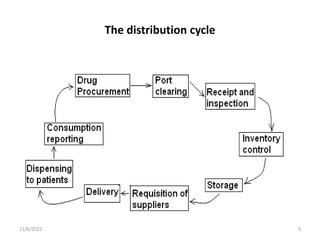
The document discusses drug distribution and stock management. It explains that drug distribution involves receiving drugs from suppliers and securely transporting them to healthcare facilities for patient use. It also outlines the objectives of maintaining constant supply and minimizing losses. The document then describes stock management, including proper storage conditions, inventory control methods like FEFO, and determining stock levels. Physical inventory counts are recommended to ensure accurate record keeping.