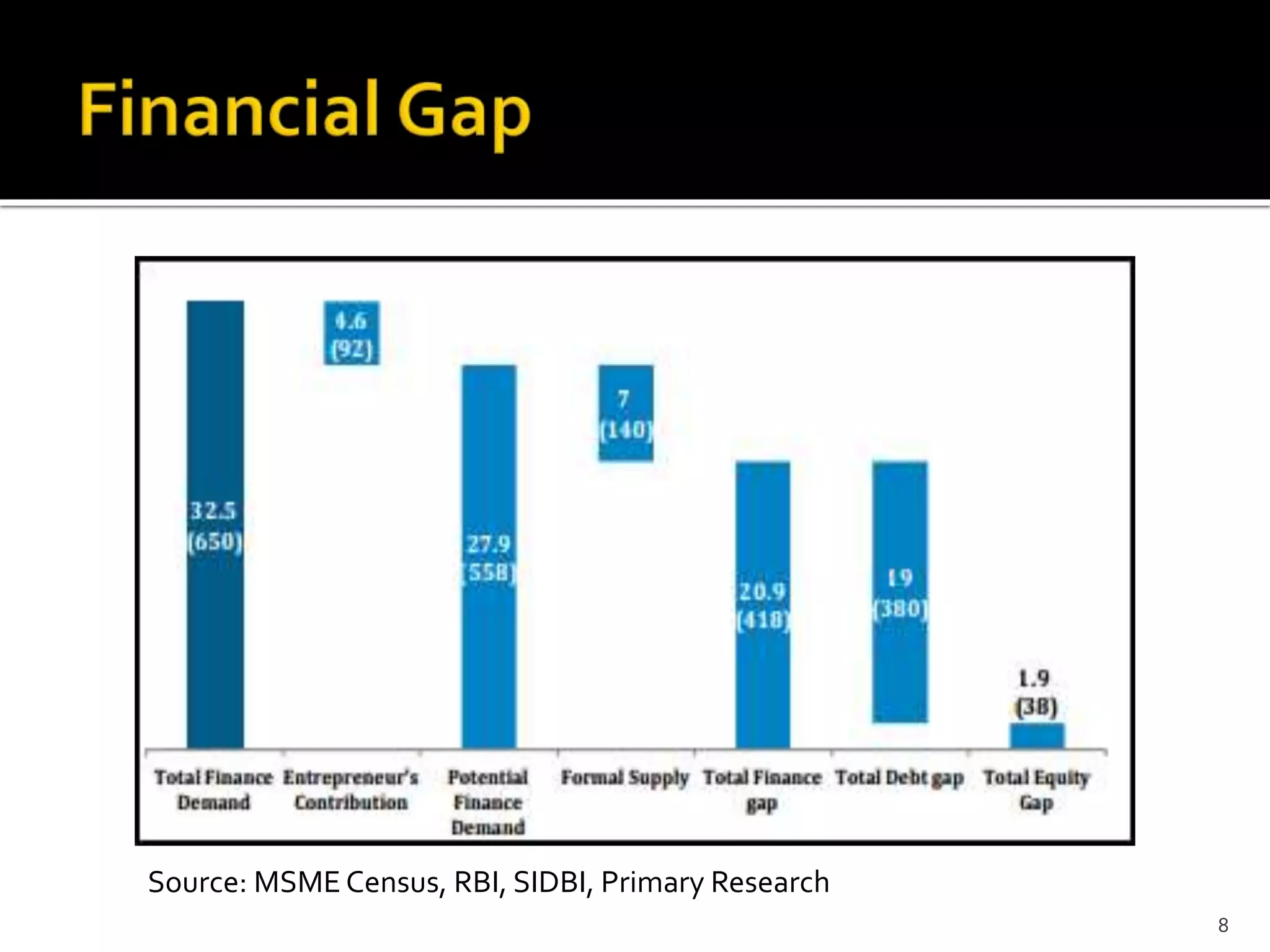
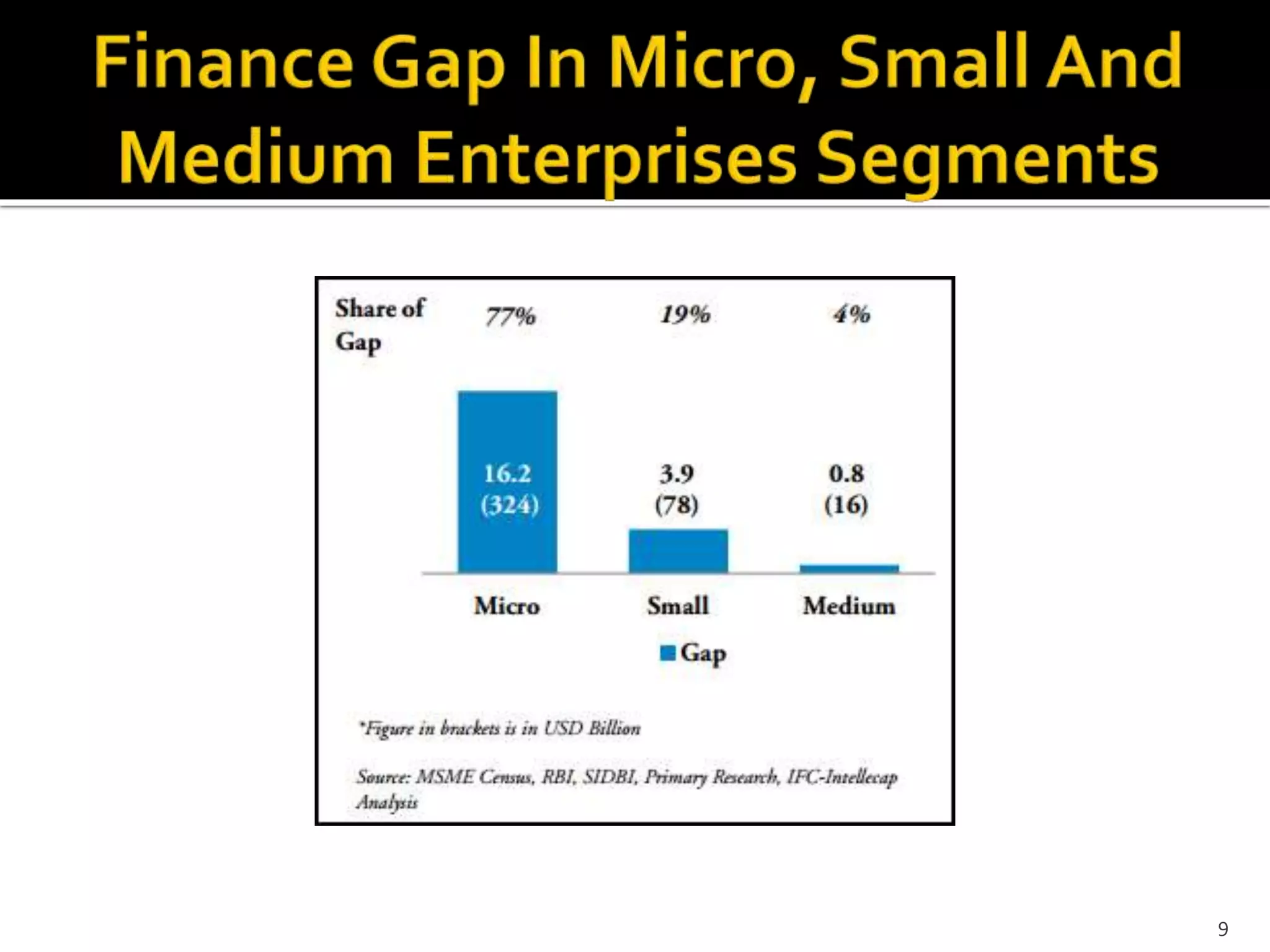
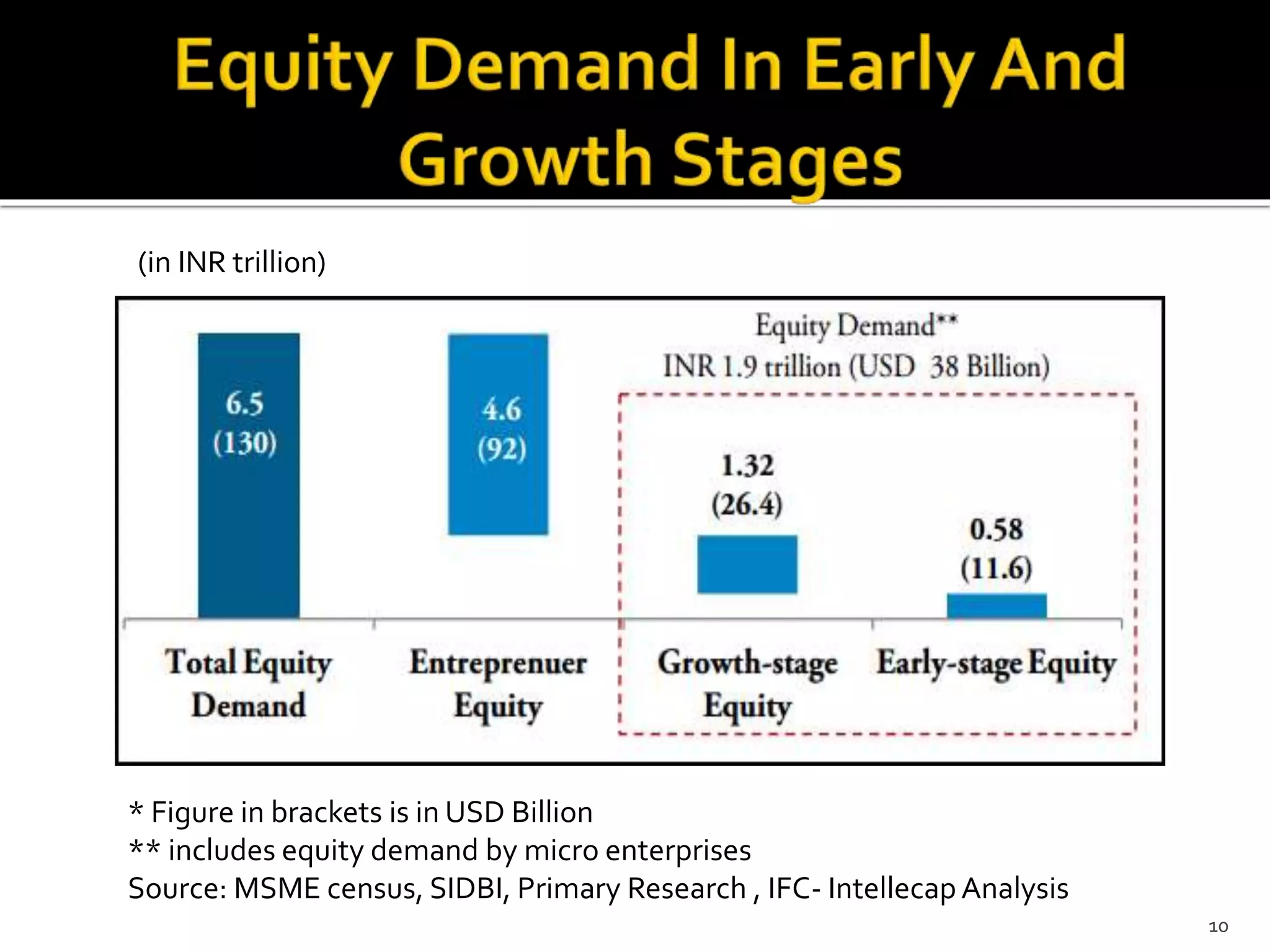
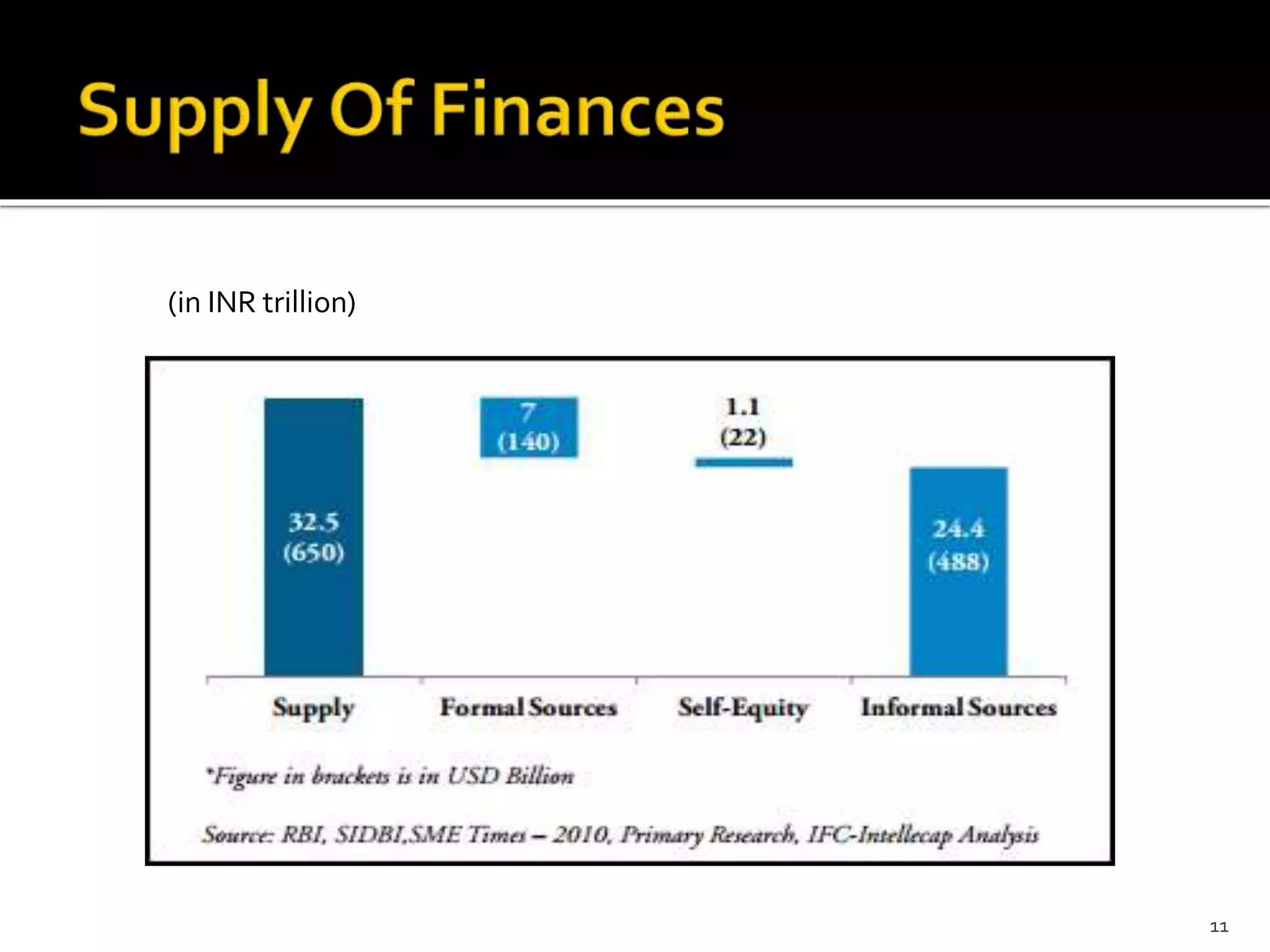
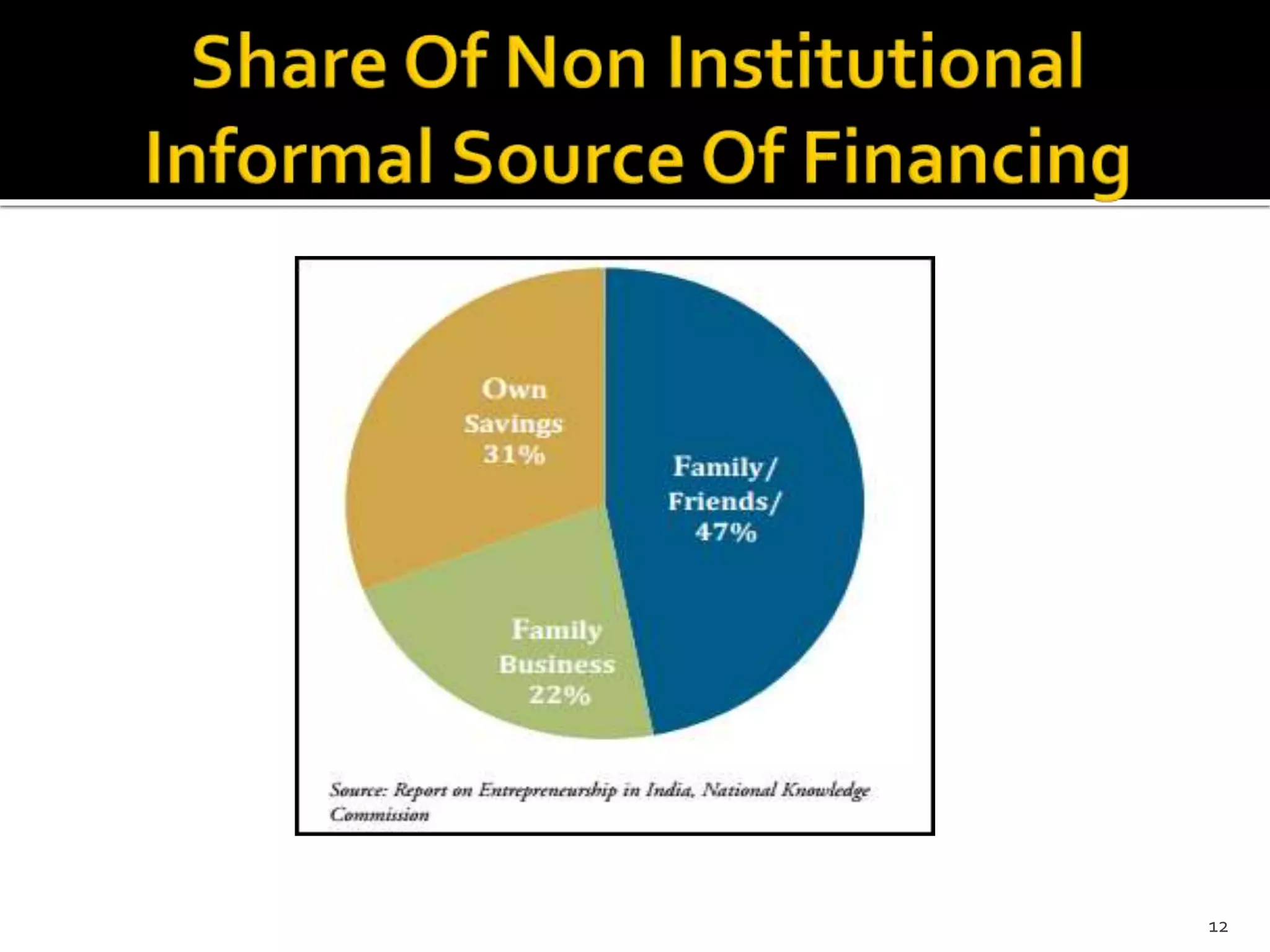
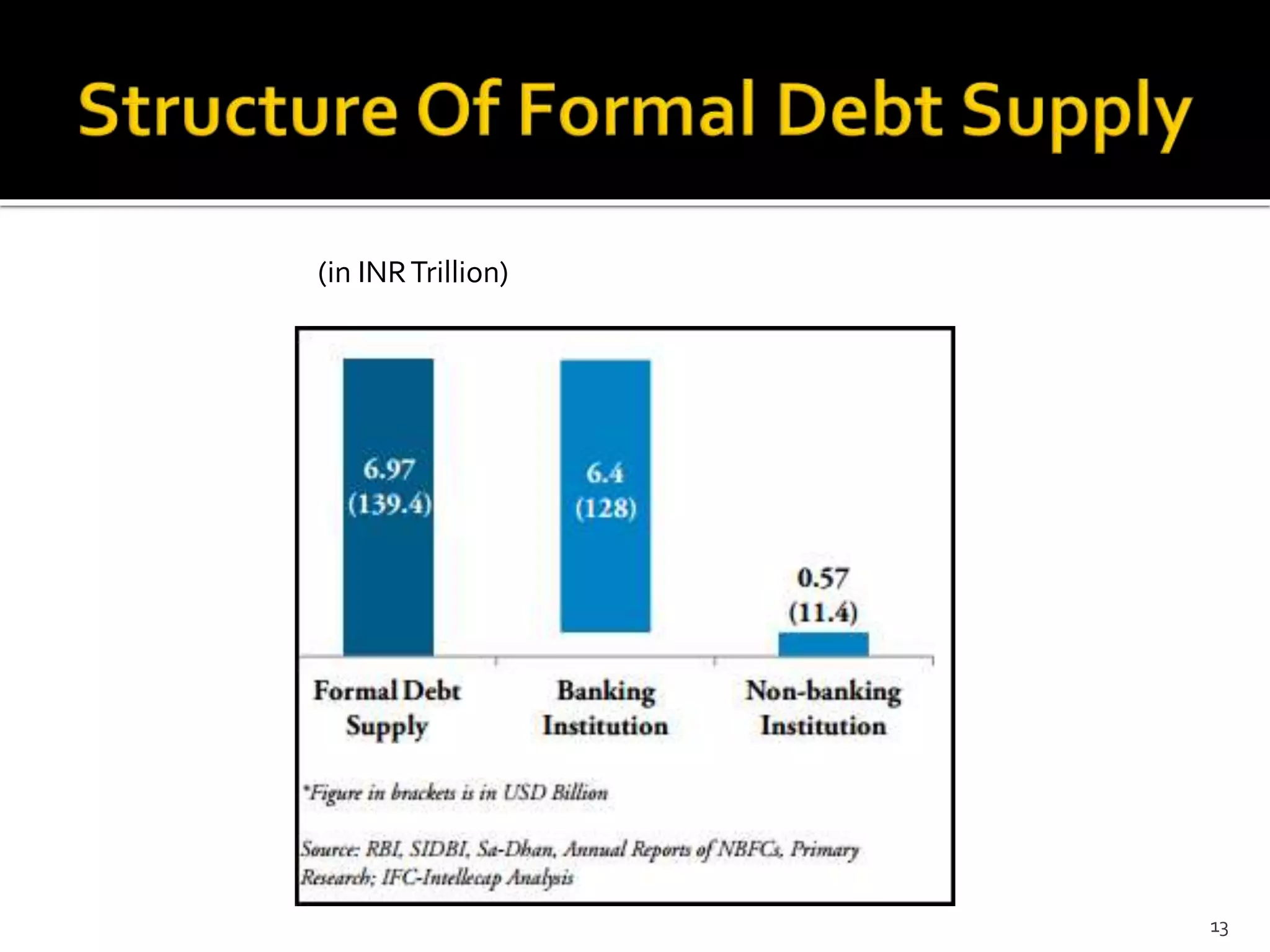
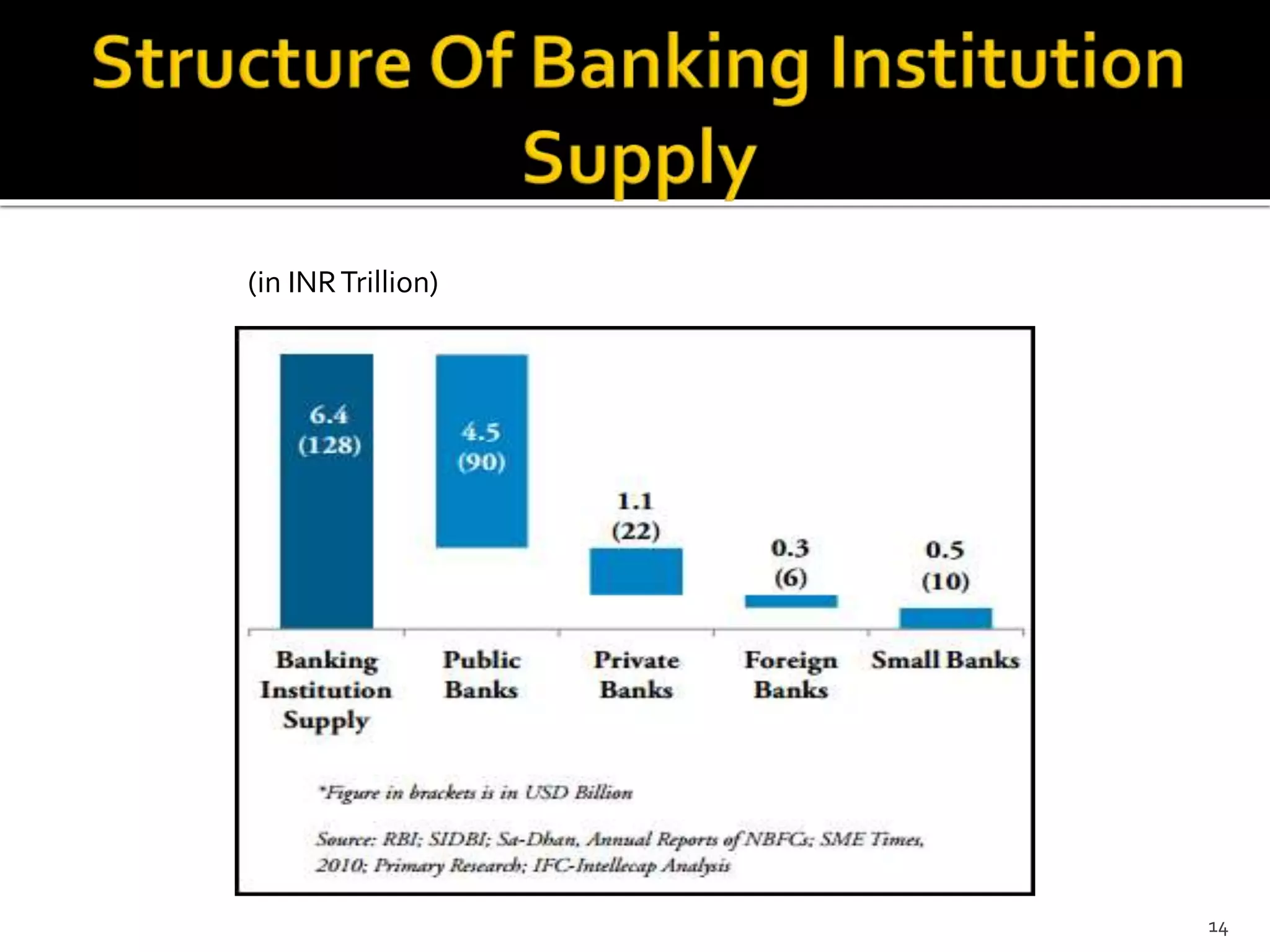
The document presents a project report analyzing the financing challenges faced by micro and small enterprises (MSEs) in the banking and financial services sector, particularly focusing on Bank of Baroda. It outlines the need for a total finance requirement of INR 32.5 trillion ($650 billion) and highlights a significant financing gap of INR 20.9 trillion ($418 billion) for MSEs. The report elaborates on data sources, research methodology, and includes various chapters addressing the problems, literature review, and proposed solutions for stimulating financing in the MSE sector.