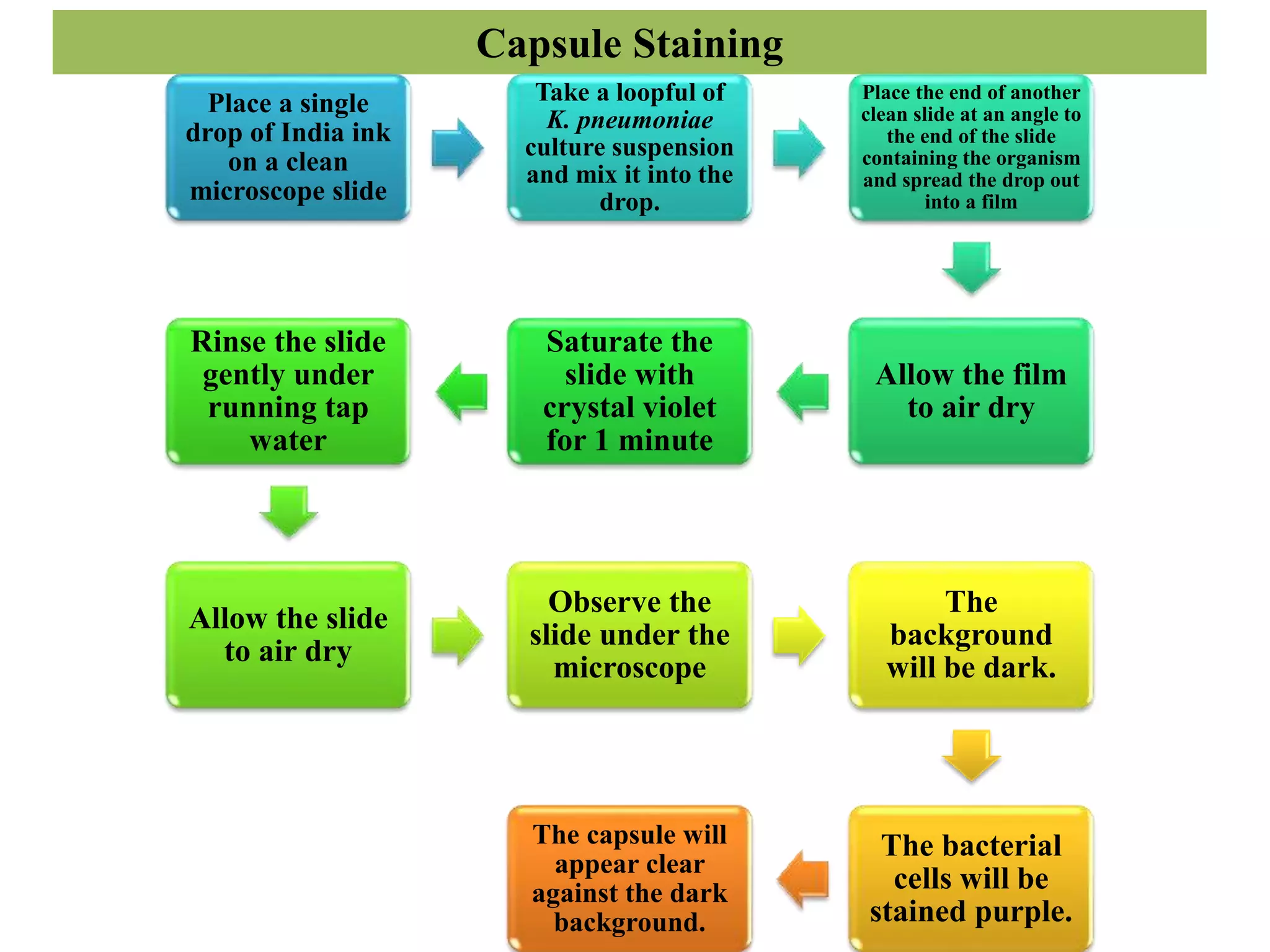
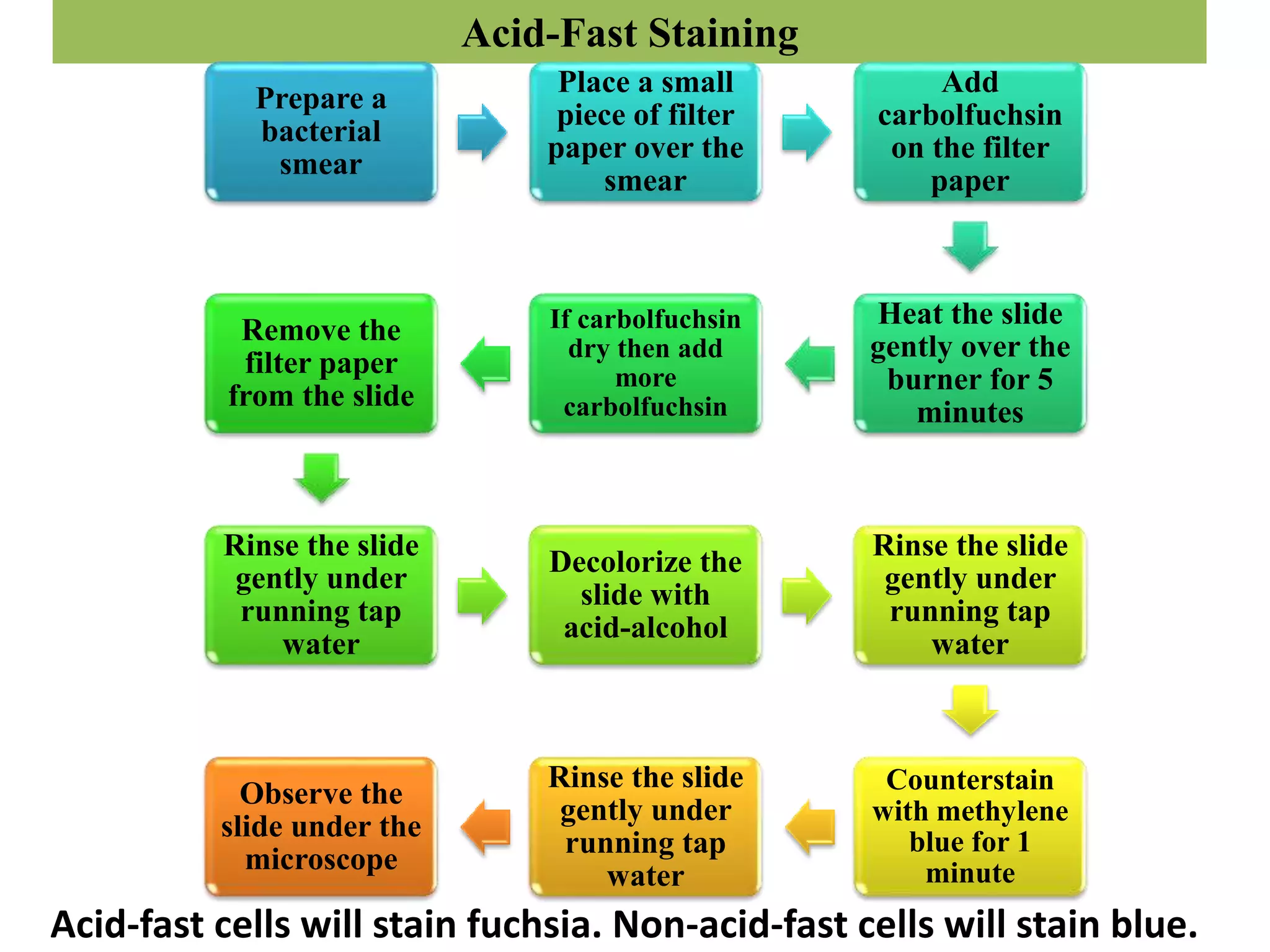
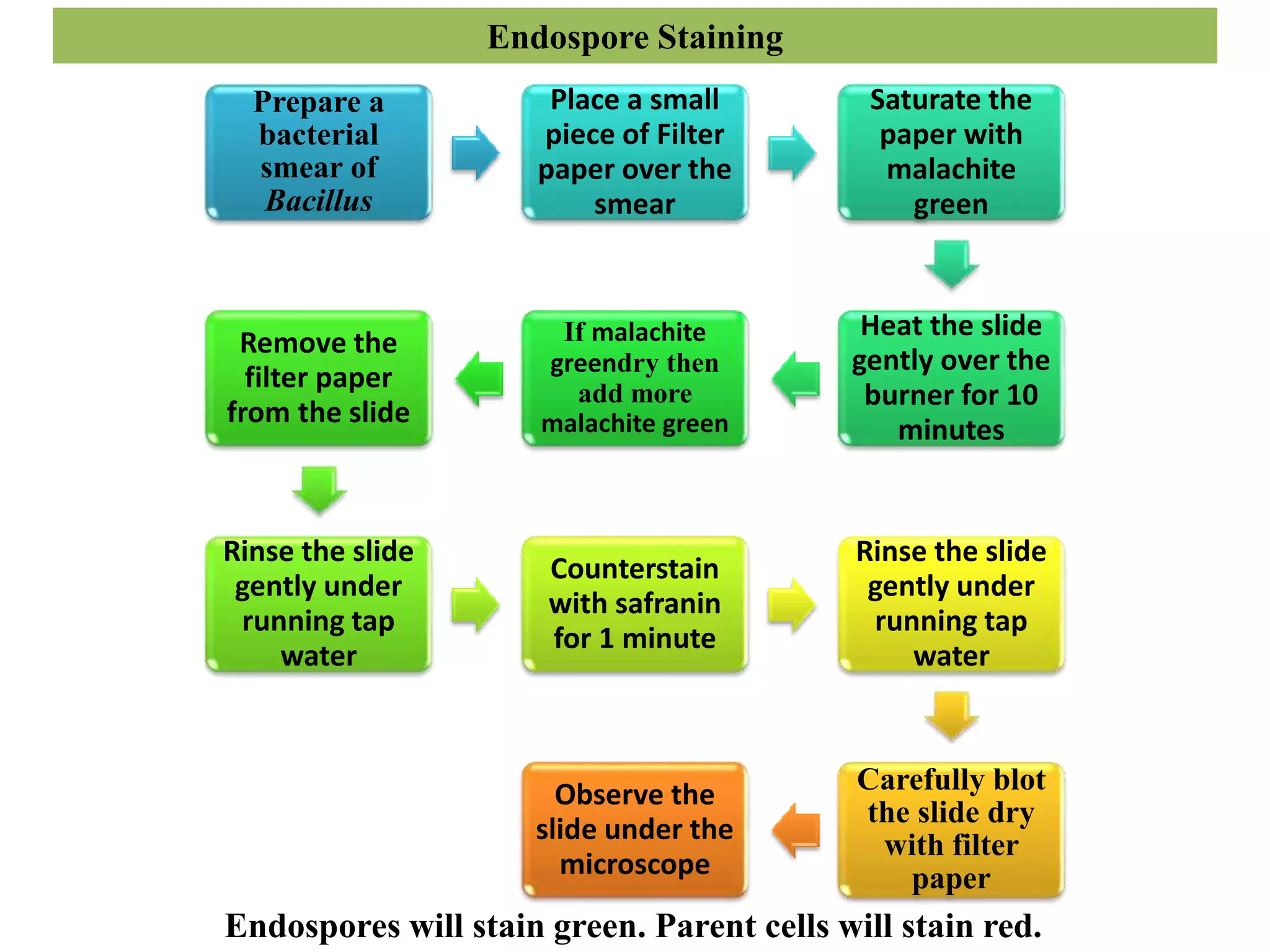
Staining is a technique used to improve contrast and study samples at the microscopic level. There are several types of stains including acidic, basic, and neutral stains. Basic staining techniques involve preparing a smear, applying a dye, rinsing, and examining under a microscope. Specific techniques are used for simple/positive staining, negative staining, Gram staining, capsule staining, acid-fast staining, and endospore staining to identify cell morphology and structure. Proper staining allows visualization of cellular and structural features that aid in identification and disease diagnosis.