Embed presentation
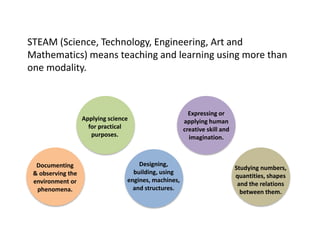





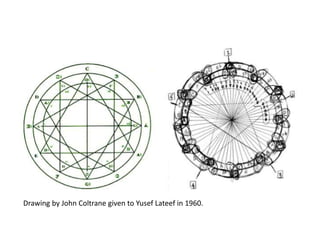

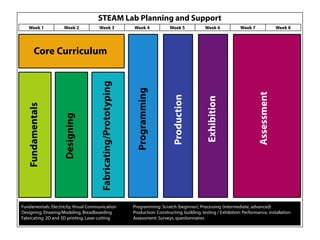

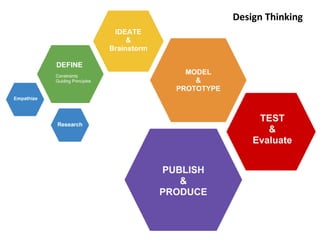
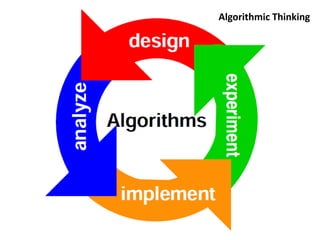






STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Art and Mathematics) involves teaching and learning using multiple disciplines. A STEAM Lab allows students to explore concepts across subjects in a creative space centered around art. The document outlines various STEAM concepts and techniques students may explore such as creating idea maps, learning to solder, creative coding, and exhibition of student work. It also provides an example of how to structure project-based STEAM learning using objectives focused on gaining student attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction.
















