The document examines the relationship between stock market returns, inflation, and real economic activity in India. It analyzes two hypotheses: the Fisher hypothesis about nominal stock returns and expected inflation, and the "proxy effect" hypothesis about macroeconomic relationships. The study uses an ARIMA model to test expectations and finds support for the Fisher hypothesis. Regression analyses show inflation is negatively linked to current and future real activity, while stock returns positively correlate with current activity alone. The results contrast previous findings for developed economies.





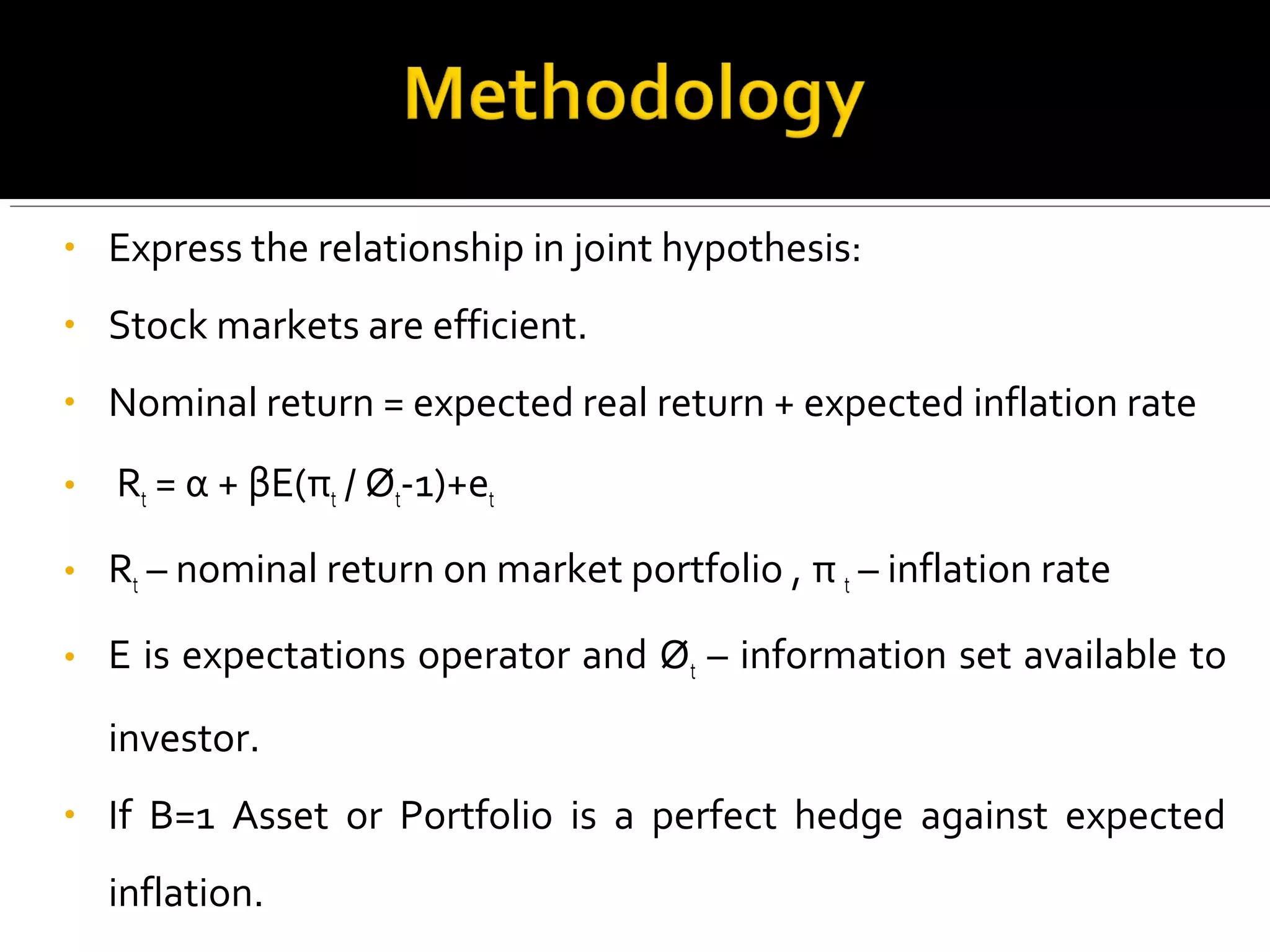
![• Real returns and expected inflation rate vary independent of
each other. This extension involves decomposing of inflation
rate into an expected and unexpected component.
• Rt = α + β1E(π t / Øt-1)+β2[(π t –E(πt/ Øt-1)]+nt’
• unexpected component=Realized inflation rate and
expected inflation rate.
• Regression of real Stock returns on current and future real
Activity.
• (Rt- Πt)= α + βΣTt+I](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stockmarketreturn-141007085122-conversion-gate01/75/Stock-market-return-7-2048.jpg)


