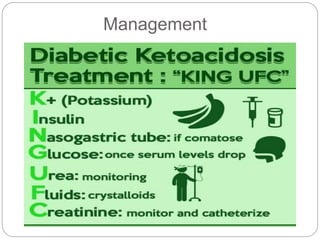
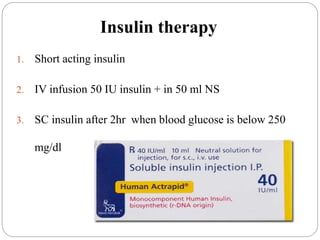
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious condition caused by insufficient insulin that prevents glucose from entering cells, resulting in hyperglycemia, polyuria, and polydipsia. It is diagnosed when blood glucose is over 250 mg/dL, blood pH is below 7.35, and bicarbonate is below 15 mEq/L. Nursing management involves three phases: assessment, management, and monitoring. Management in the first 24-48 hours focuses on fluid resuscitation and insulin therapy to correct electrolyte imbalances and lower blood glucose while closely monitoring vital signs and lab values.