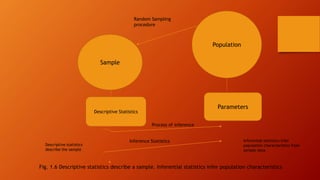
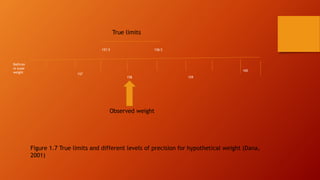
This document discusses statistics and data analysis as tools for researchers. It defines key concepts such as variables, constants, populations, samples, descriptive statistics, and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics are used to describe samples, while inferential statistics allow generalizing about populations from samples. Random sampling is emphasized as it allows each population member an equal chance of being selected. The scientific method, involving hypotheses testing, is also discussed. Statistics and data analysis provide a systematic way to examine data and gain insights, though they do not prove definitive conclusions.