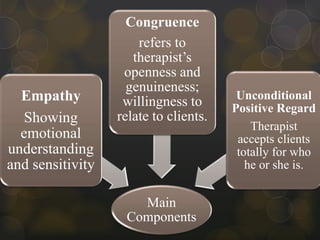
Client-centered therapy, also known as person-centered therapy, was developed by Carl Rogers in the 1940s-1950s. It is a nondirective approach where the client takes an active role in treatment and the therapist provides empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard. The goal is to help clients resolve incongruences and fully accept themselves so they can better understand and express their feelings, lower defensiveness, and develop more positive relationships. The therapist listens without judgment and helps the client gain self-awareness and autonomy through the therapeutic process.