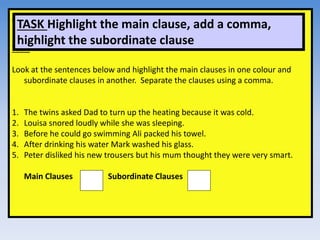
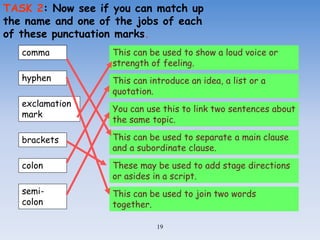
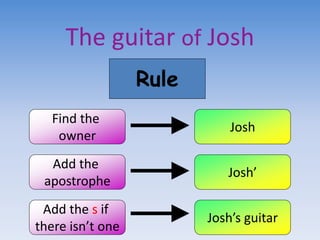
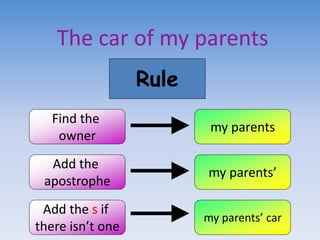
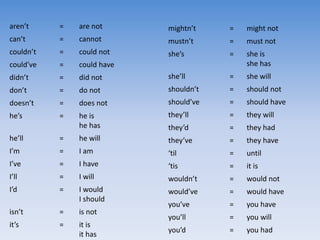
This document provides information and examples about teaching grammar, punctuation, and spelling (SPaG) in a 40 minute lesson. It discusses teaching homophones, using apostrophes correctly, identifying main and subordinate clauses in sentences, and other grammar topics. Examples of common homophones, correct apostrophe use, and identifying clauses in sentences are provided, along with exercises for students to practice these skills.