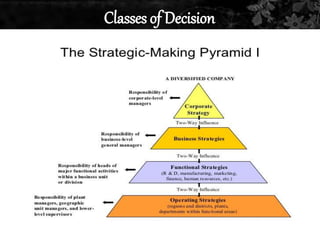
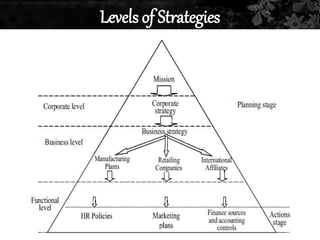
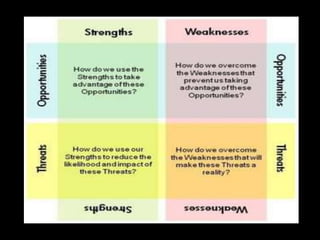
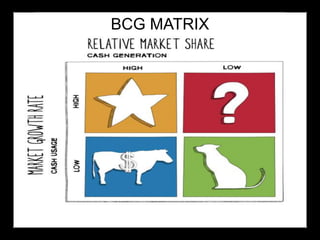
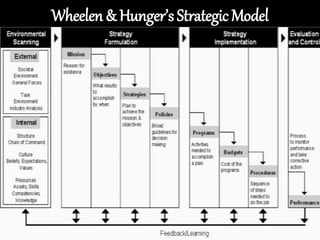
This document discusses strategic management. It defines strategic management as the continuous planning, monitoring, analysis and assessment necessary for an organization to meet its goals. There are three main classifications of decisions: corporate, business, and functional. The document also discusses various strategic management frameworks and tools, including Porter's generic strategies, the BCG matrix, SWOT analysis, and the Wheelen and Hunger strategic management model. Finally, it outlines the benefits of strategic management for organizations.