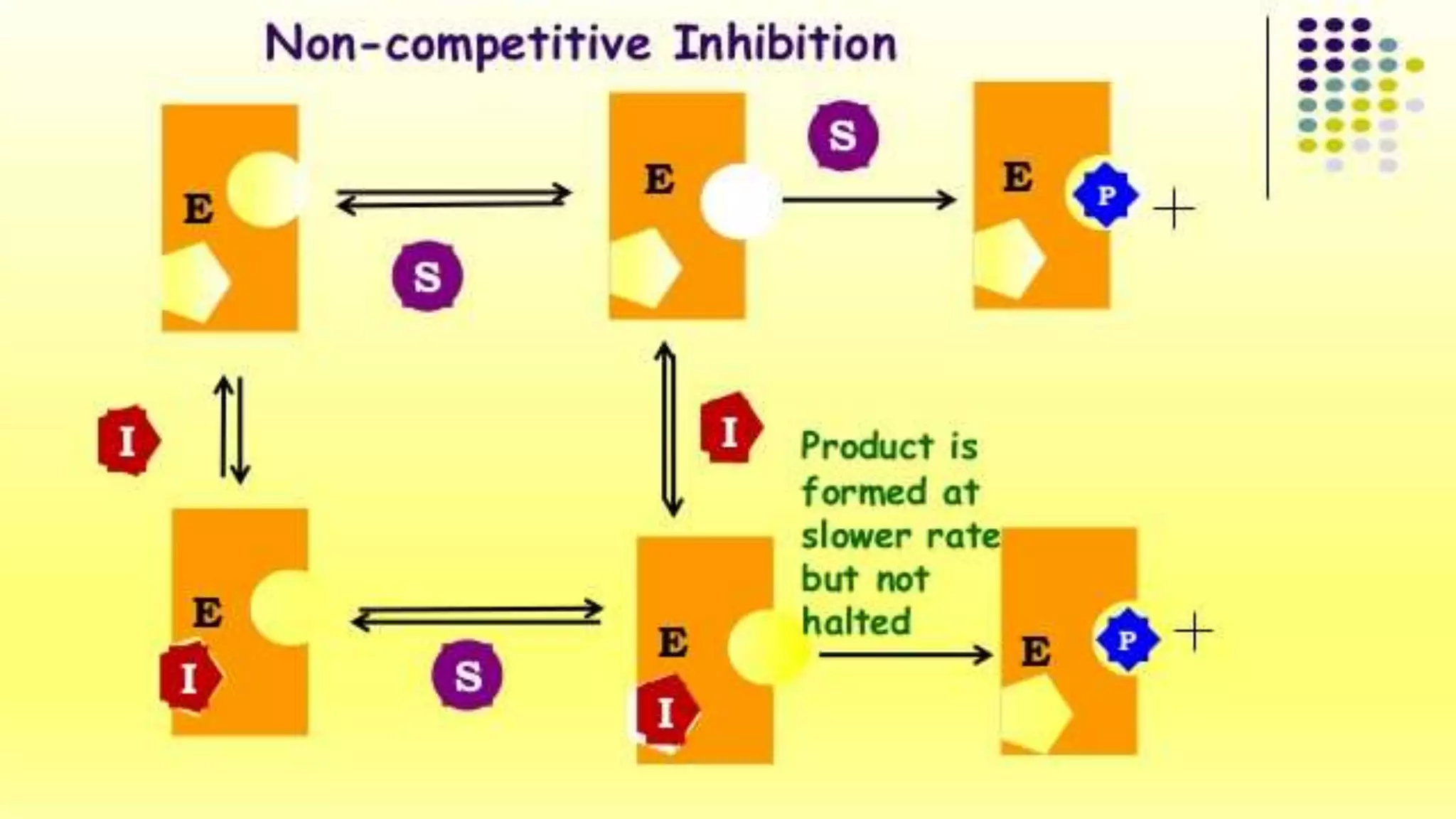
This document discusses different types of enzyme inhibitors. It begins by defining an enzyme inhibitor as a compound that decreases the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by interfering with substrate binding or enzyme turnover. There are several types of reversible inhibition, including competitive inhibition where the inhibitor binds to the substrate binding site, and non-competitive inhibition where the inhibitor binds elsewhere. Irreversible inhibition occurs when the inhibitor binds covalently and cannot dissociate from the enzyme. Suicide inhibition is a specialized form using the enzyme's reaction to inactivate itself. Allosteric inhibition involves binding of effectors to allosteric sites that regulate enzyme activity. Enzyme inhibitors have important applications as drugs, antibiotics, and in studying enzyme mechanisms








![Uncompetitive Inhibition
• I binds only to the ES complex , not to free E
• I - causes structural distortion of the active site - E catalytically
inactive
• I can’t be reversed by increasing the [S] since I doesn't compete
with S for the same binding site](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bbc205sri-210415025030/75/Enzyme-Inhibitors-10-2048.jpg)






