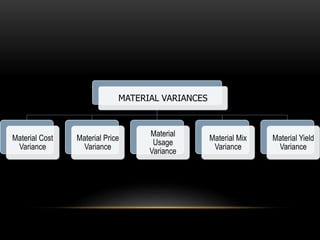
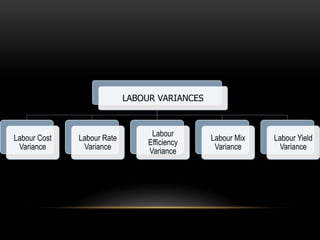
Standard costing involves establishing standard costs, comparing them to actual costs, and analyzing variances. It provides several benefits including aiding management, measuring efficiency, and promoting cost consciousness. Variance analysis examines differences between standard and actual material and labor costs. Material variances include material cost, price, usage, mix, and yield variances. Labor variances include labor cost, rate, efficiency, mix, and yield variances.