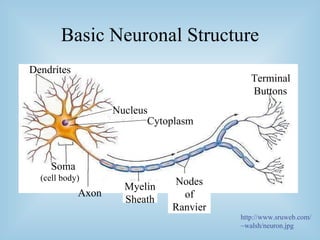
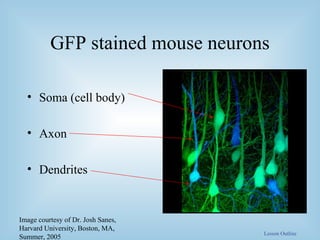
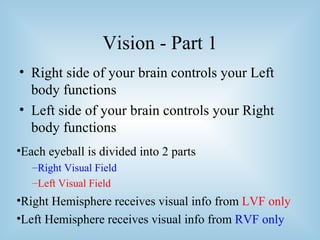
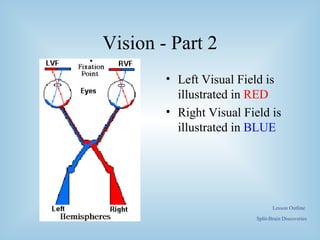
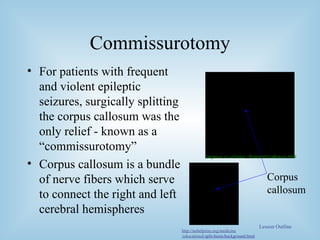
The document provides an overview of the split-brain phenomenon. It discusses the basic structure of neurons and the brain, left and right hemisphere specialization, and how vision is processed differently in each hemisphere. It then describes split-brain patients who had their corpus callosum severed, and the discoveries this revealed about brain lateralization of functions like language and face recognition. Studies on these patients contributed to understanding of brain localization of function.