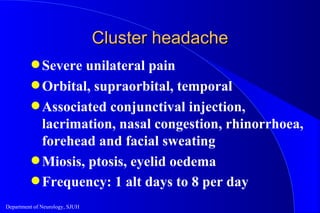
The document discusses various types of acute headaches that require urgent evaluation in the emergency department. It covers neurological emergencies that can cause acute headaches like subarachnoid hemorrhage and raised intracranial pressure. The most important part of evaluating acute headaches is taking a thorough history. It then describes characteristics of different headache types like migraines, cluster headaches, and tension headaches that may present acutely. It highlights that a CT scan identified subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, and meningitis as causes of sudden onset headaches in some emergency department patients.