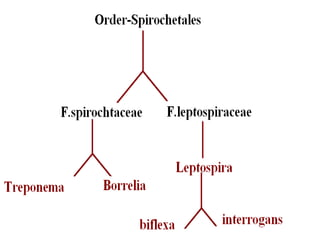
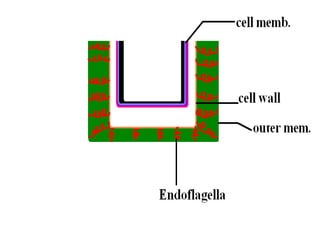
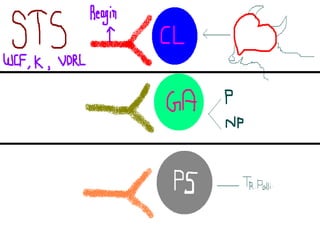
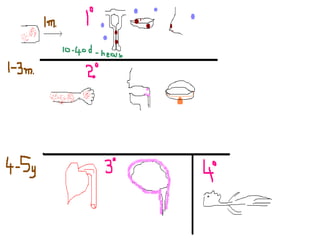
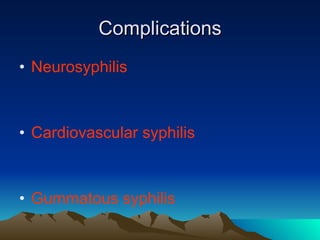
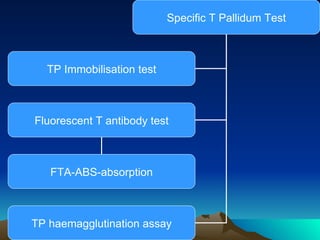
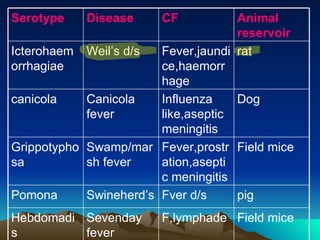
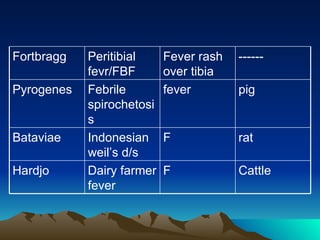
This document summarizes information about Spirochetes bacteria including Treponema pallidum, the causative agent of syphilis. It describes the morphology, stages of infection (primary, secondary, tertiary), methods of diagnosis (microscopy, serological tests), treatment (penicillin), and prevention of syphilis. It also discusses other Spirochetes bacteria such as Borrelia burgdorferi which causes Lyme disease, and Leptospira interrogans which can cause Weil's disease.