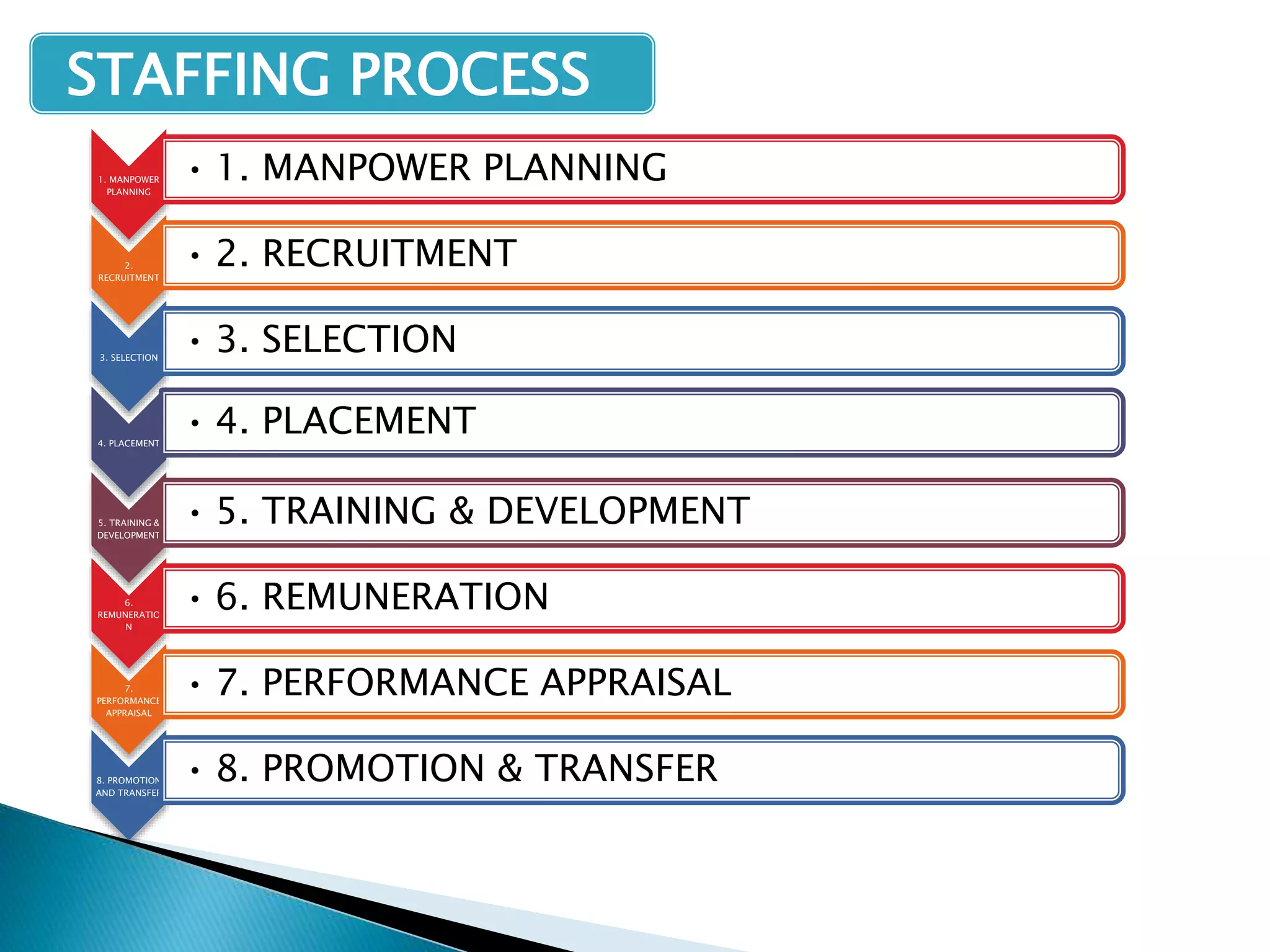
The document outlines the essential aspects of staffing as a management function, emphasizing its importance in recruiting, training, and developing employees to optimize organizational performance. It details various types of staffing strategies, the staffing process, and the vital role of manpower planning in ensuring efficient human resource allocation. Furthermore, it discusses key components like recruitment methods, selection processes, employee training, remuneration, performance appraisal, and the significance of promotions and transfers in workforce management.