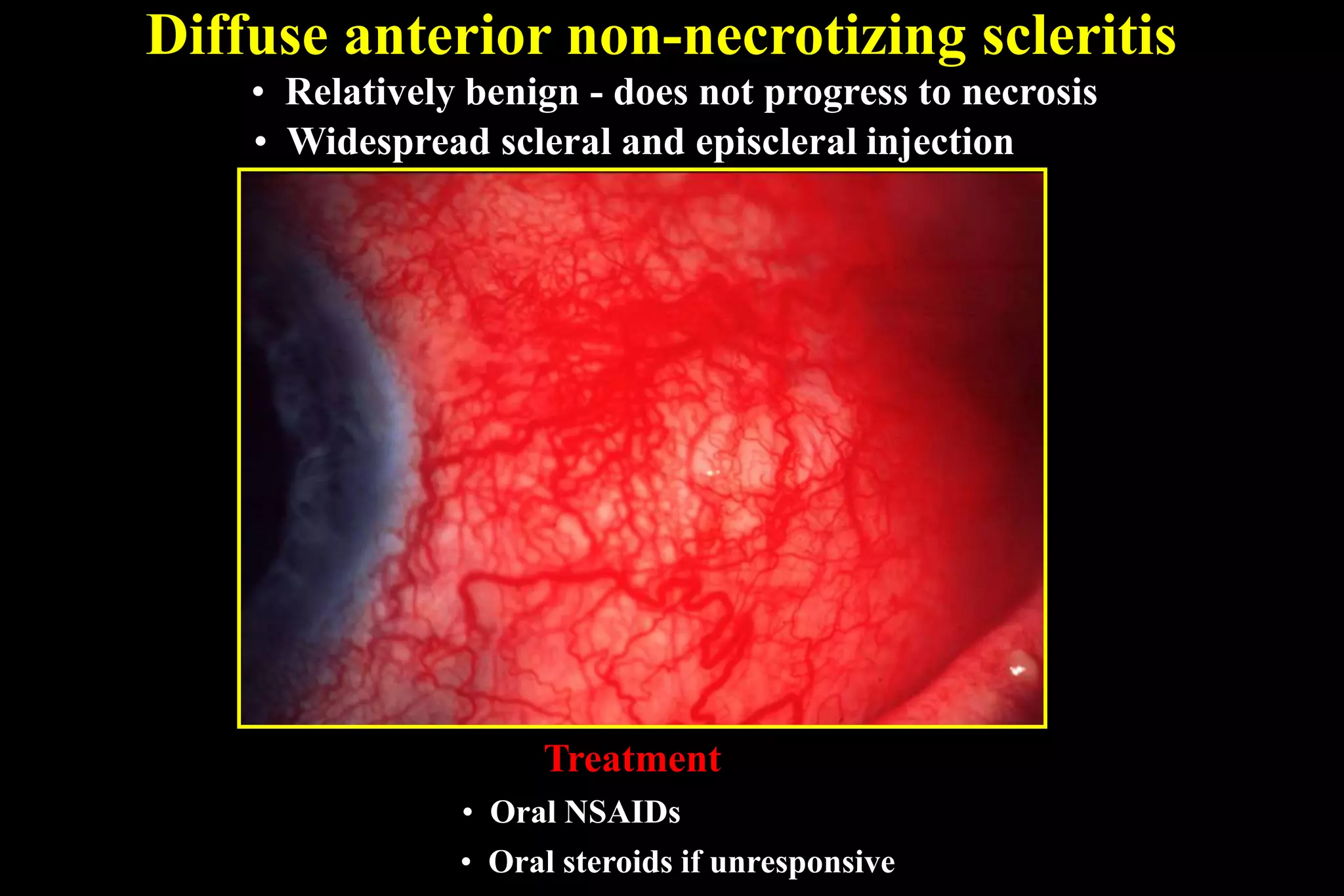
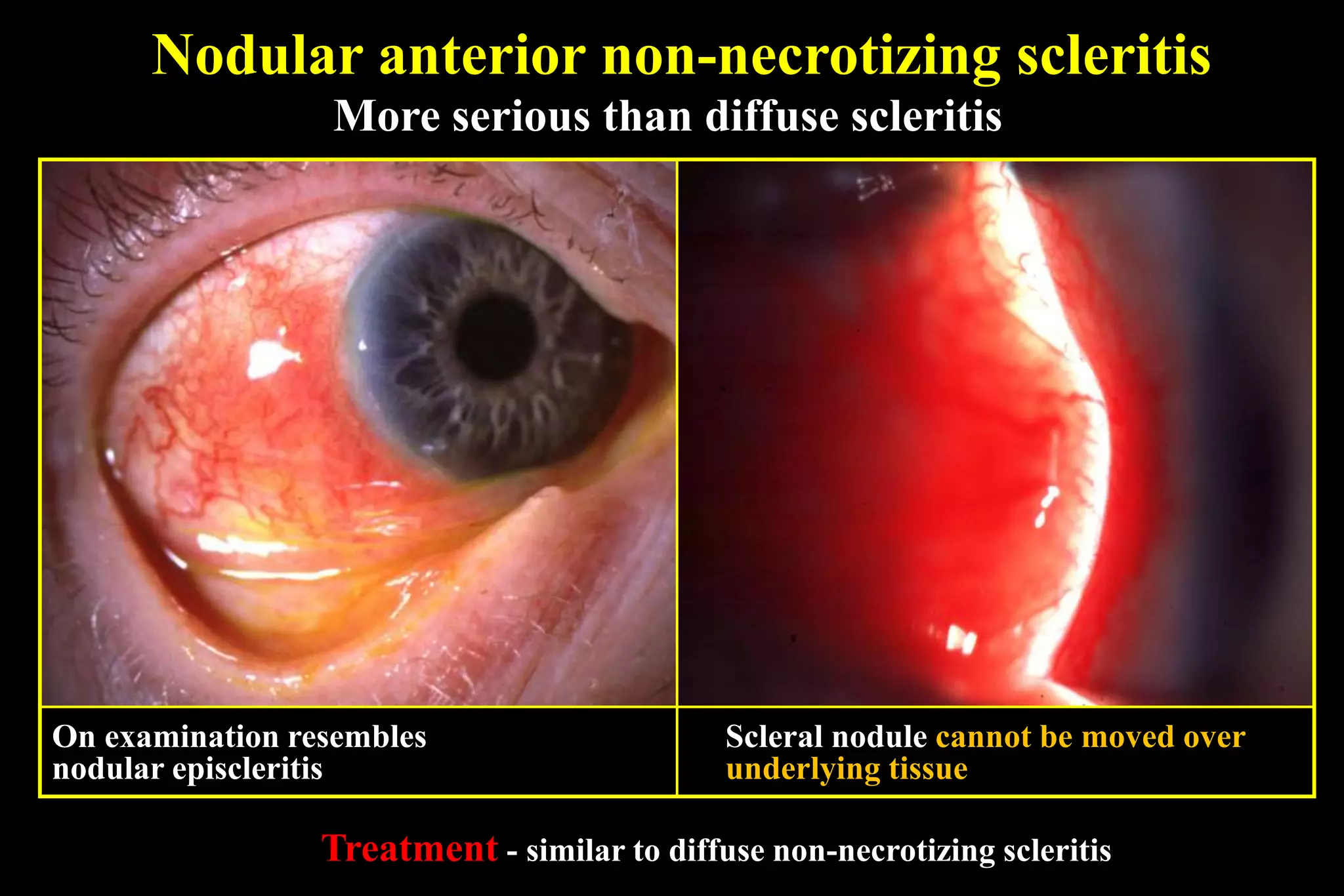
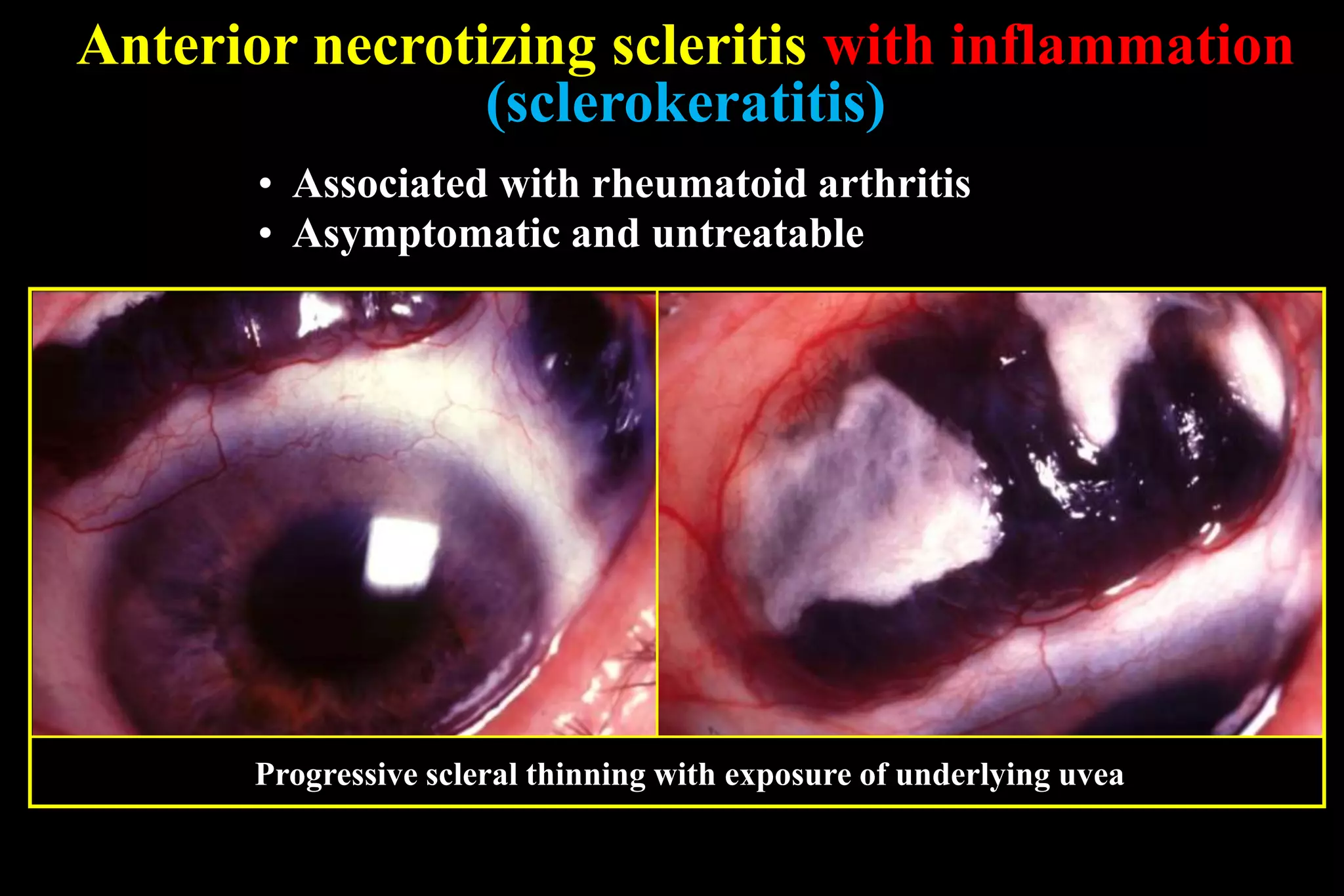
The sclera is the dense outer layer of the eyeball. It can develop two types of inflammation - episcleritis and scleritis. Episcleritis is more common and self-limiting, often affecting young adults, while scleritis is more severe and can be associated with underlying systemic diseases. Scleritis presents with redness and swelling of the sclera and is classified as anterior or posterior depending on location. Imaging like ultrasound and CT are useful for diagnosing posterior scleritis. Treatment involves topical or oral steroids, with immunosuppressants used for severe or resistant cases. Complications can include scleral thinning and staphylomas if left untreated.