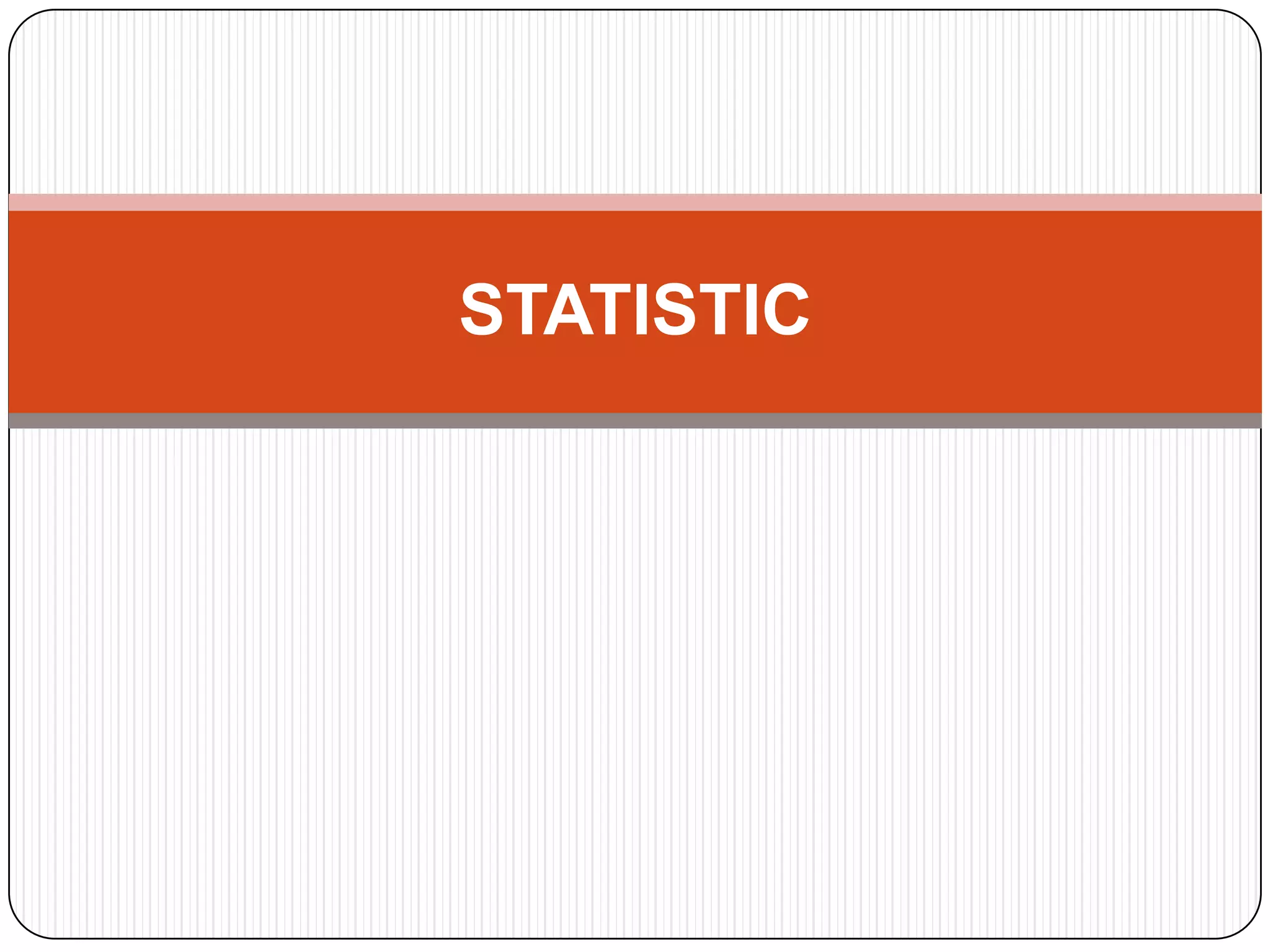
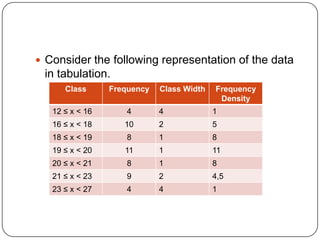
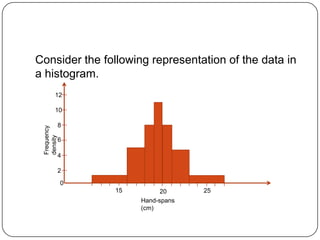
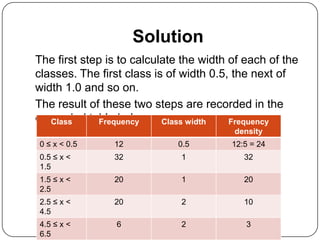
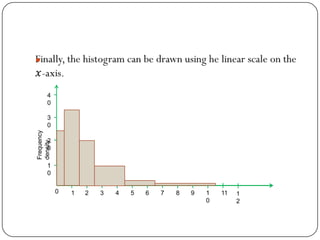
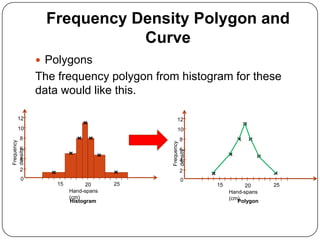
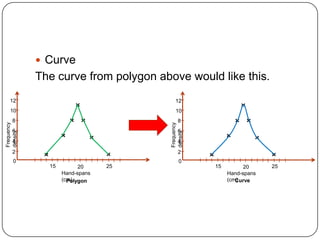
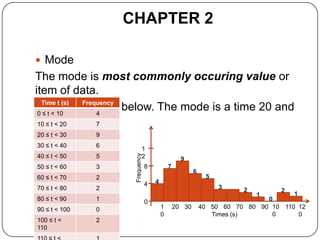
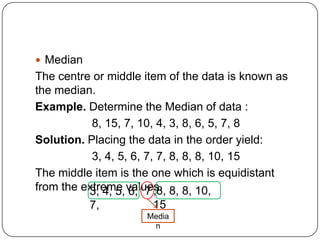
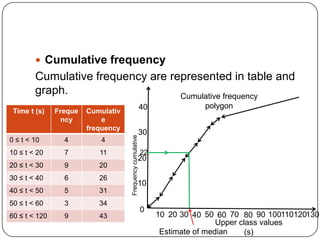
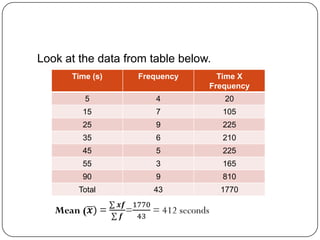
The document discusses histograms, frequency polygons, and other statistical concepts. It provides an example of children's hand span data displayed in a histogram with class intervals. It also shows how to construct a frequency polygon from the histogram and develop a curve from the polygon. Additionally, it defines statistical terms like mode, median, and cumulative frequency and provides examples of calculating each from sets of data.