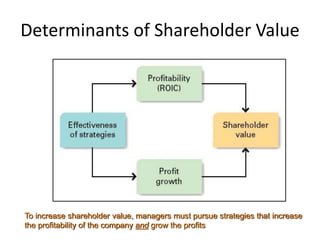
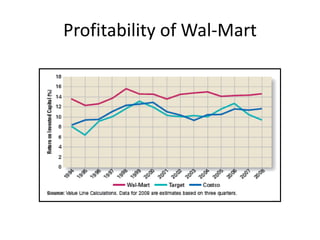
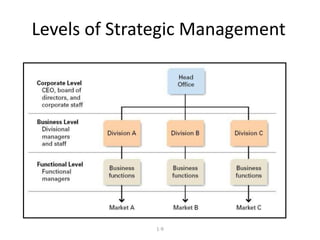
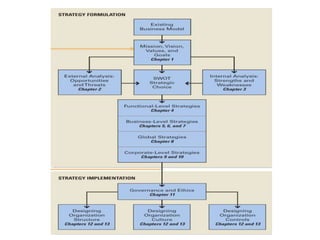
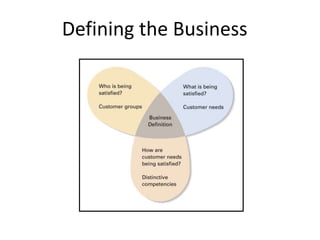
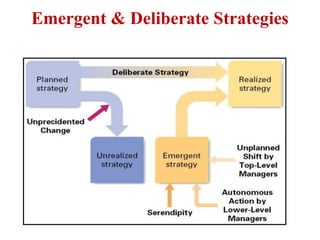
Strategic management involves analyzing internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats to develop strategies that achieve competitive advantage and superior performance. Effective strategy implementation then requires aligning organizational structure, culture and controls behind the chosen strategies to maximize shareholder value over the long run. Strategic leadership and decision-making processes aim to formulate strategies that sustain competitive advantage despite an unpredictable environment.