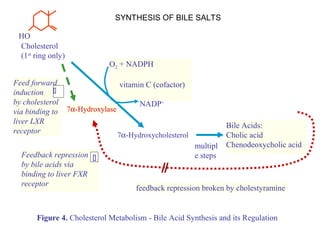
Cholesterol biosynthesis is a multi-step process that begins with acetyl-CoA and occurs primarily in the liver and other tissues. Key steps include the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate by the rate-limiting enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Cholesterol can then be used for membrane structure, steroid hormone synthesis, or converted to bile acids which are secreted in the bile. Cholesterol levels are regulated by feedback inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase and uptake/secretion of cholesterol and bile acids. Statins lower cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase.