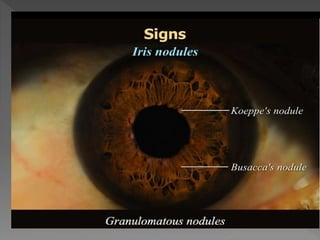
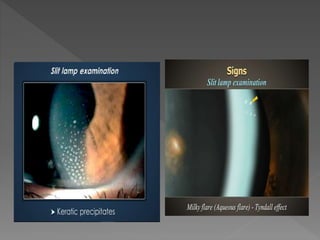
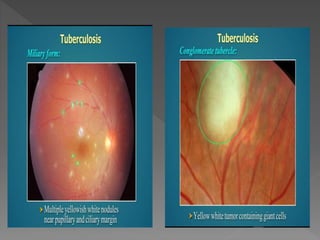
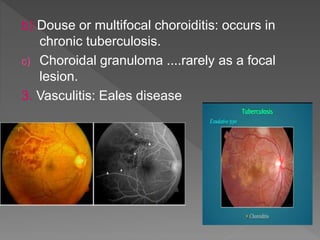
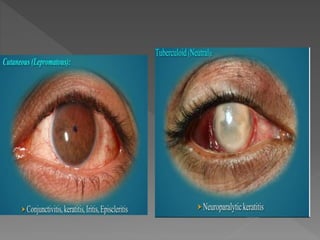
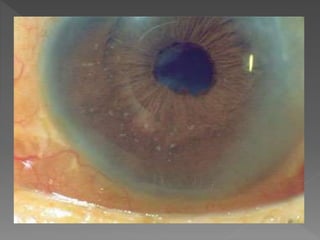
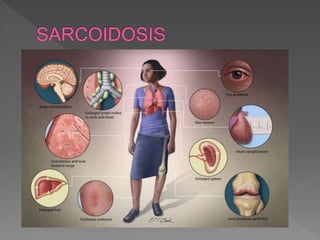
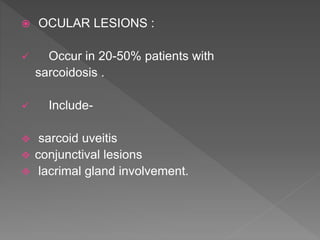
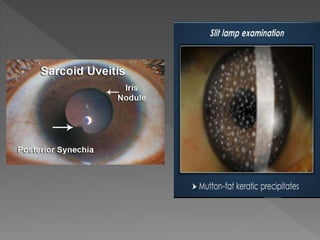
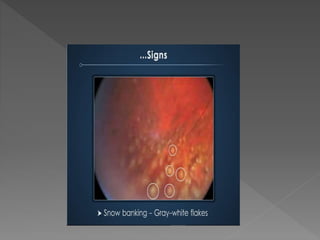
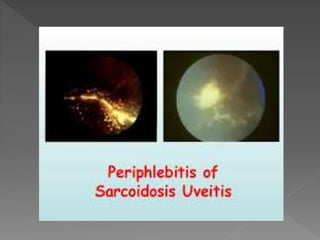
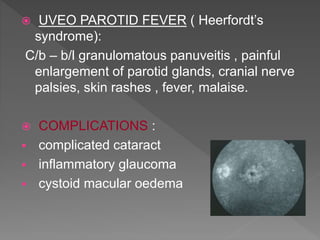
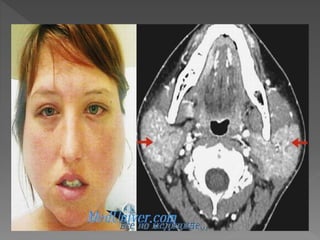
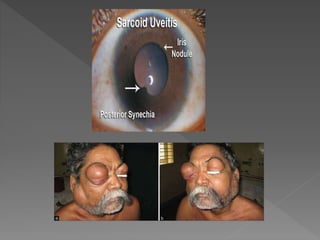
This document discusses various types of granulomatous uveitis including tuberculosis (TB), leprosy, and sarcoidosis. It provides details on the etiology, clinical features, signs, course, classifications, and treatments of these conditions. Granulomatous uveitis is characterized by insidious onset, minimal pain, slight photophobia, minimal ciliary congestion, thick and broad-based posterior synechiae, and nodular lesions in the fundus. Specific treatments involve anti-tuberculous drugs for TB, dapsone for leprosy, and topical, periocular or systemic steroids for sarcoidosis depending on severity.























![Sravani gembali.pptx[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sravanigembali-181022063344/85/Sravani-gembali-pptx-1-42-320.jpg)
![Sravani gembali.pptx[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sravanigembali-181022063344/85/Sravani-gembali-pptx-1-43-320.jpg)
![Sravani gembali.pptx[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sravanigembali-181022063344/85/Sravani-gembali-pptx-1-44-320.jpg)