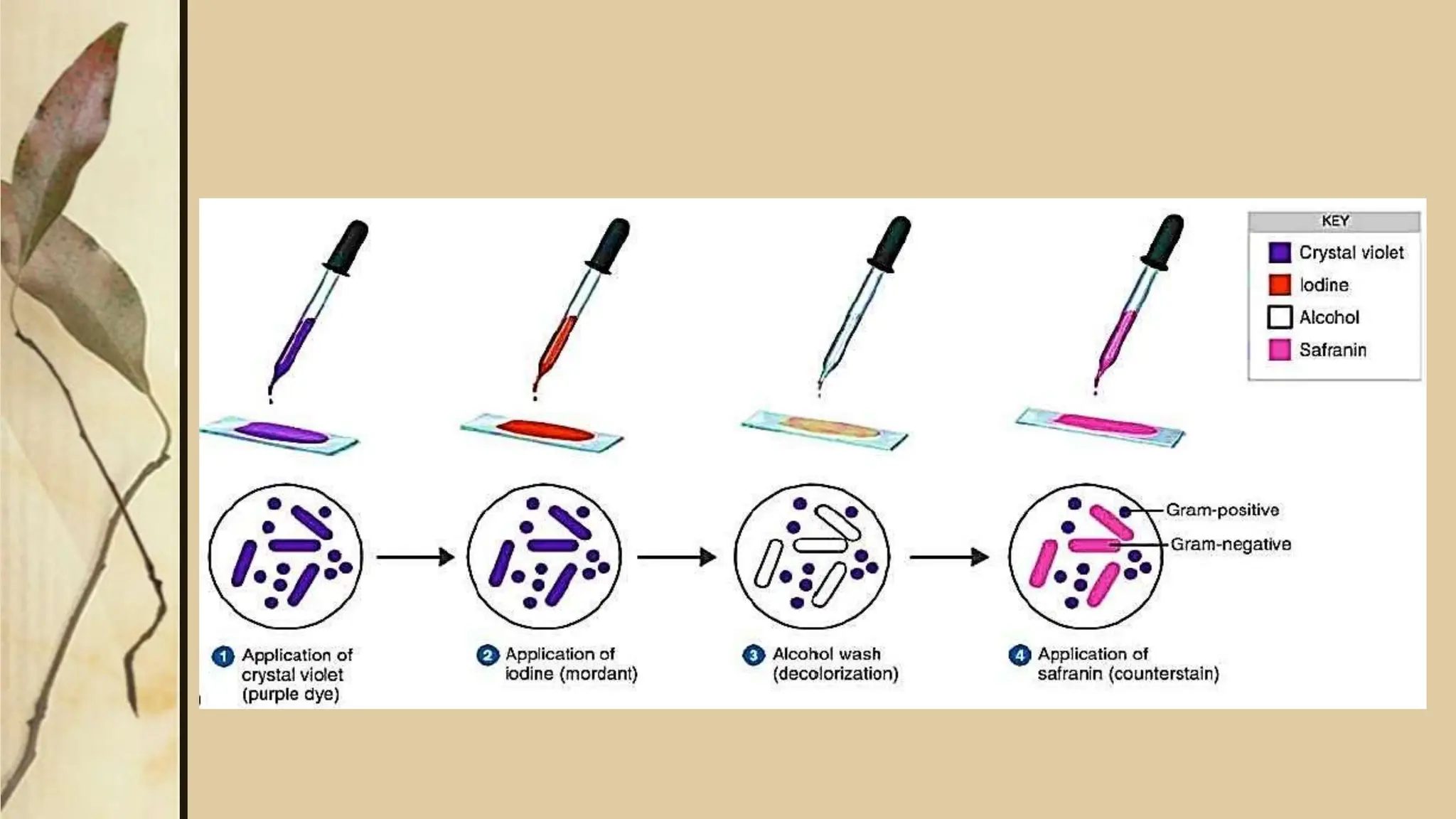
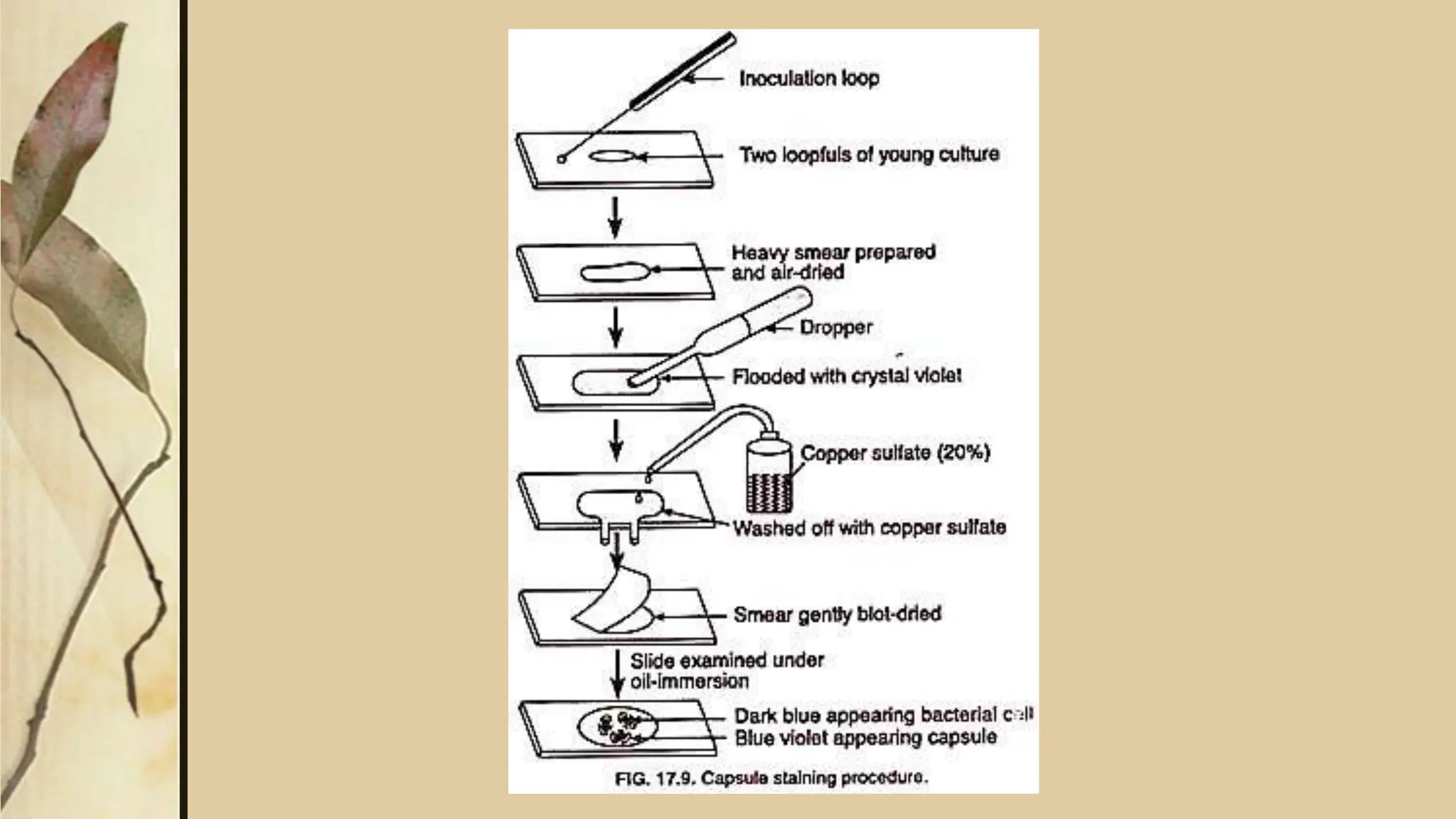
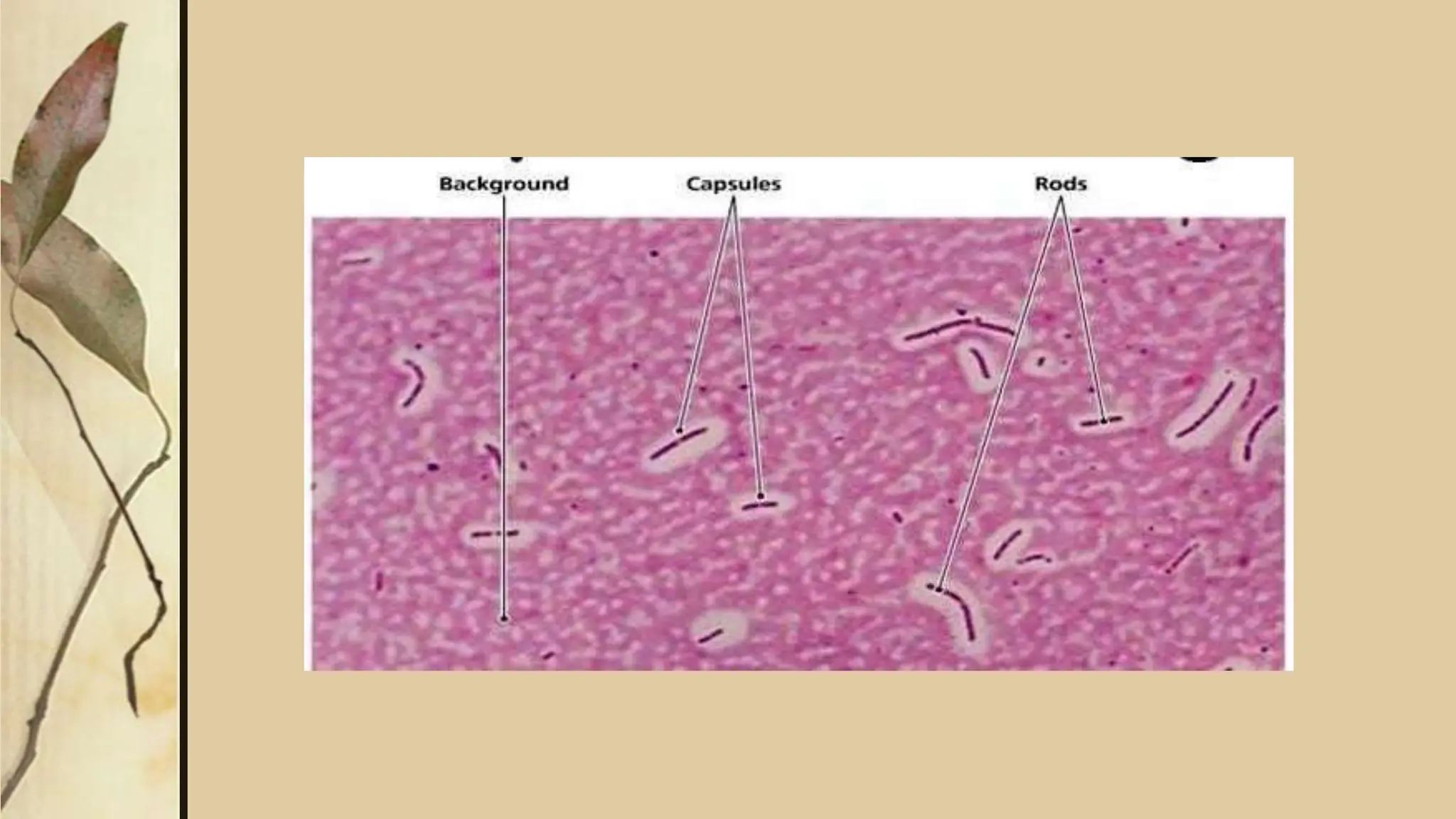
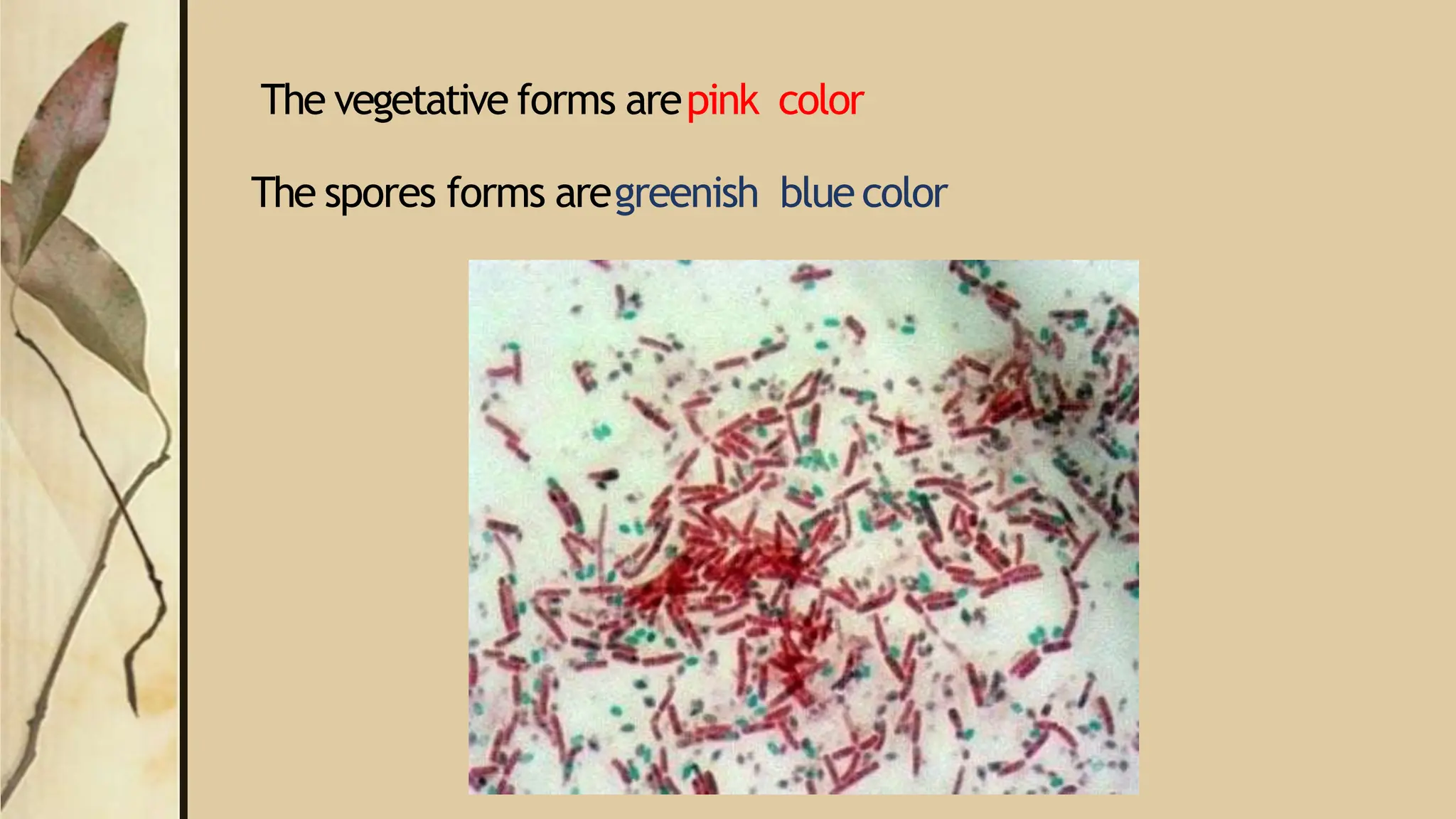
This document discusses various staining techniques used to visualize microorganisms under a microscope. It begins by explaining why staining is necessary since microorganisms cannot be seen with the naked eye. It then covers different types of staining including simple staining, Gram staining, acid-fast staining, negative staining, and specialized staining techniques for flagella, capsules, and spores. Each staining method is described in 1-2 sentences and includes the basic procedure and results.