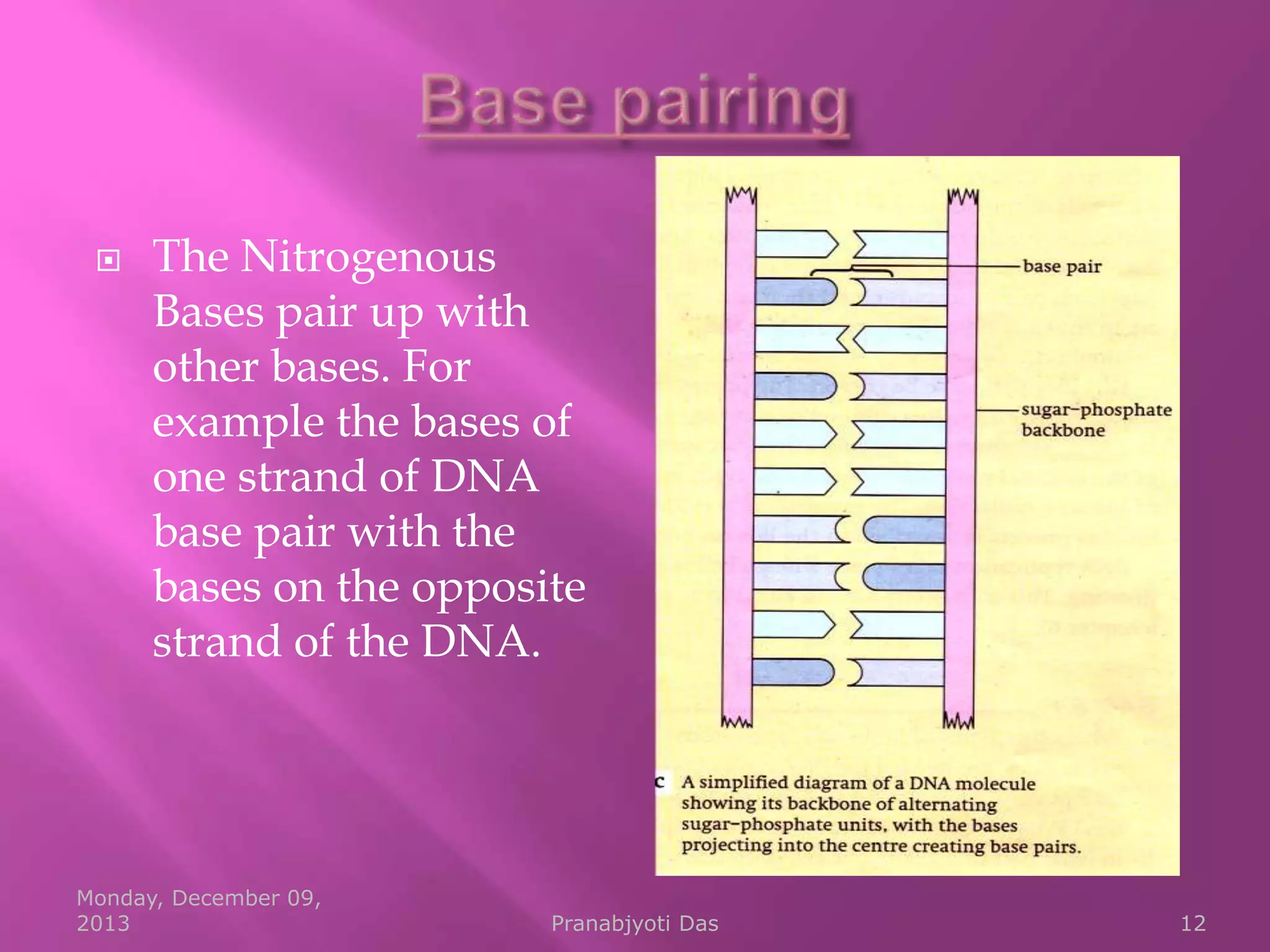
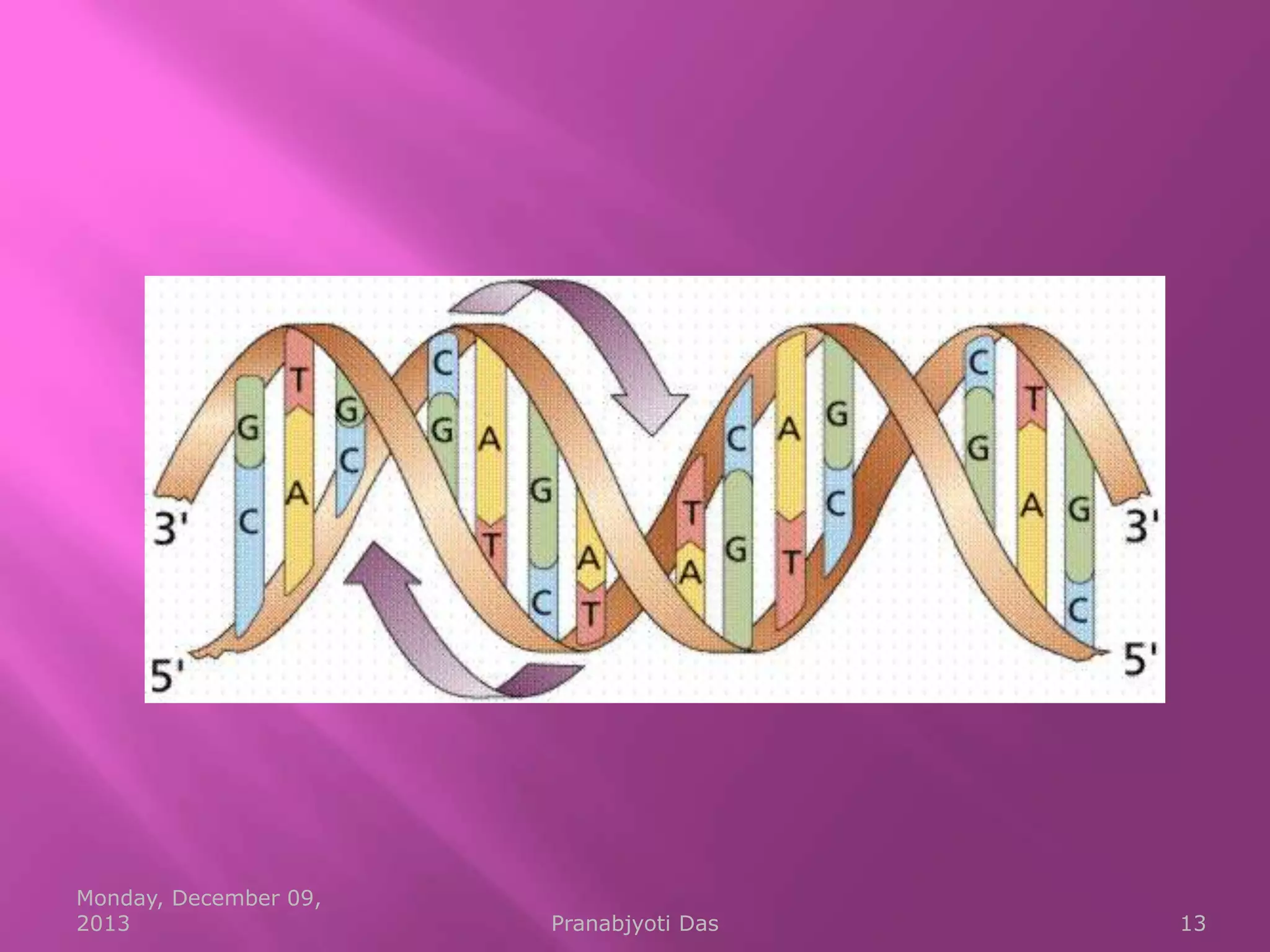
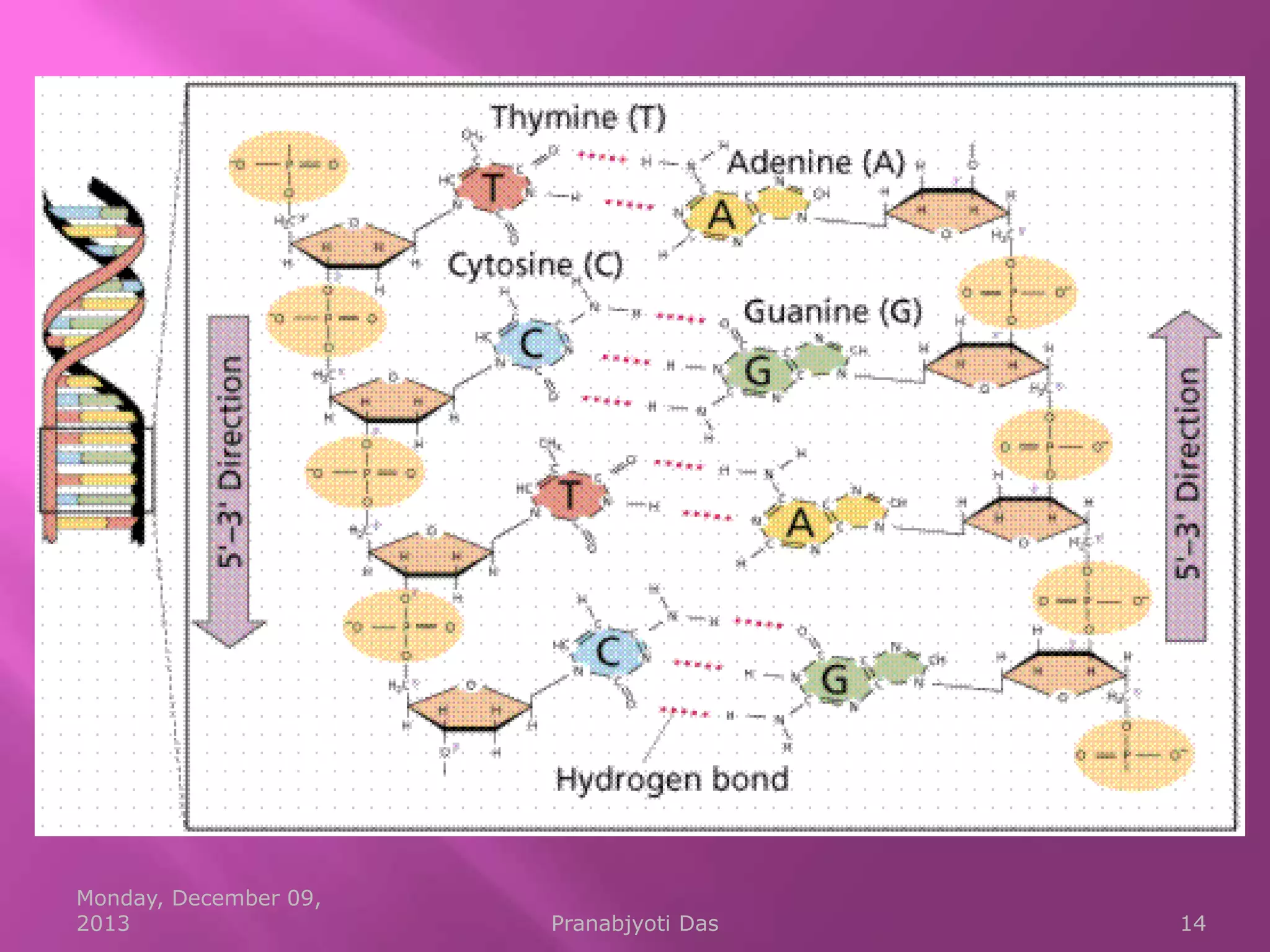
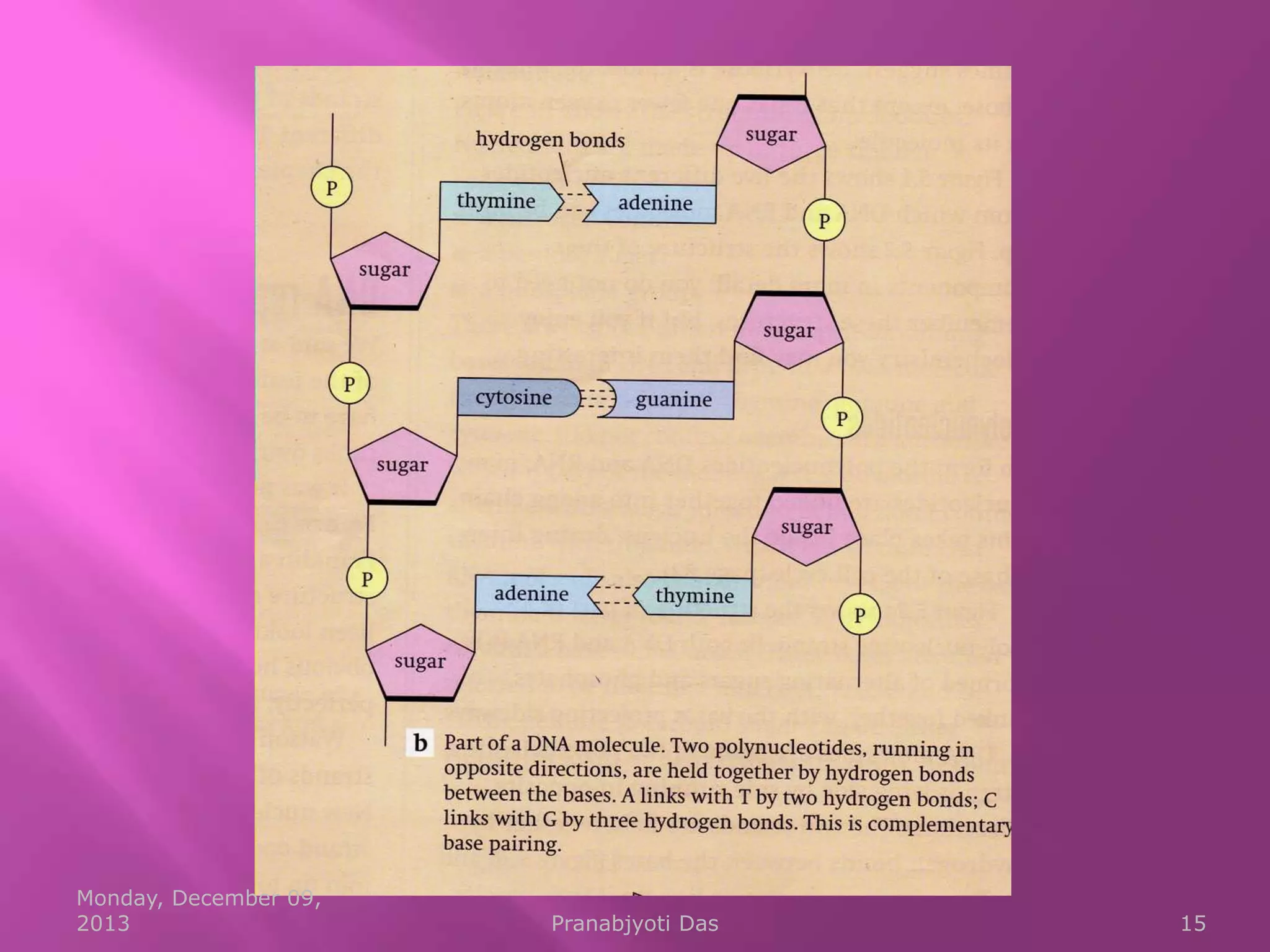
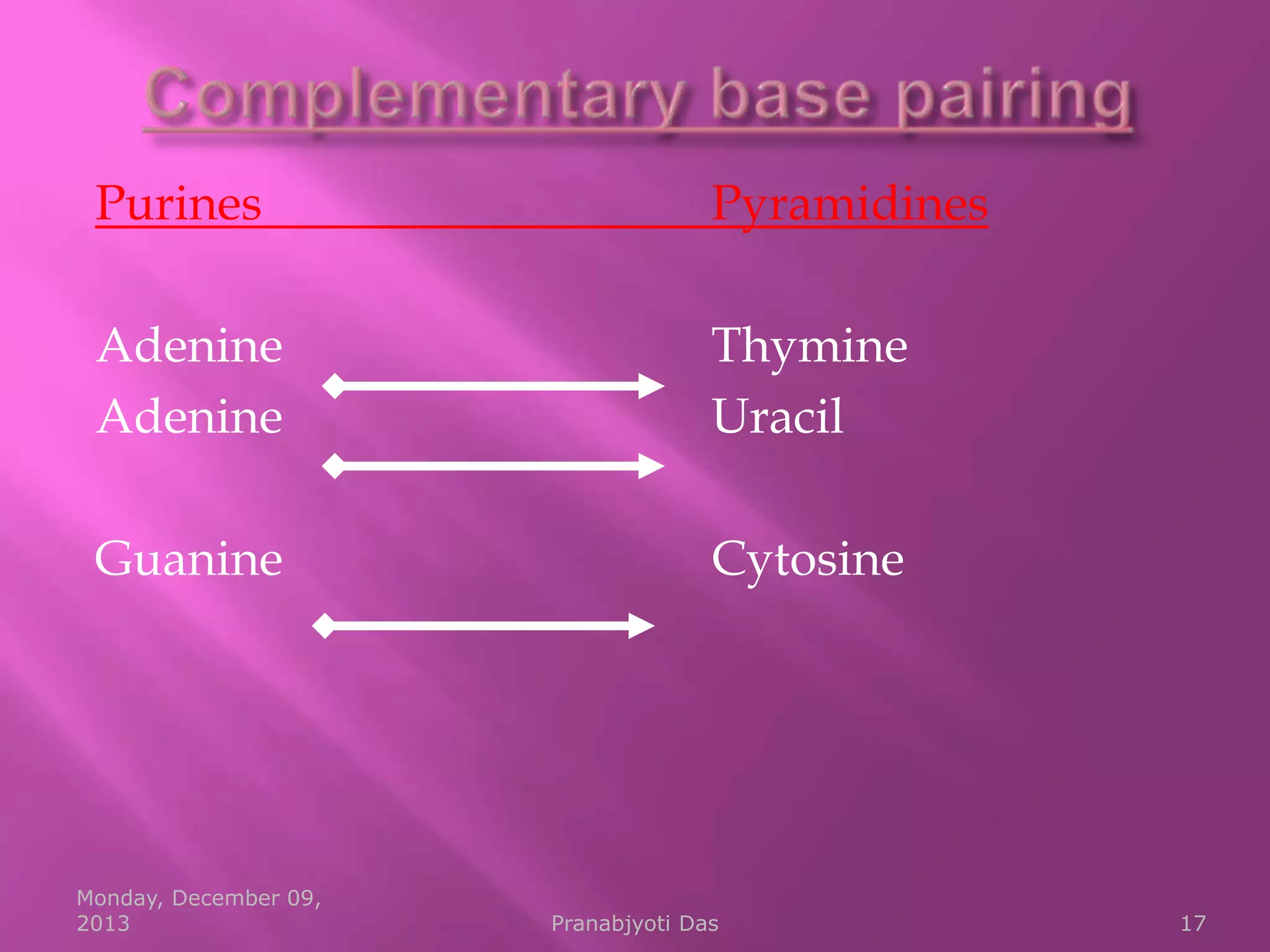
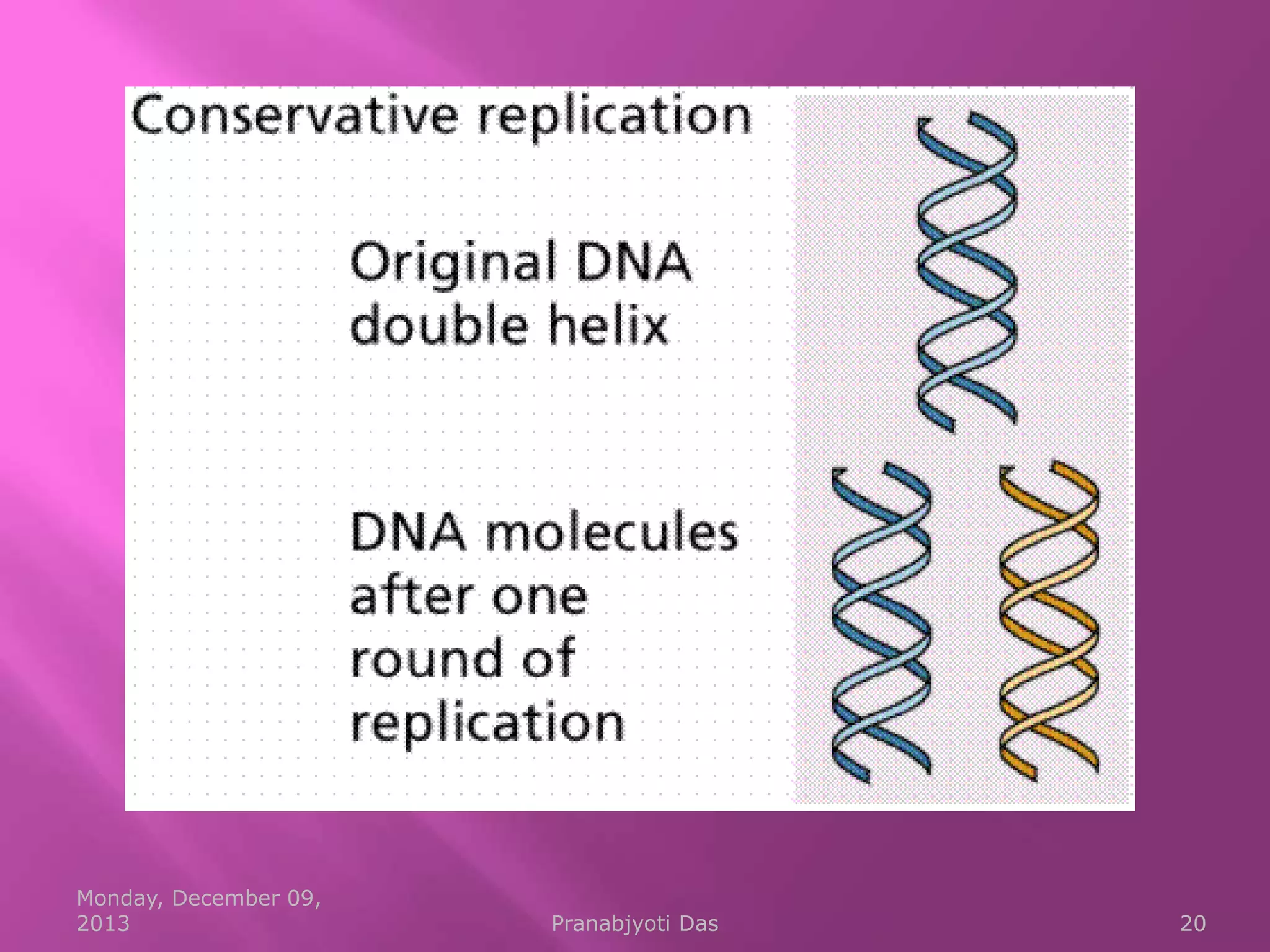
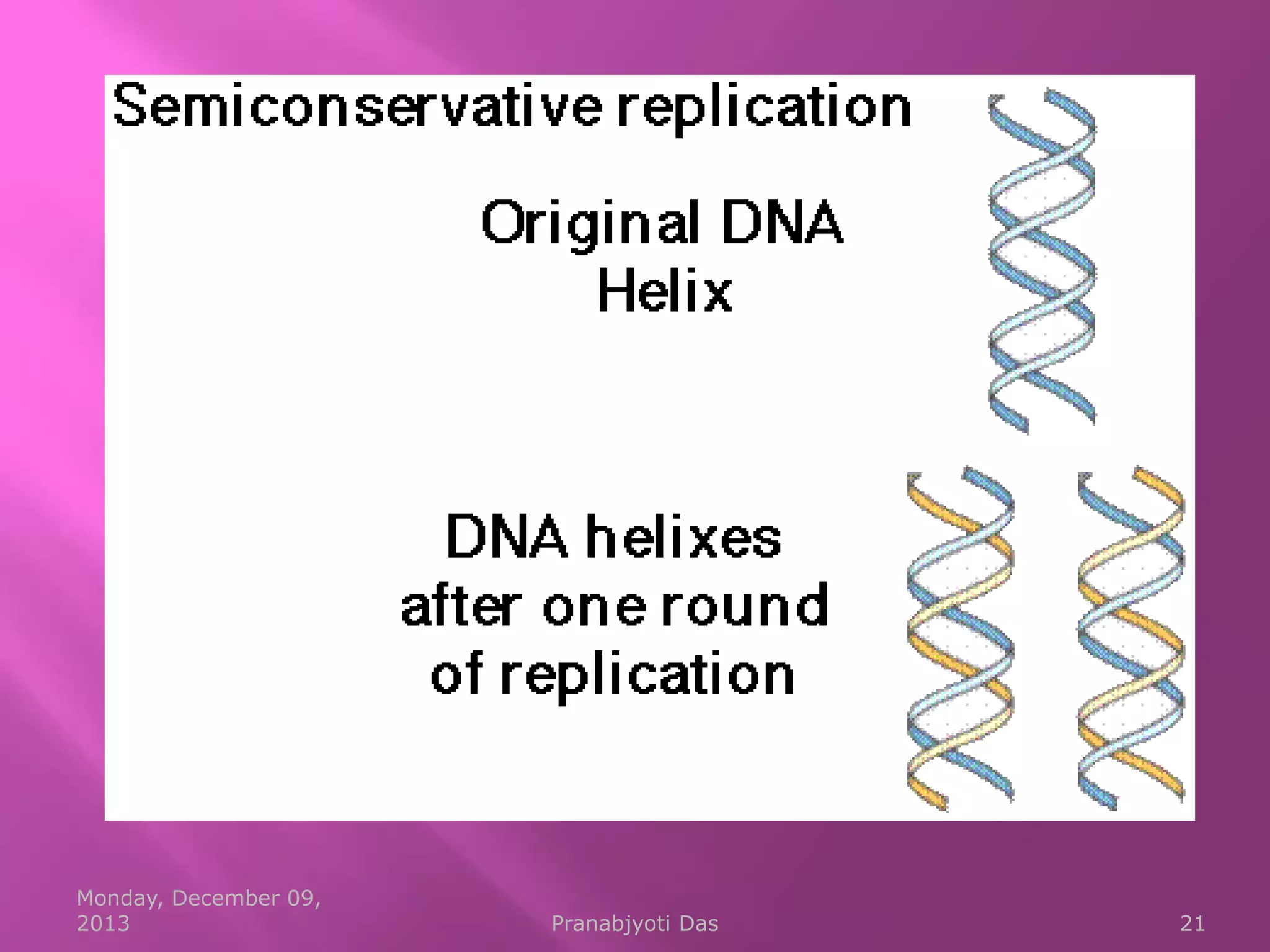
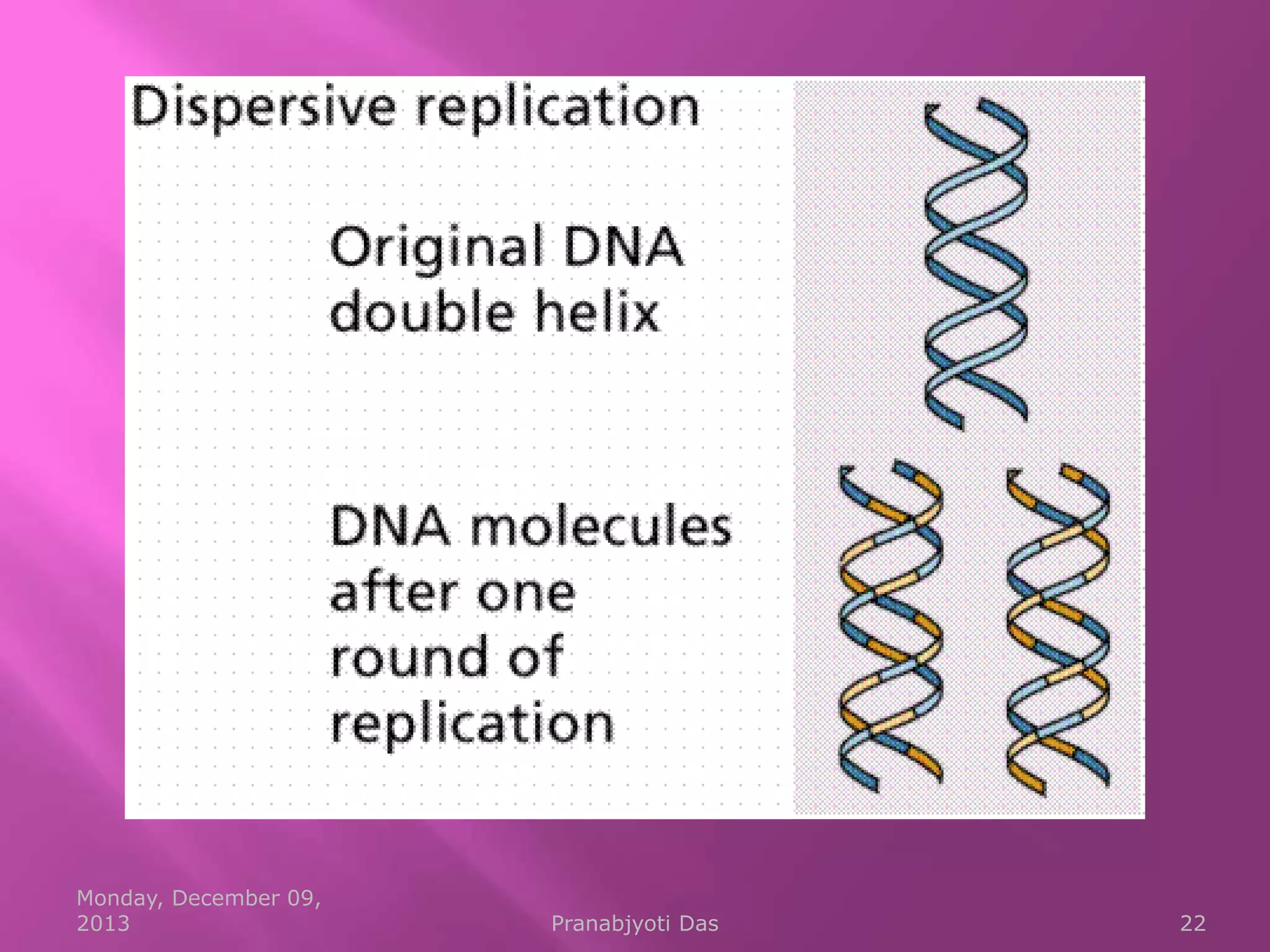
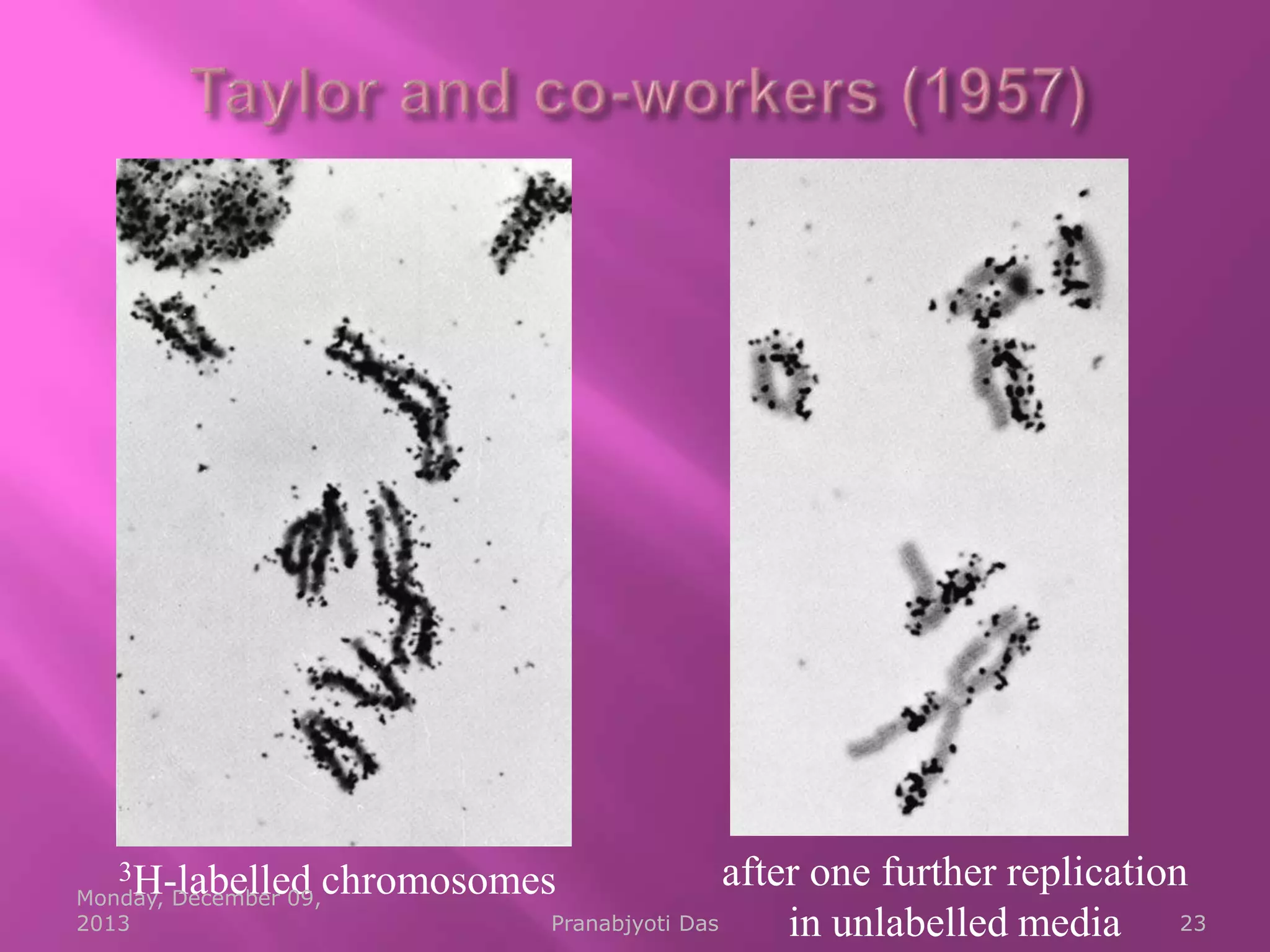
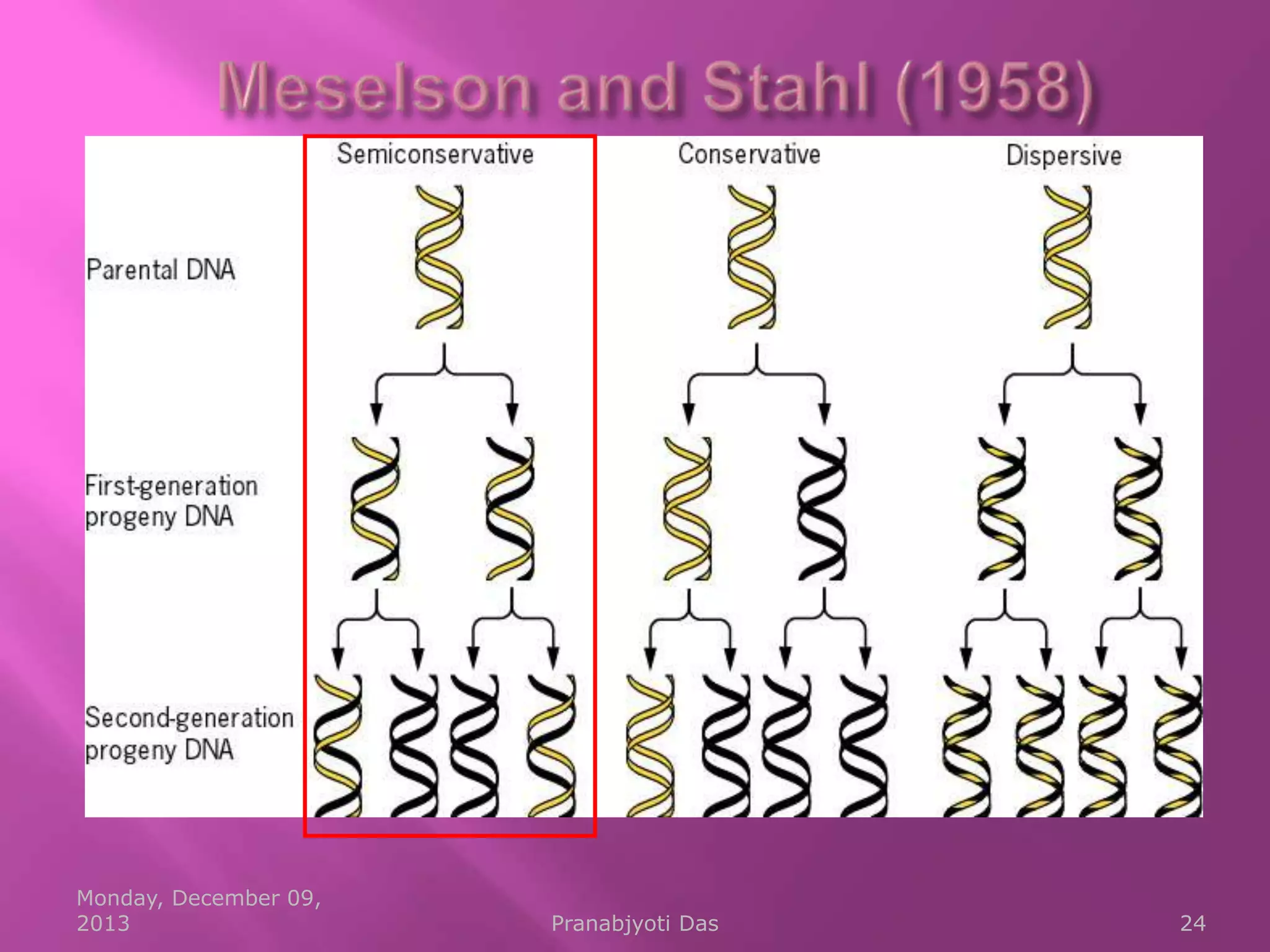
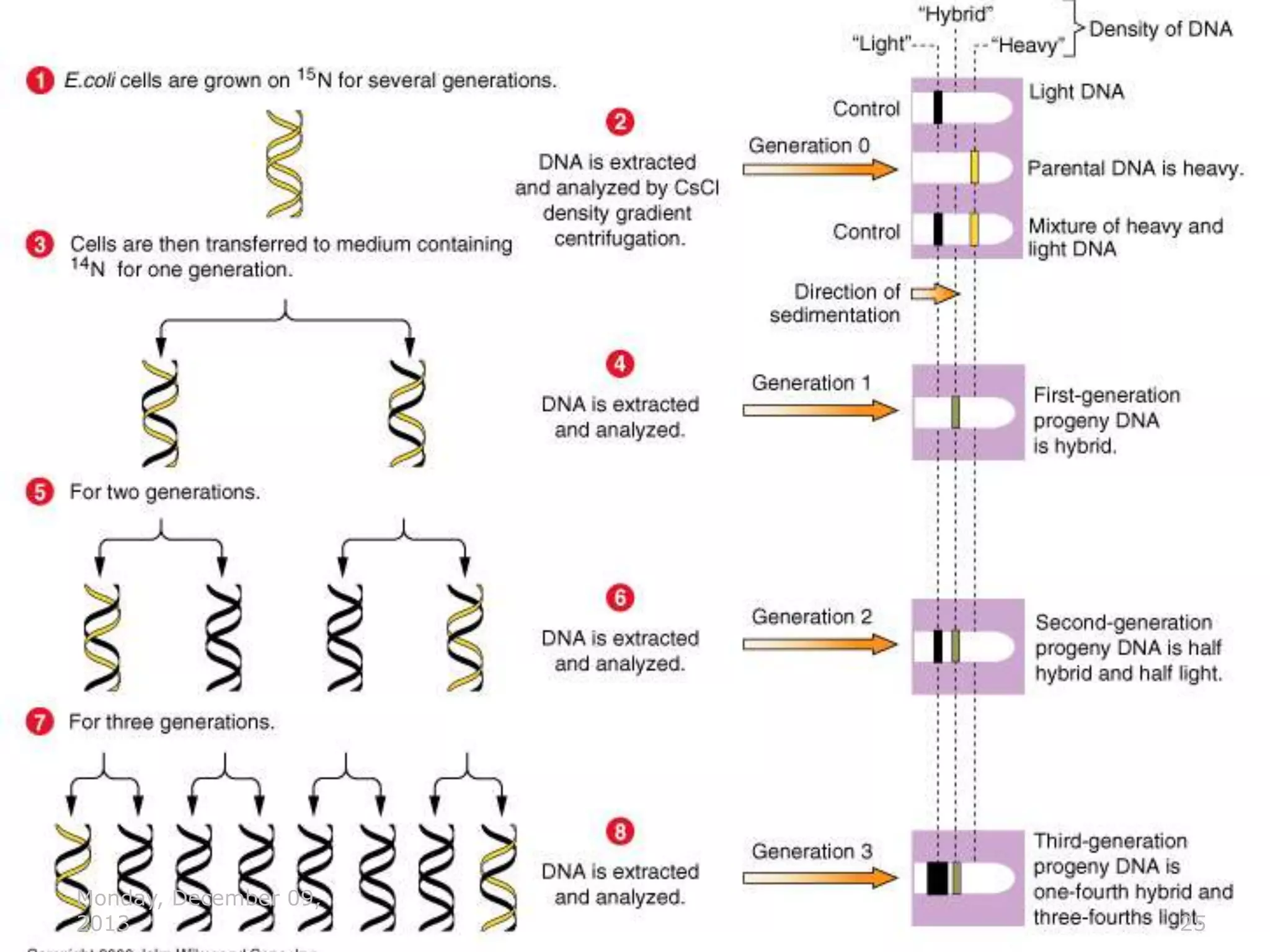
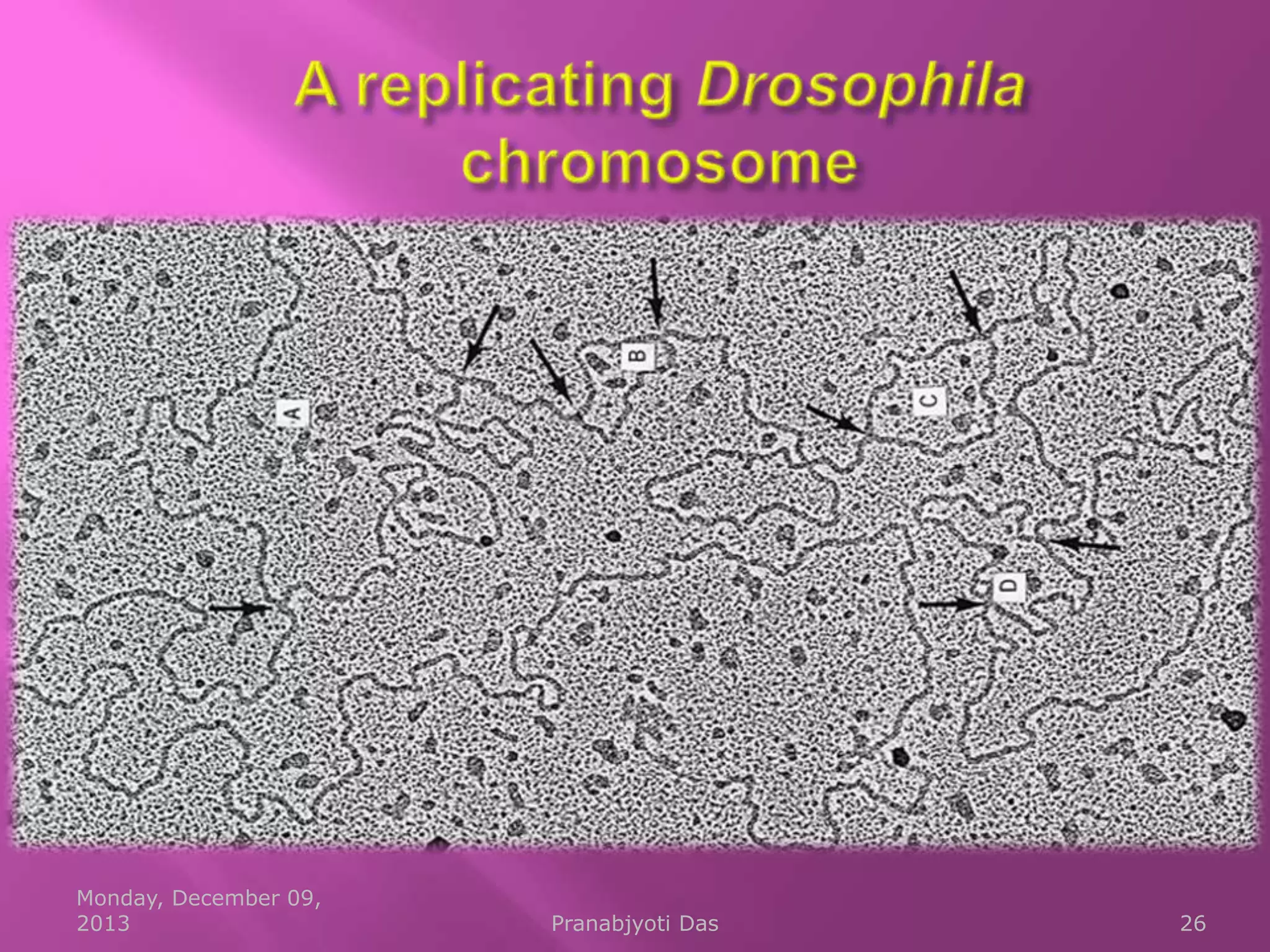
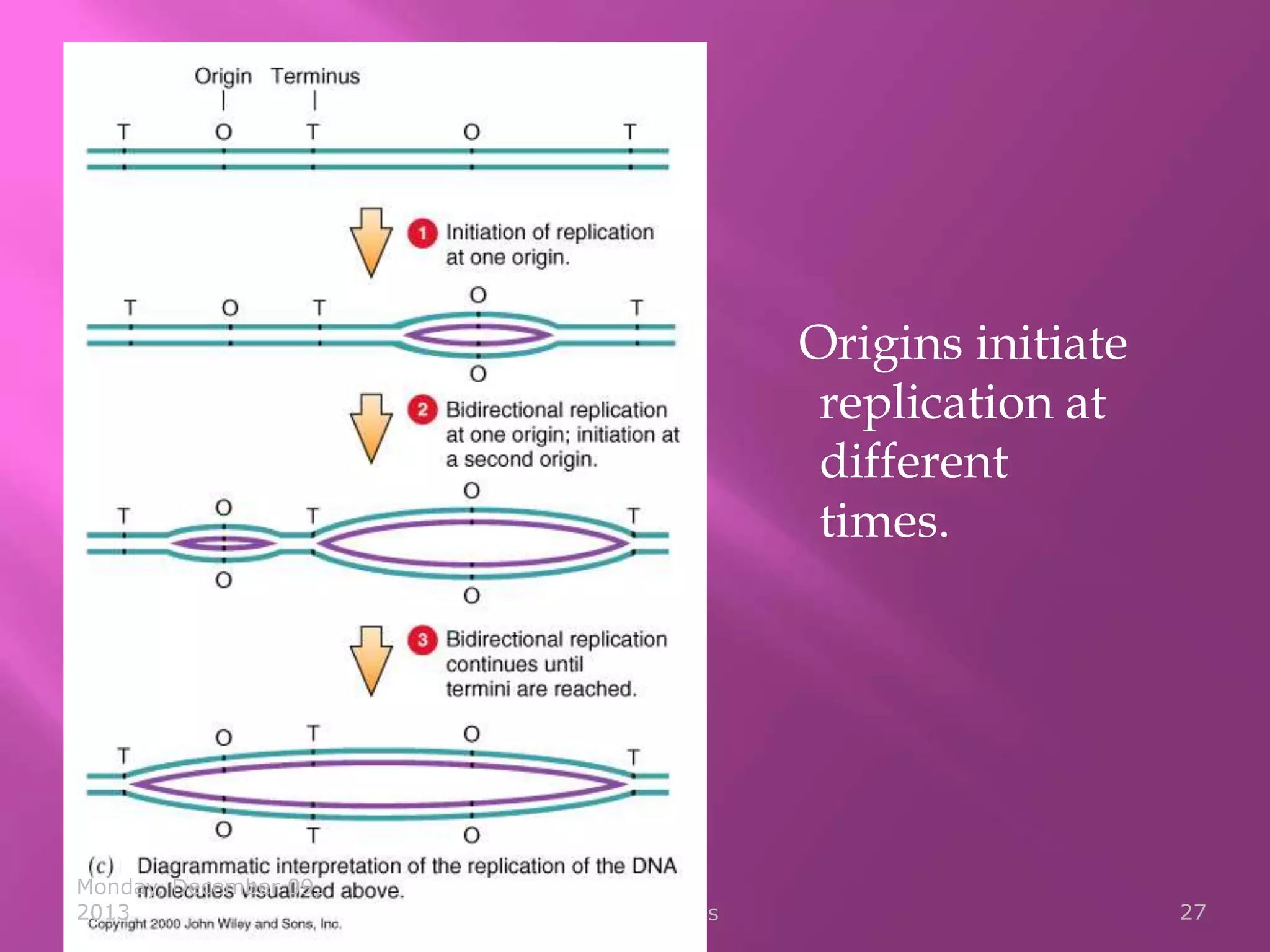
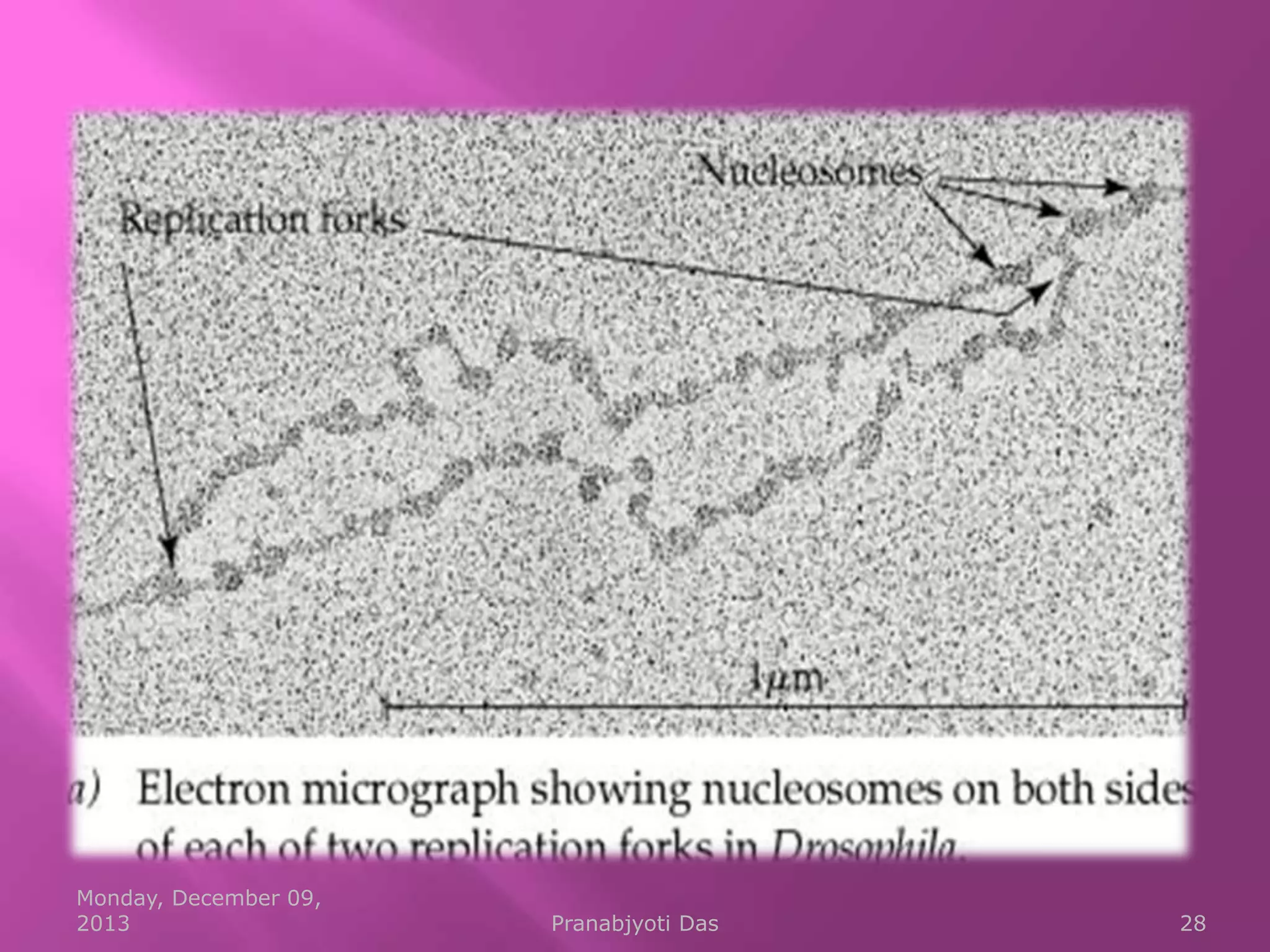
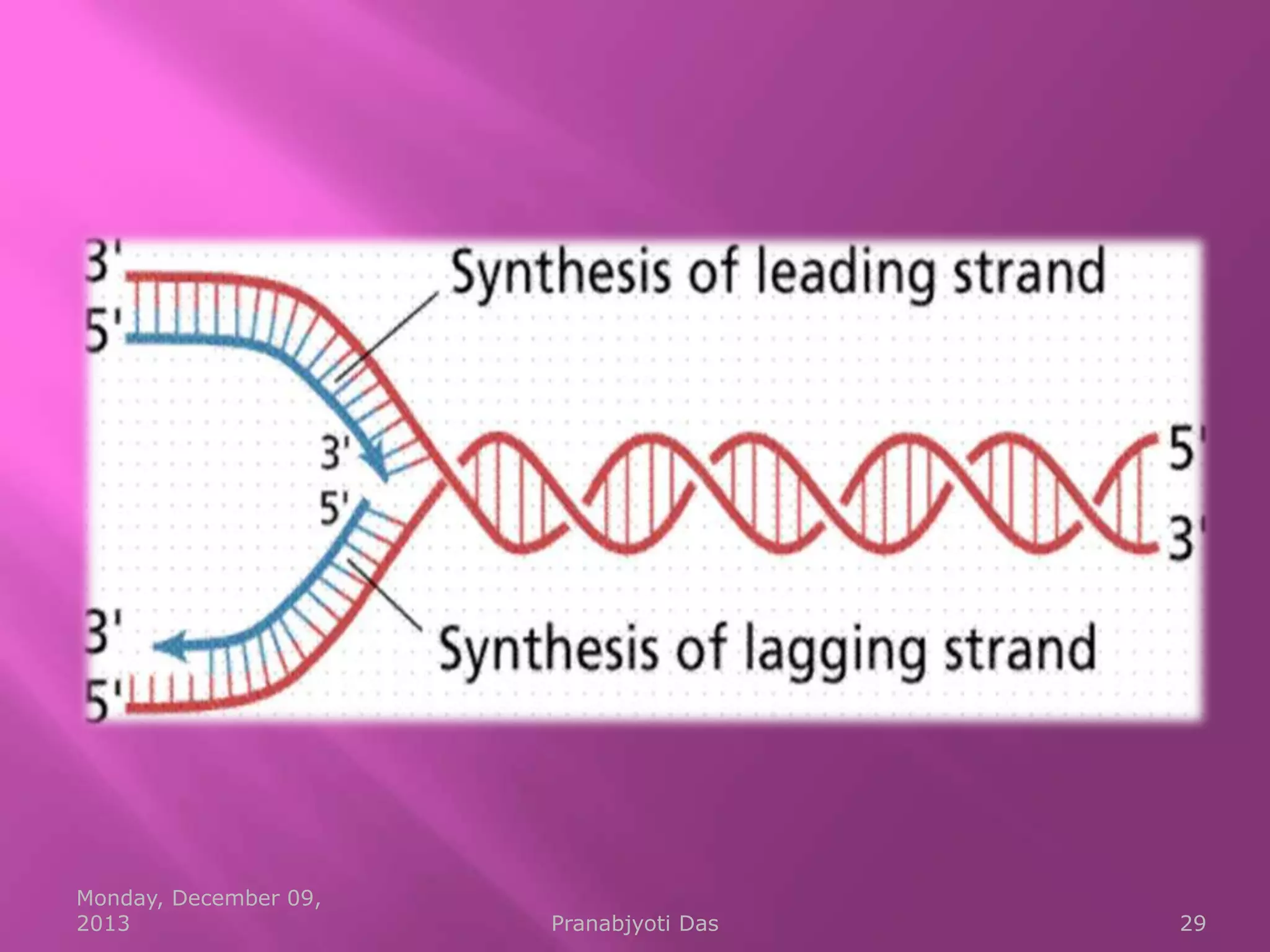
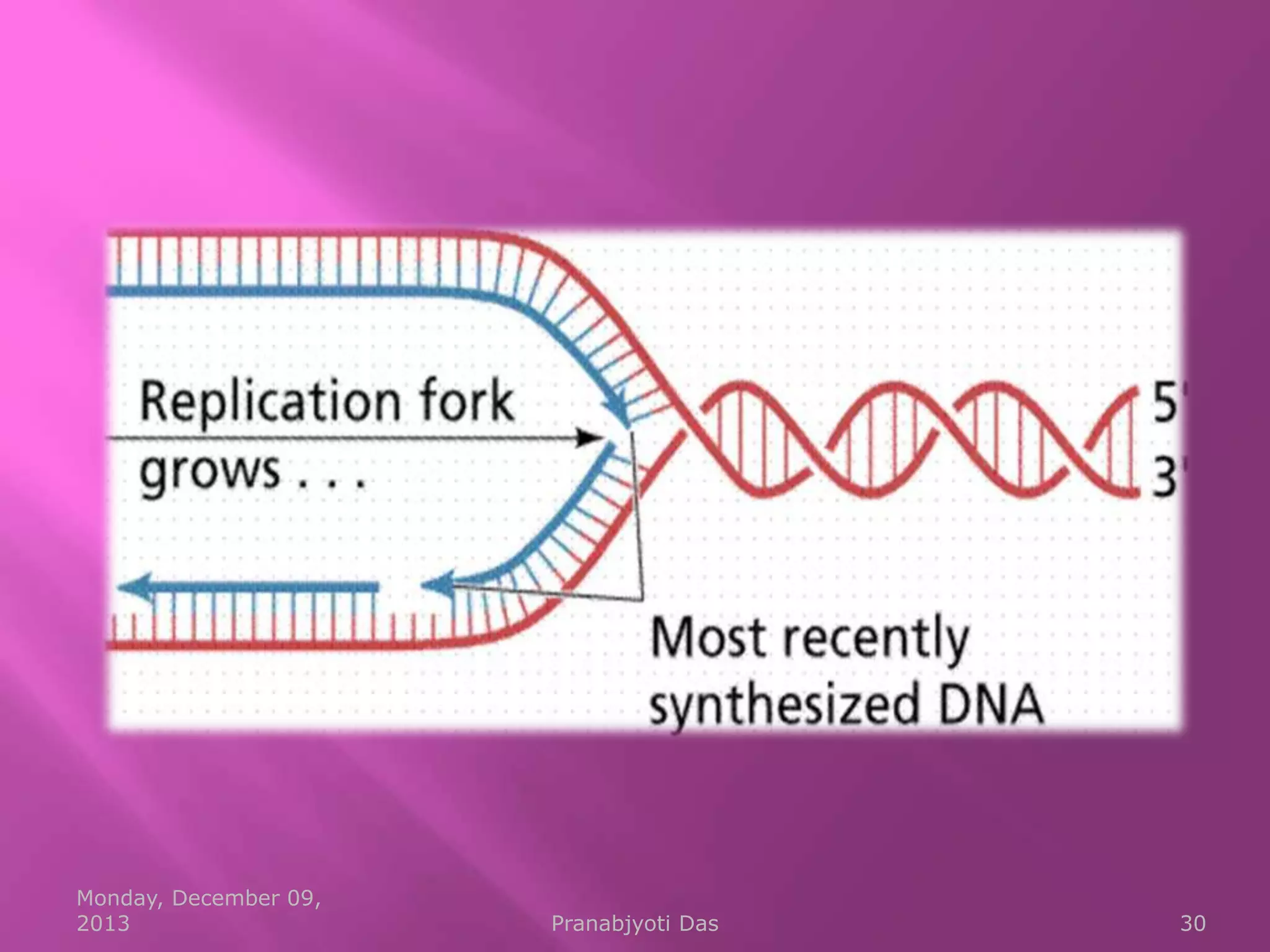
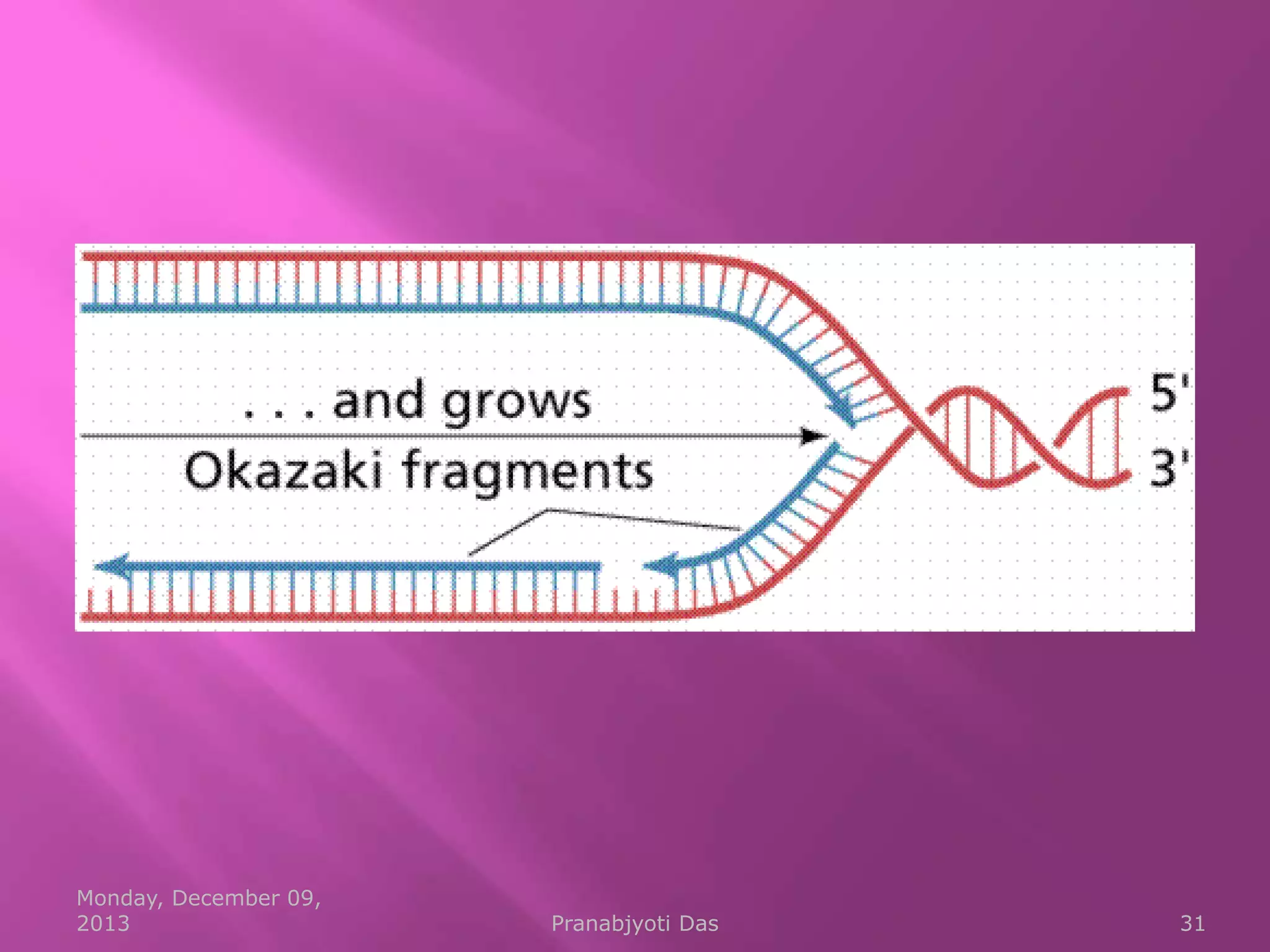
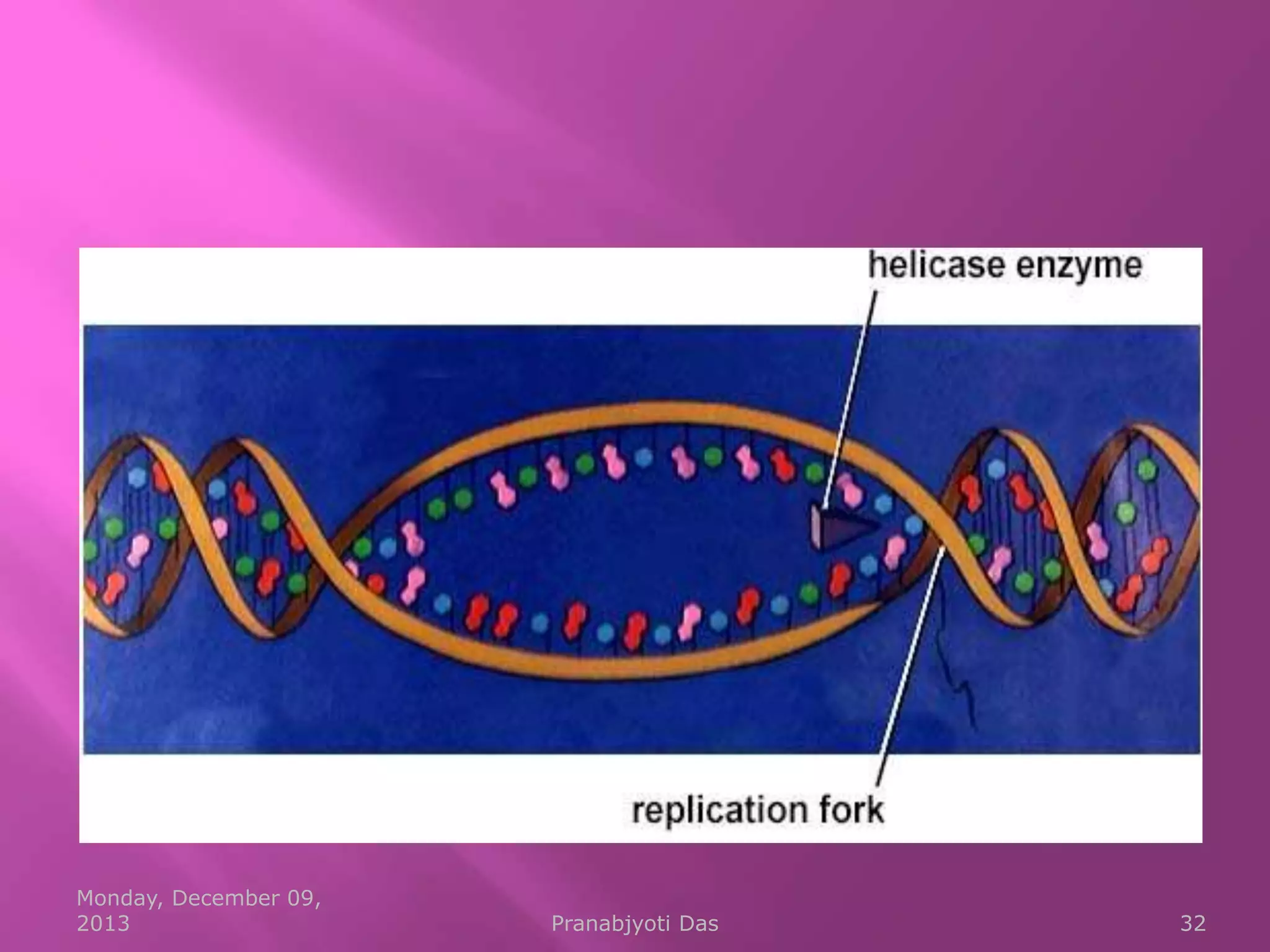
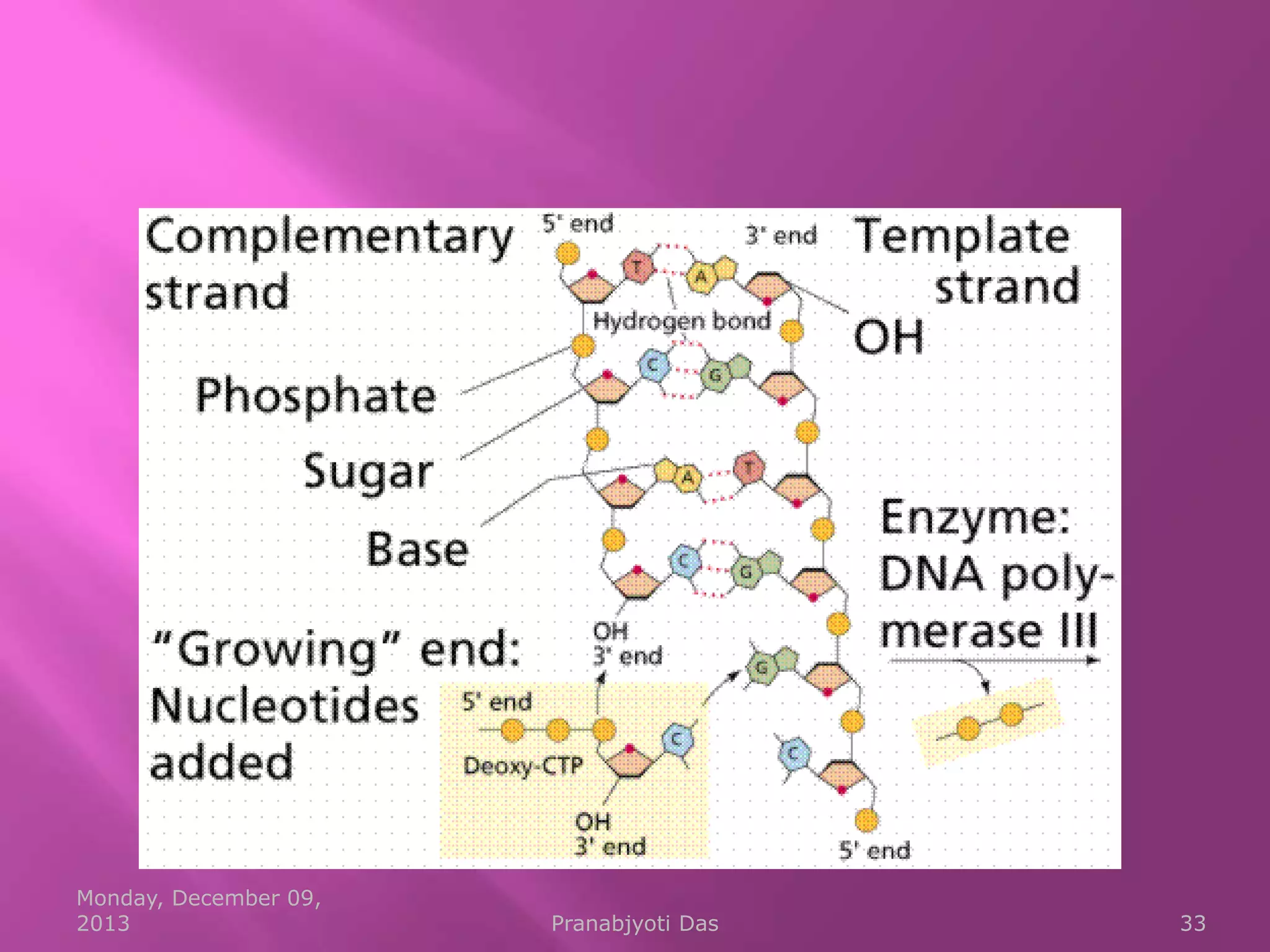
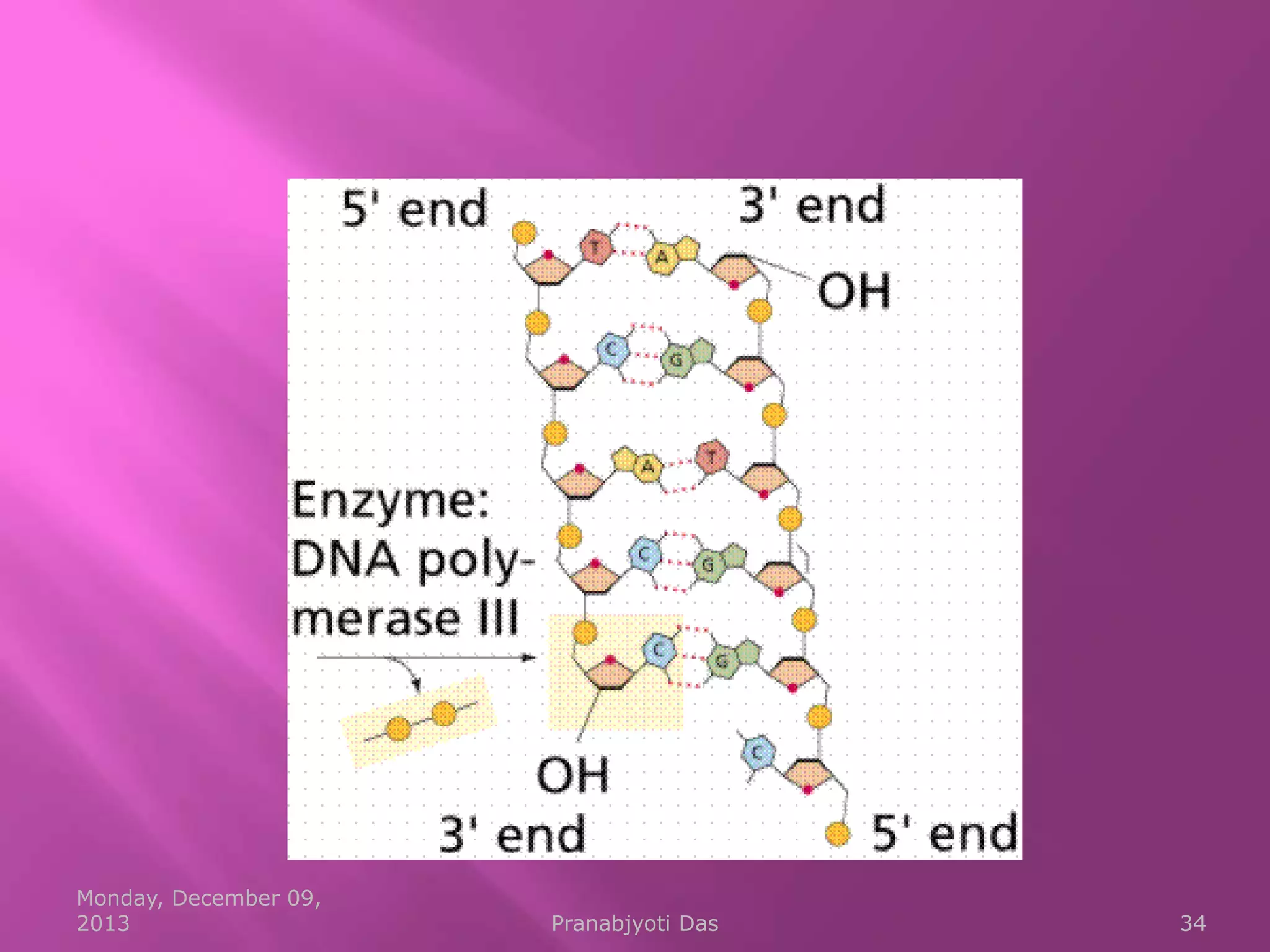
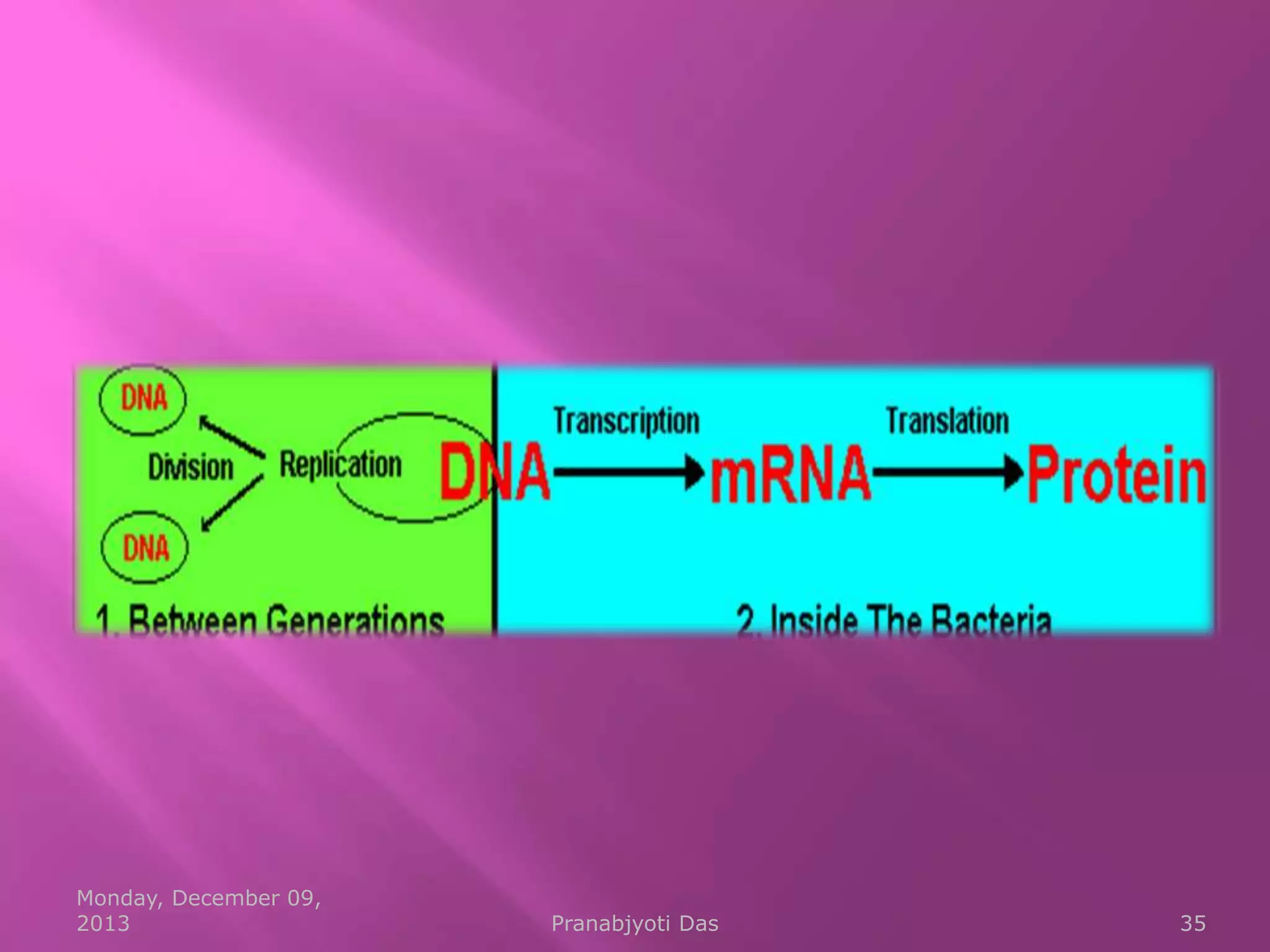
Genetic material is either DNA or RNA. DNA contains genes that code for proteins and is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is single-stranded. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids and contain a sugar, phosphate, and nitrogenous base. DNA nucleotides contain the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine, while RNA contains adenine, cytosine, guanine and uracil instead of thymine. The bases on one strand pair with those on the other through hydrogen bonding in a specific way - adenine pairs with thymine/uracil and cytosine pairs with guanine. DNA replicates accurately to ensure progeny cells have the same genetic makeup.