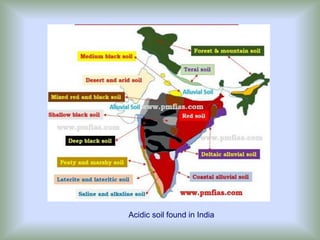
Acidic soils occupy approximately 60% of the earth's land area. Soils become acidic when elements that are naturally acidic in reaction, like hydrogen ions, increase in concentration and lower the soil pH below 7. Acidic soils commonly form in humid, high rainfall areas due to leaching of basic cations like calcium and magnesium. They can also form from acidic parent materials like igneous rocks or due to excessive application of acid-forming fertilizers. Acidic soils have light texture, low organic matter and water holding capacity, and contain clay minerals like kaolinite. They negatively impact plant growth through both direct toxicity of hydrogen ions and indirect effects like aluminum toxicity and phosphate fixation. Approximately 49 million hectares of