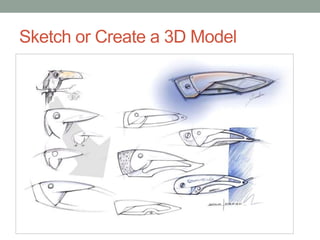
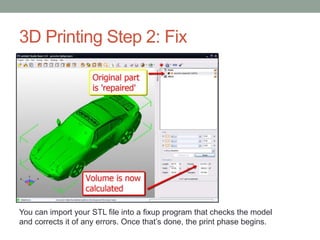
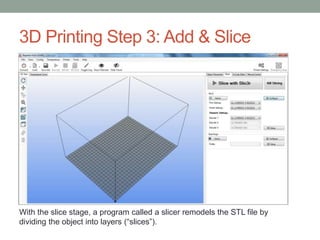
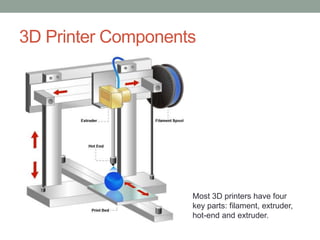
This document provides an overview of biomimicry and 3D printing for a workshop. It defines biomimicry as modeling design and production on biological entities and processes. It describes the key steps to 3D printing as modeling an object, fixing any errors, slicing it into layers, and printing. It also explains that 3D printers use materials like plastic instead of ink to create solid, three-dimensional objects. The workshop will include a live demo and discussion of biomimicry examples as well as the components of 3D printers.