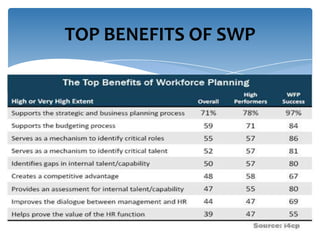
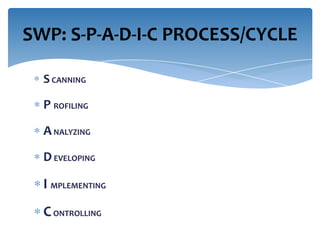
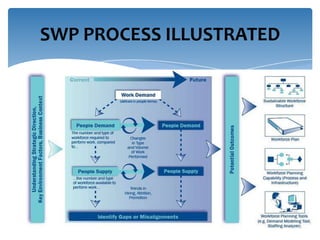
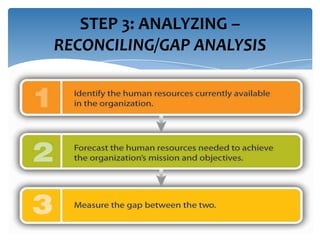
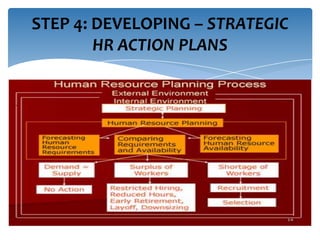
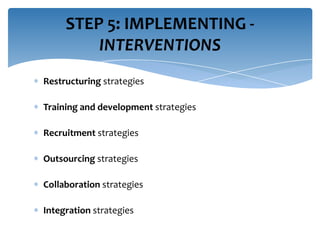
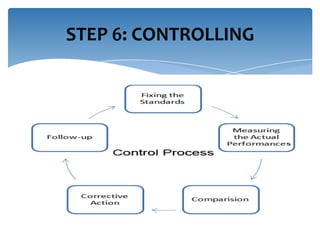
Strategic workforce planning (SWP) is a proactive management process that helps organizations anticipate future labor needs and align workforce skills with business goals. It involves steps such as scanning, profiling, analyzing, developing, implementing, and controlling to ensure an adequate workforce that meets strategic objectives. By identifying workforce gaps and planning accordingly, organizations can achieve better productivity, competitive advantages, and enhanced employee engagement.