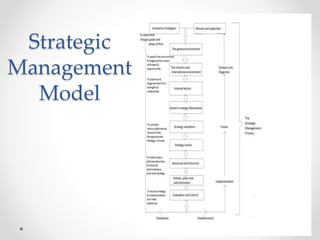
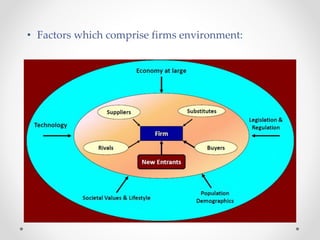
This document outlines the strategic management model process in 6 steps: 1) strategic elements, 2) environmental and organizational analysis, 3) identification of strategic alternatives, 4) choice of strategy, 5) implementation of strategy, and 6) evaluation and control. It defines strategic management as a stream of decisions and actions to develop effective strategies to achieve corporate objectives. The process allows firms to anticipate changing conditions and provide clear direction, though conditions may change too fast for planning.