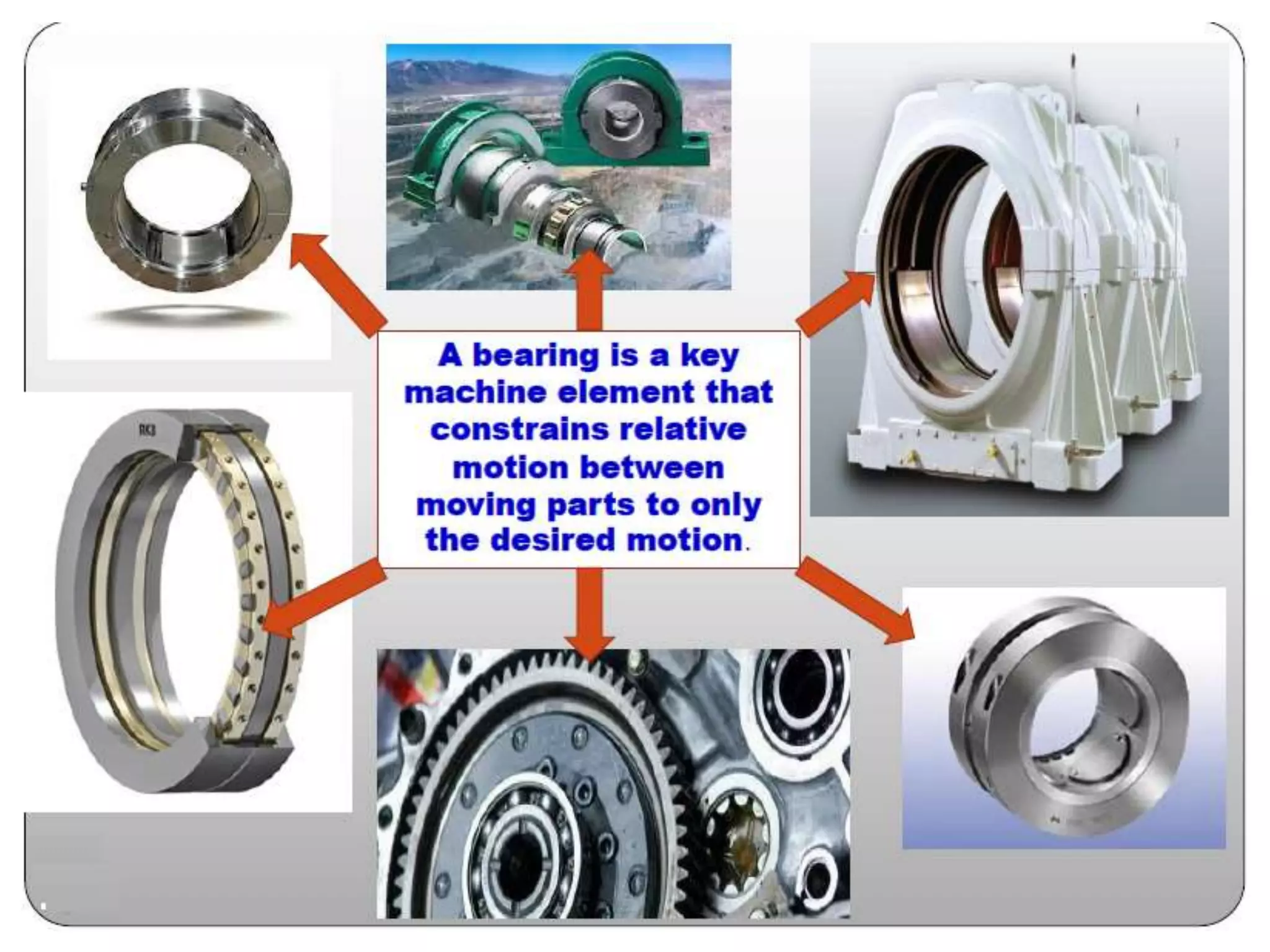
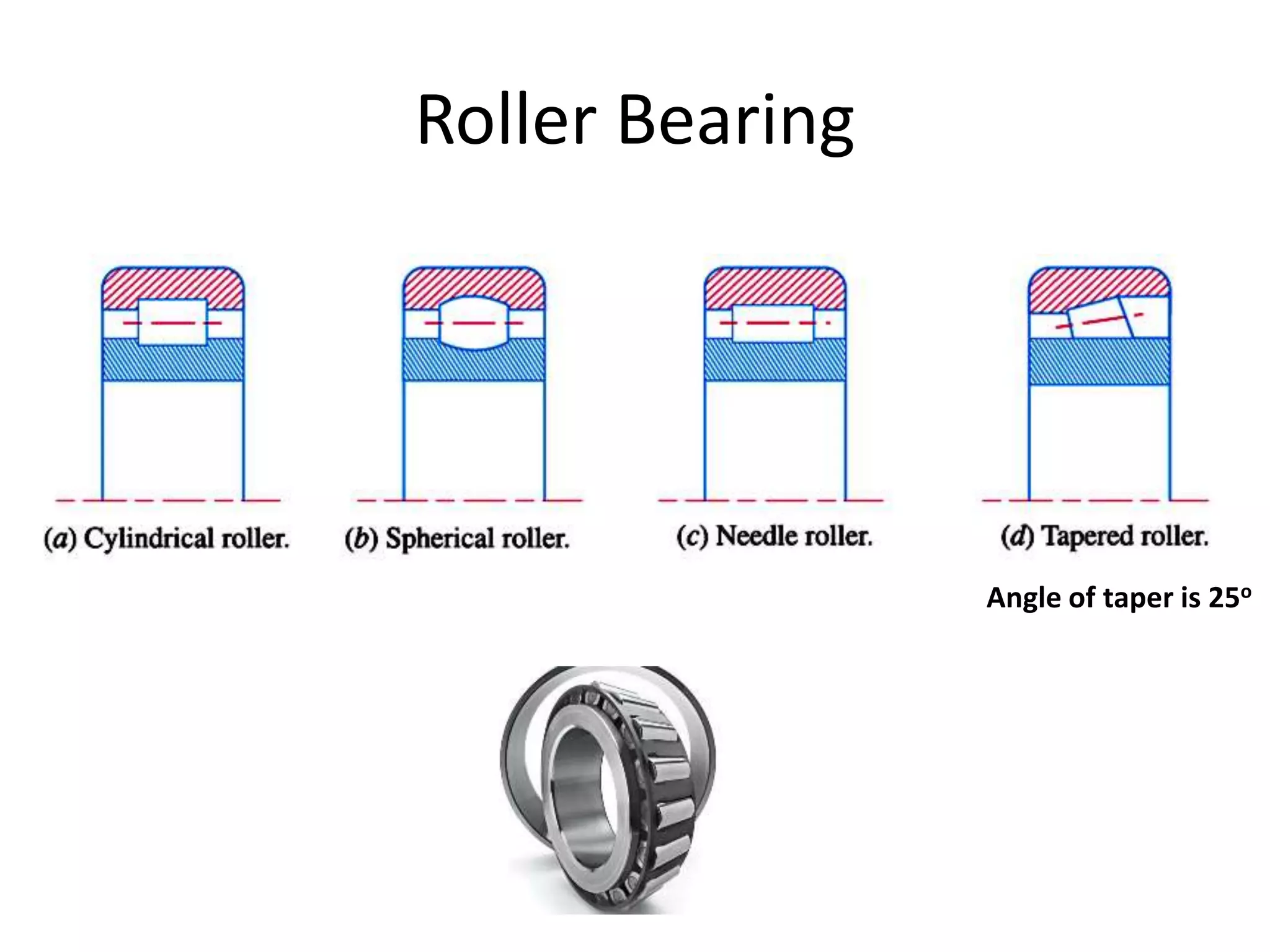
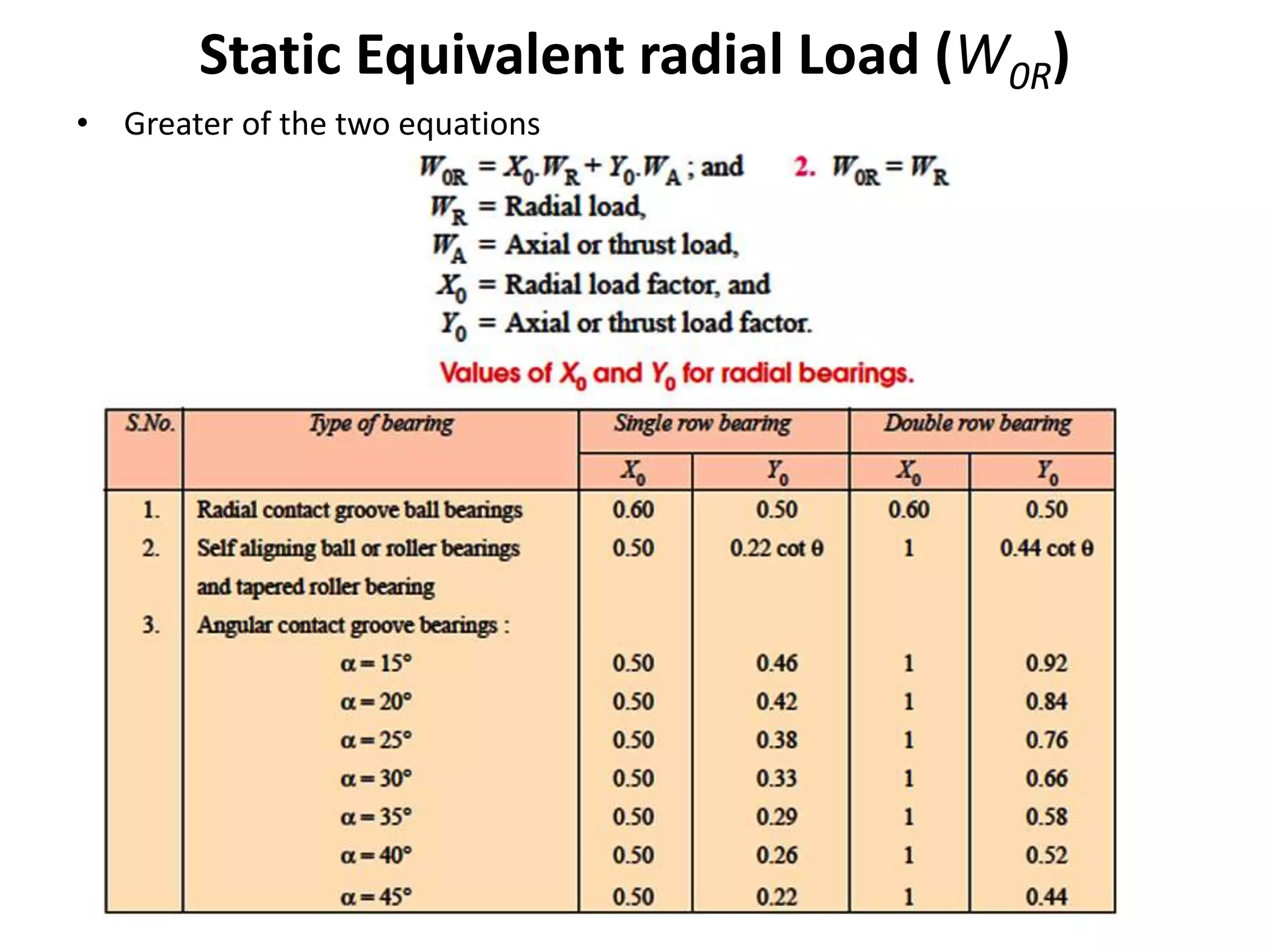
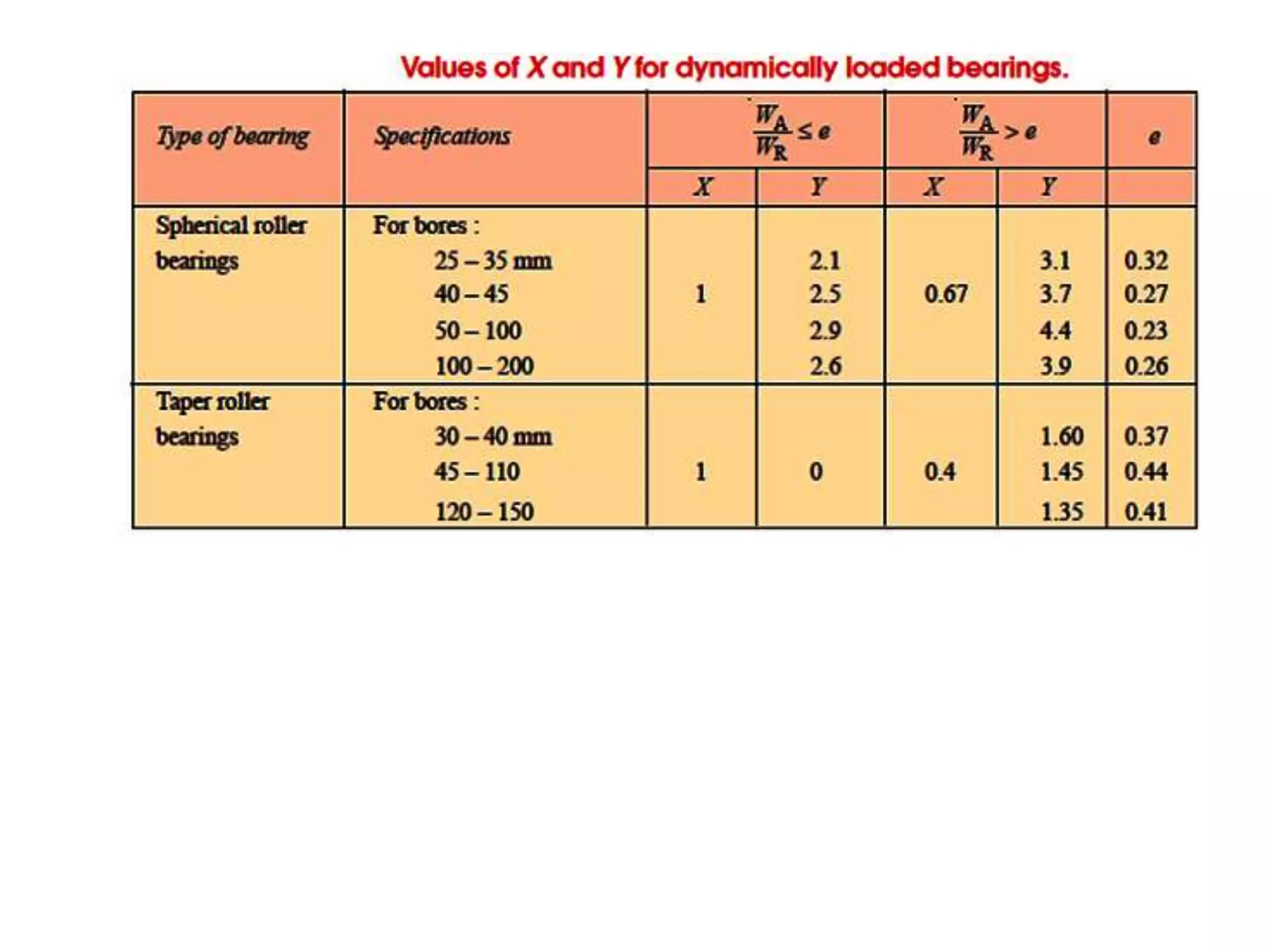
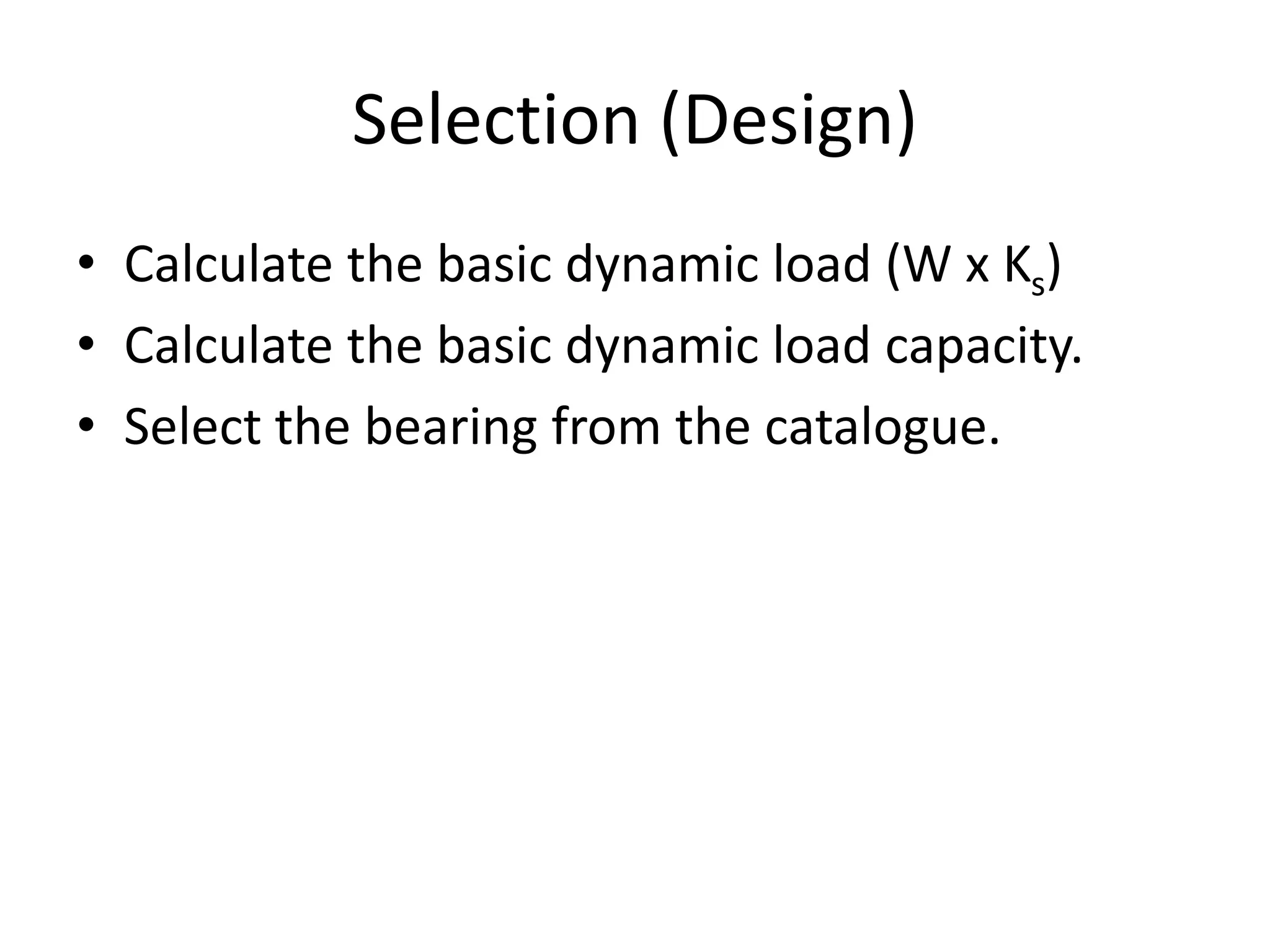
The document discusses various types of bearings, focusing on rolling contact bearings (anti-friction) and sliding contact bearings, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages. It details the selection criteria, classifications, and rating systems for different bearing types, including ball and roller bearings, along with their designations and load capacities. Additionally, it provides information on bearing life and reliability, emphasizing the design and manufacturing considerations for optimal performance.