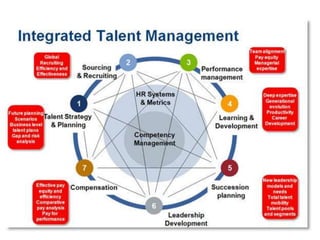
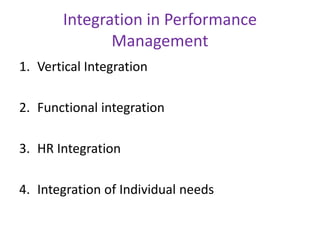
The document outlines various strategies in strategic human resource management, focusing on flexibility through outsourcing, multi-skilling, and talent management. It emphasizes the importance of continuous performance management over traditional appraisal systems to foster a high-performance culture and align individual contributions with organizational goals. Issues related to annual confidential reports and the obstacles companies face in implementing performance management systems are also discussed, highlighting the need for a structured approach to boost employee motivation and overall organizational effectiveness.