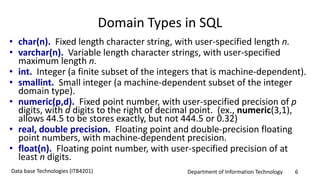
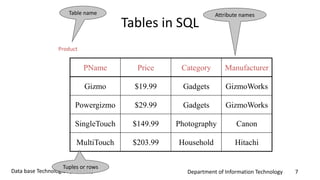
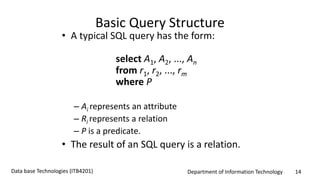
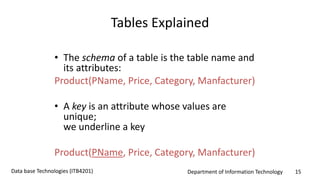
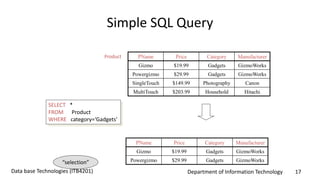
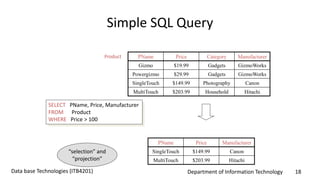
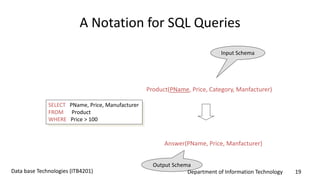
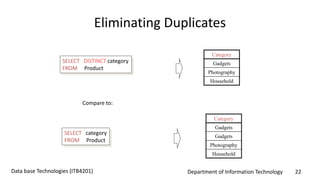
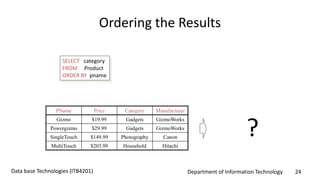
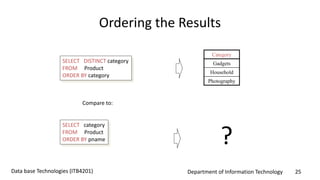
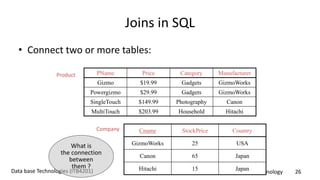
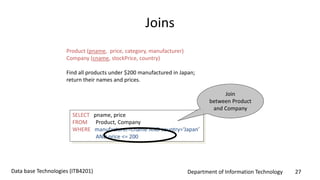
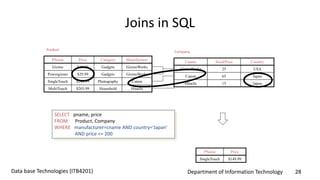
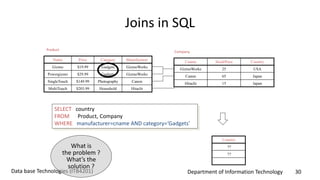
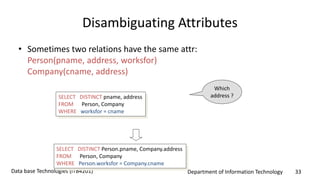
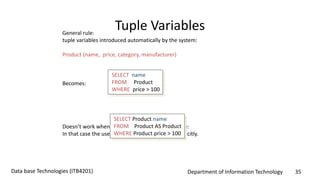
This document discusses an introduction to Structured Query Language (SQL). It covers SQL concepts like data definition language to create and modify database tables, data types, queries to select data from one or multiple tables, filtering with selections, ordering results, and joining tables. The document is presented as part of a university course on database technologies by the Department of Information Technology.