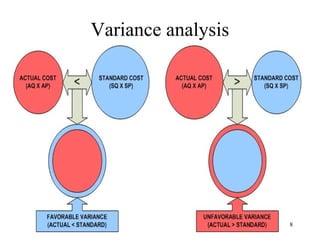
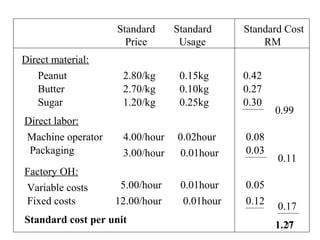
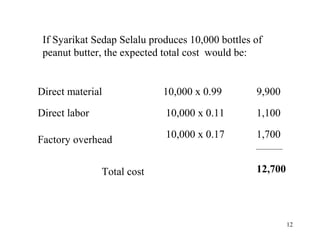
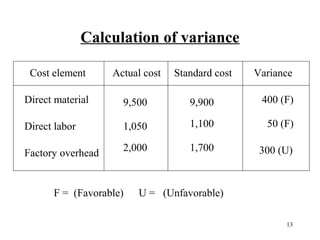
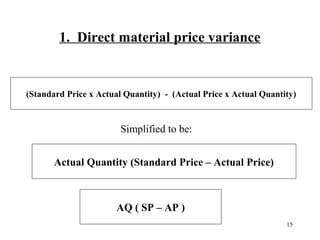
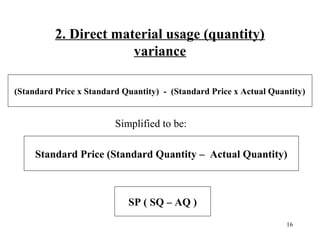
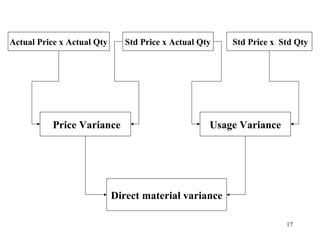
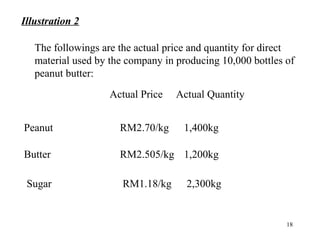
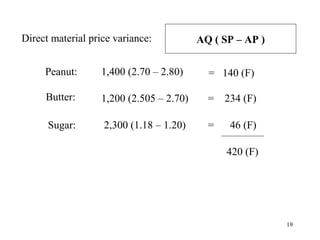
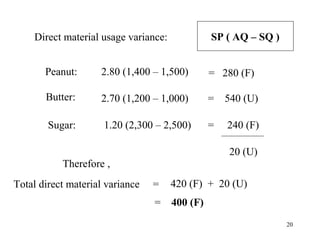
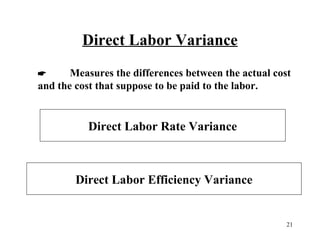
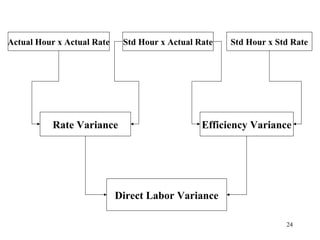
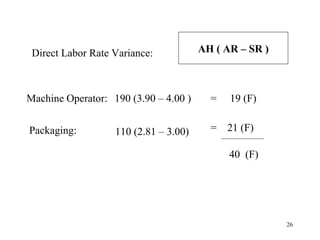
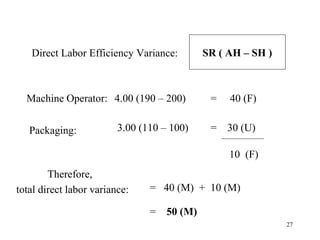
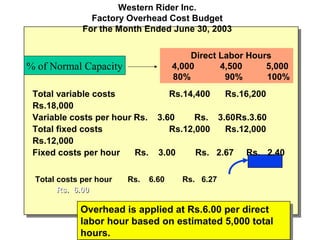
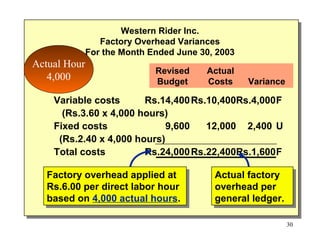
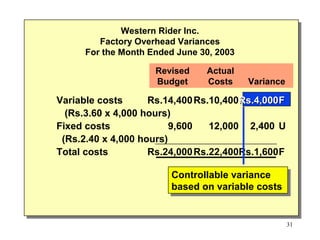
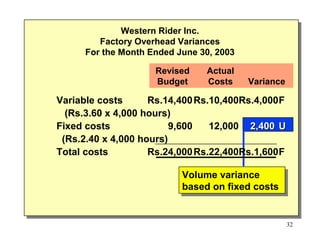
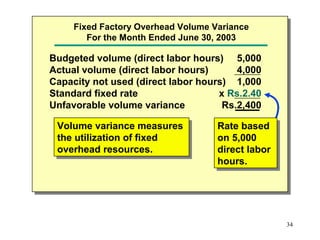
Standard costing involves setting predetermined expected costs for cost components like direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead. Variances are calculated as the difference between actual and standard costs. This includes direct material, direct labor, and factory overhead variances. The direct material variance has a price and usage component. The factory overhead variance separates variable from fixed costs, with the controllable variance measuring variable cost efficiency and volume variance measuring fixed cost utilization.