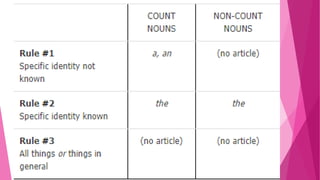
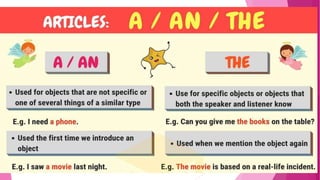
This document provides information about the usage of articles (a, an, the) in English. It discusses the differences between definite and indefinite articles, and explains the rules for using "a" versus "an". It also covers exceptions, such as using "an" before words beginning with consonants that have vowel sounds. Additionally, it addresses the omission of articles in certain cases, like with uncountable nouns, pronouns, and abstract nouns. The document aims to clearly define the different types of articles and the guidelines for applying them correctly in sentences.