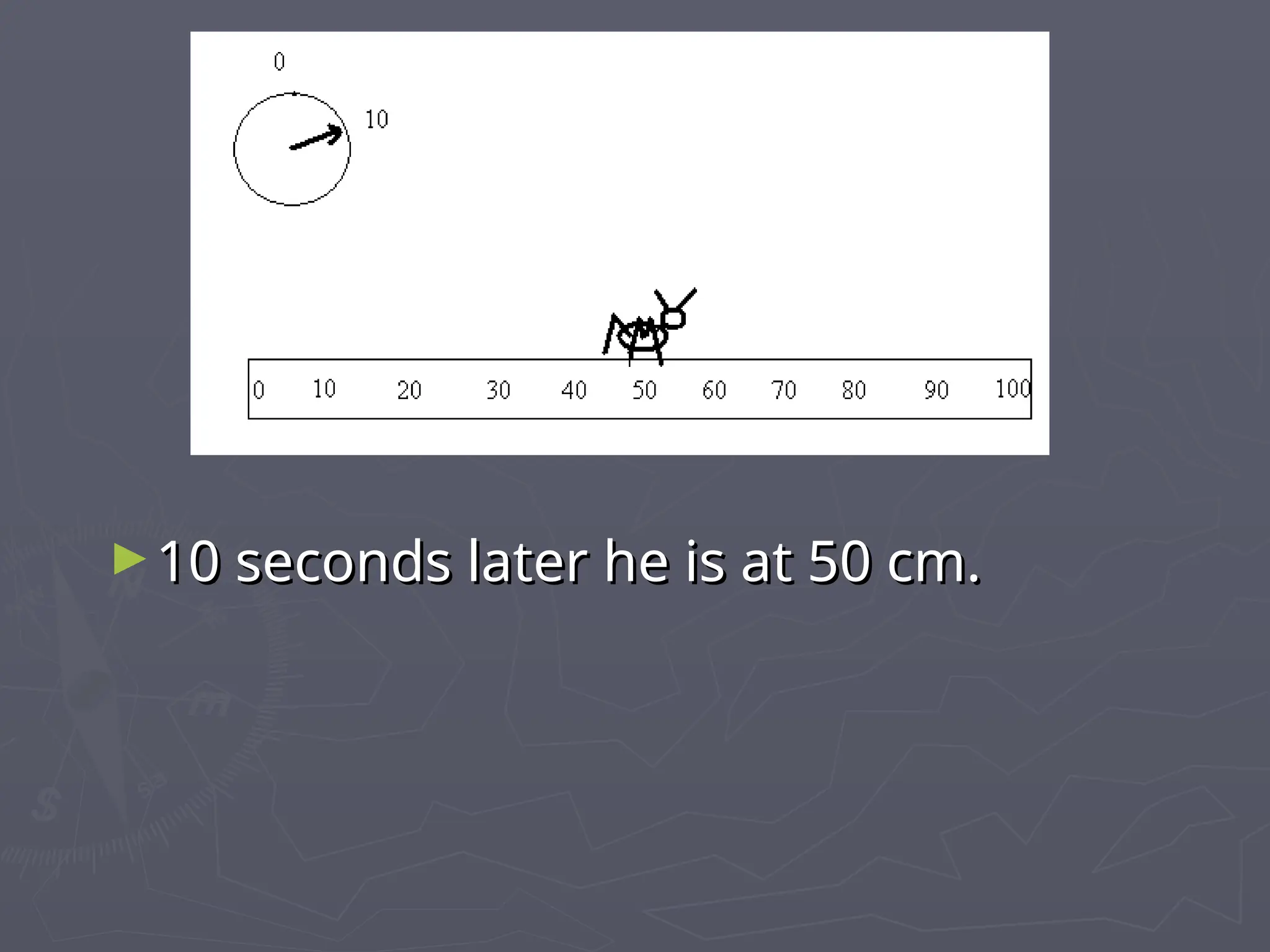
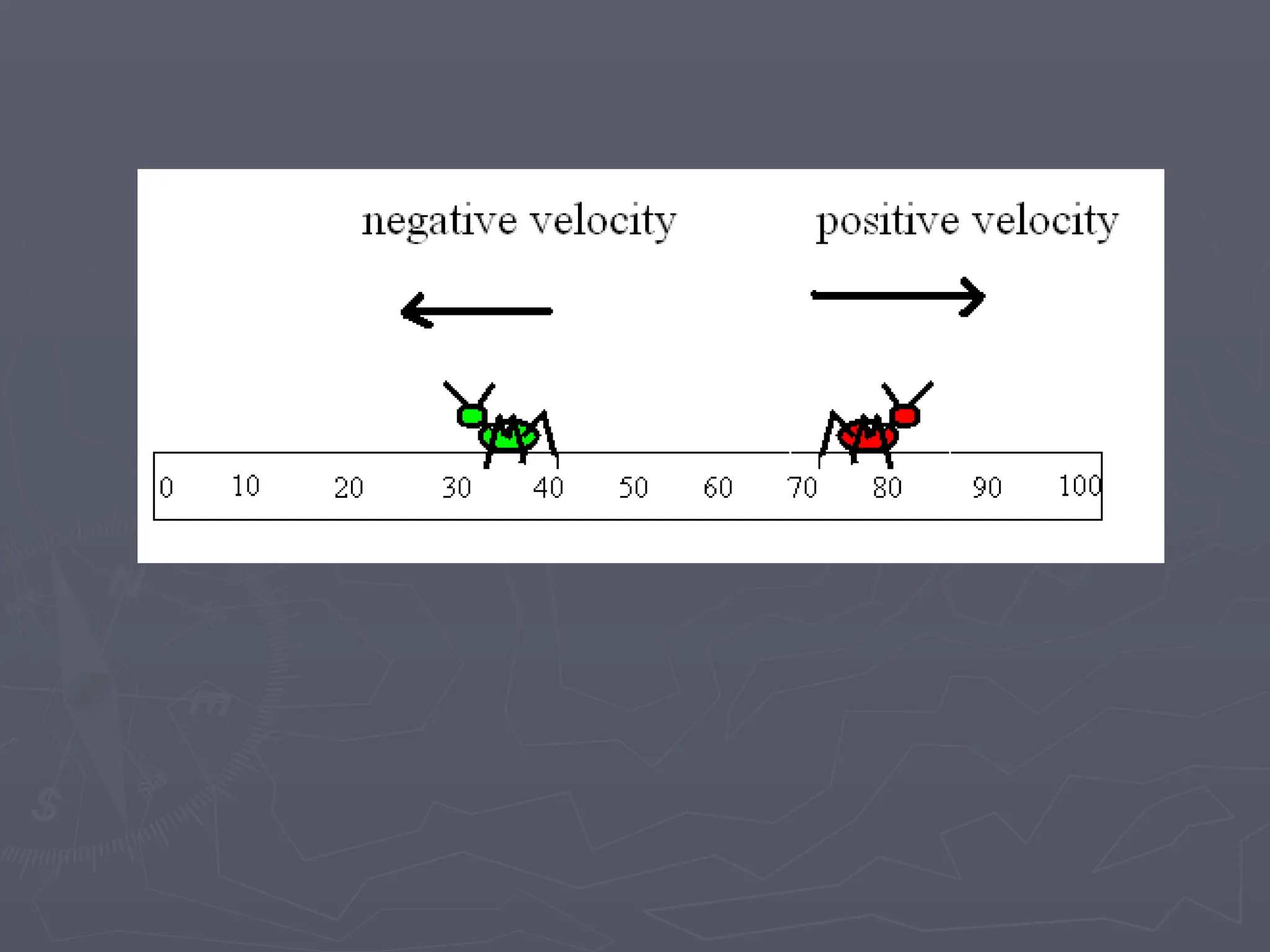
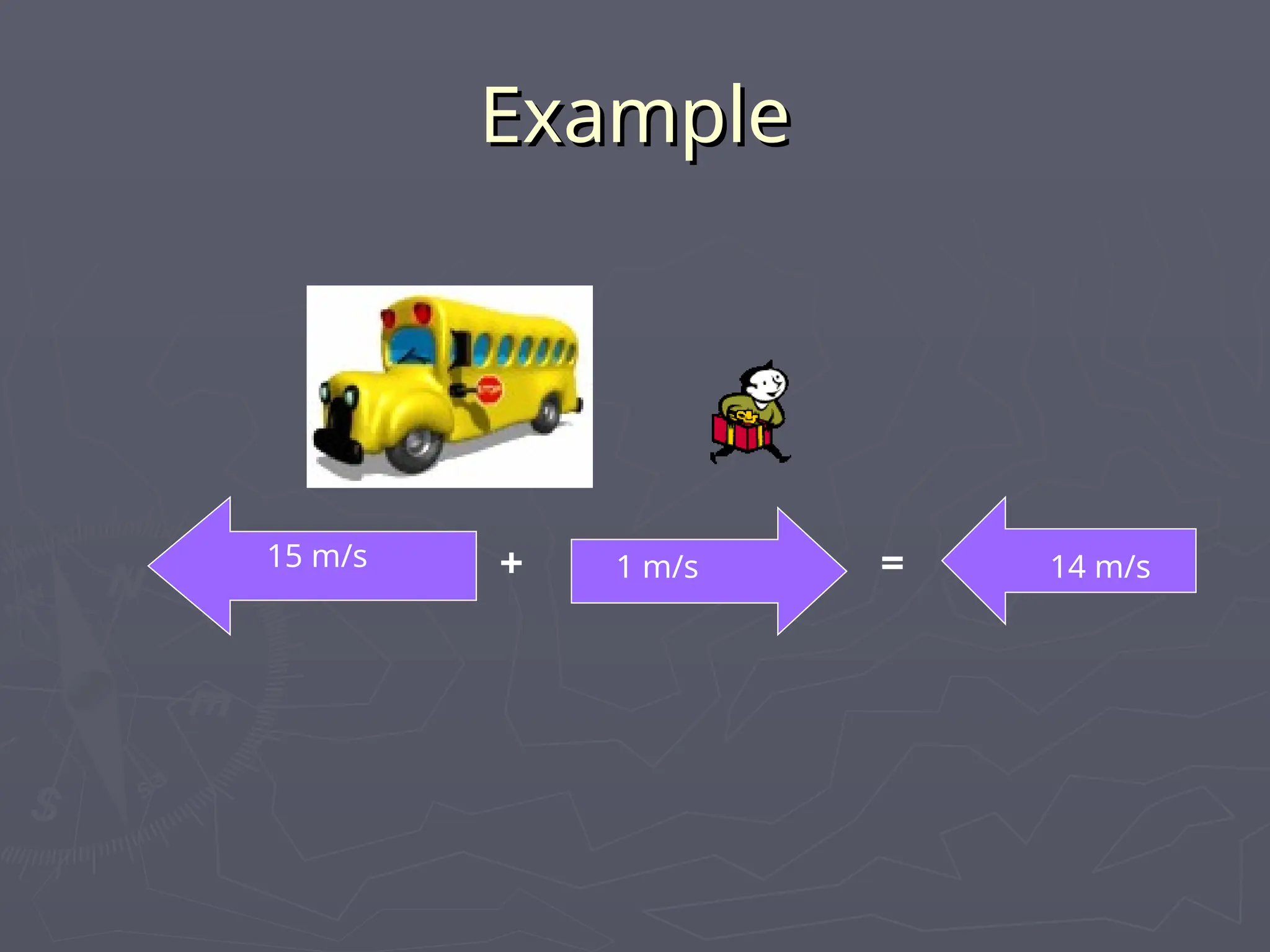
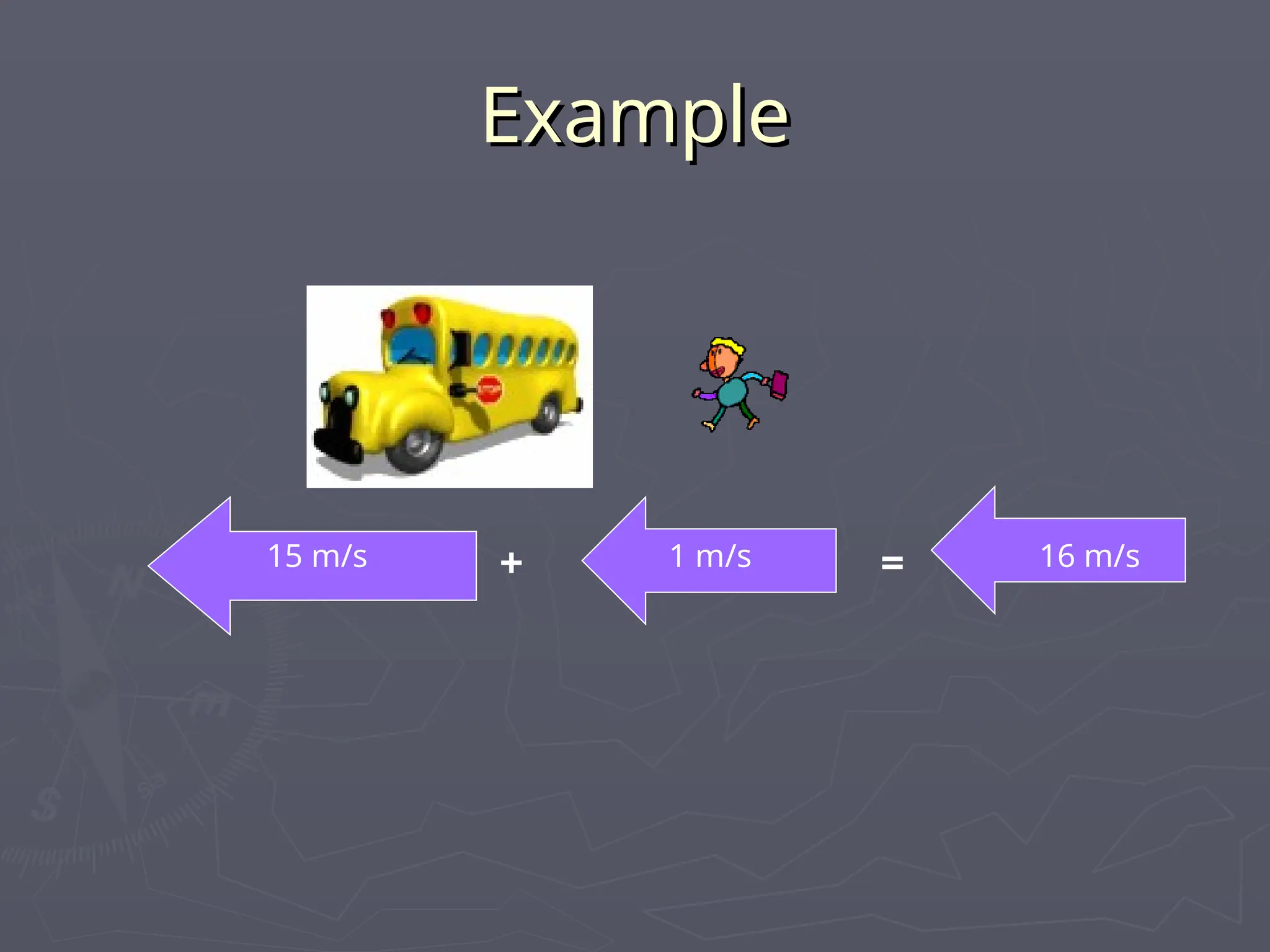
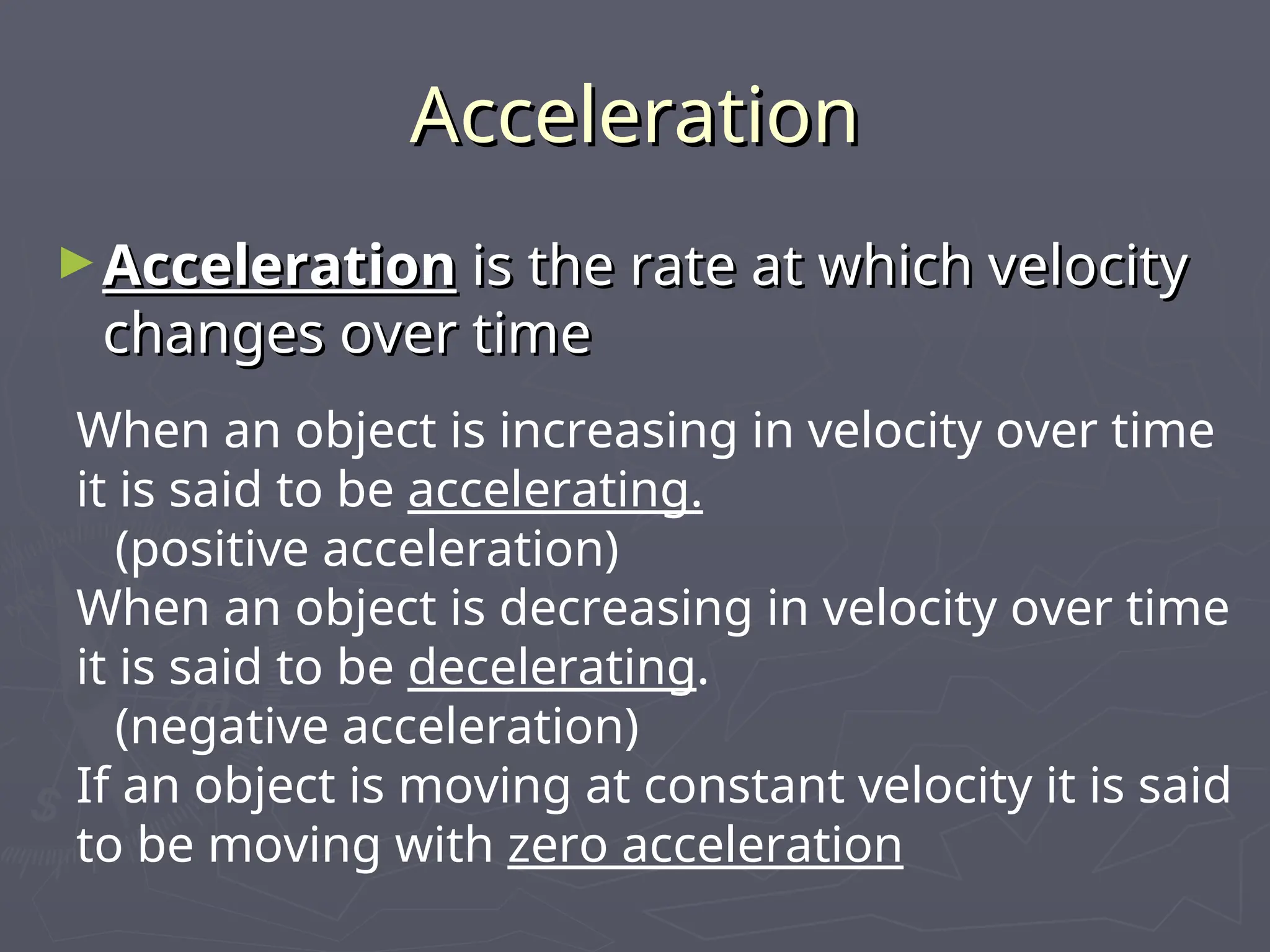
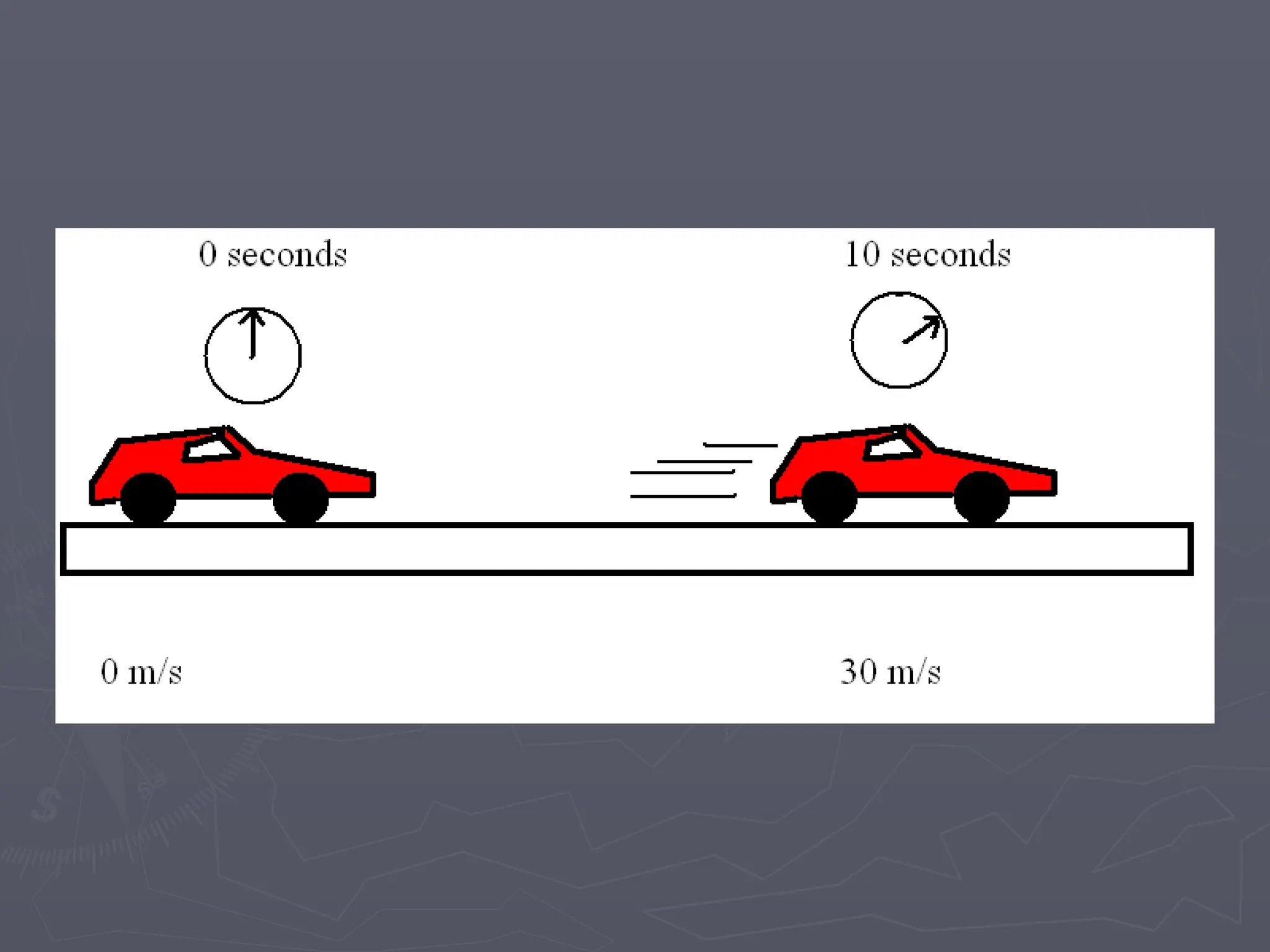
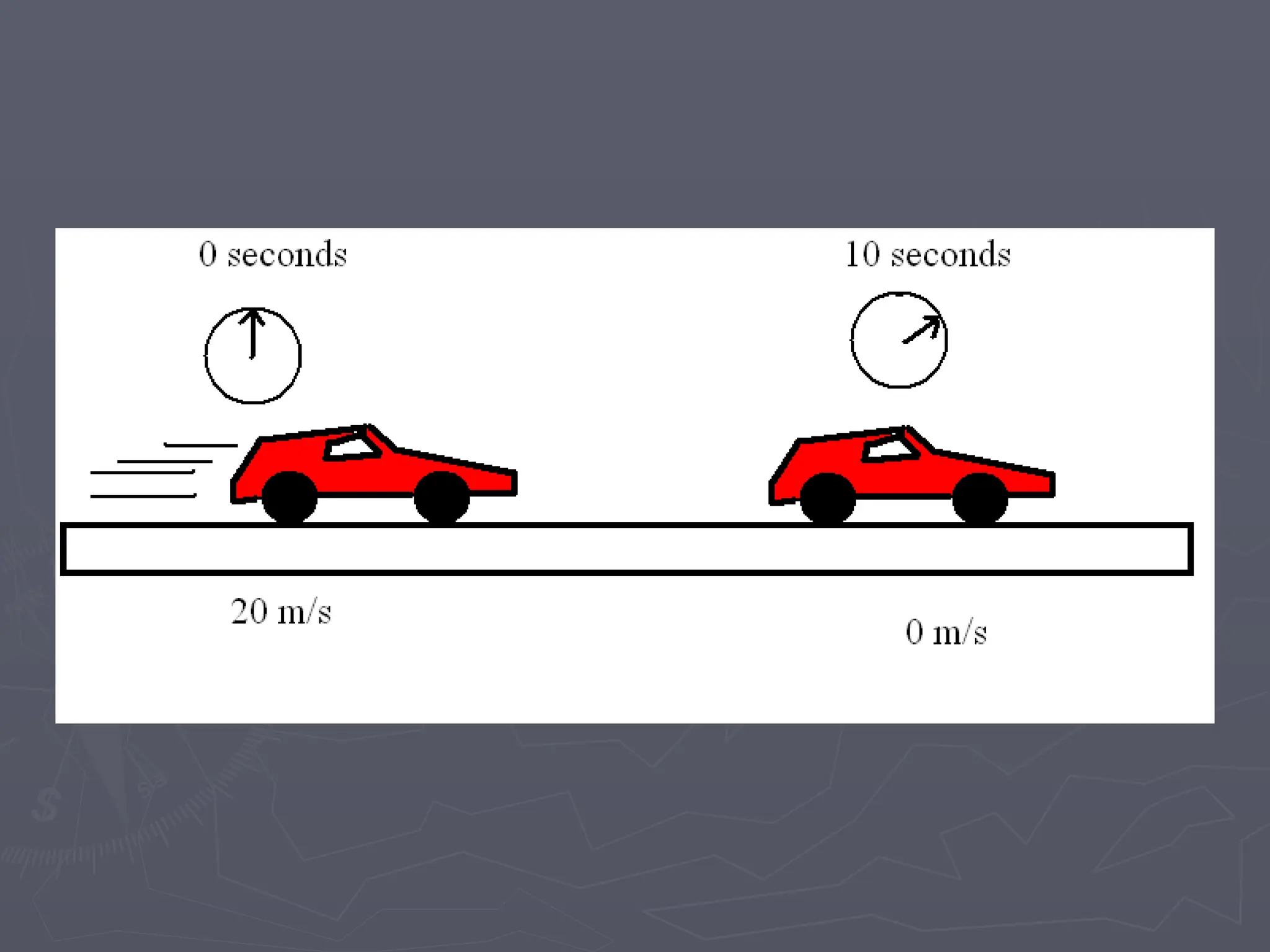
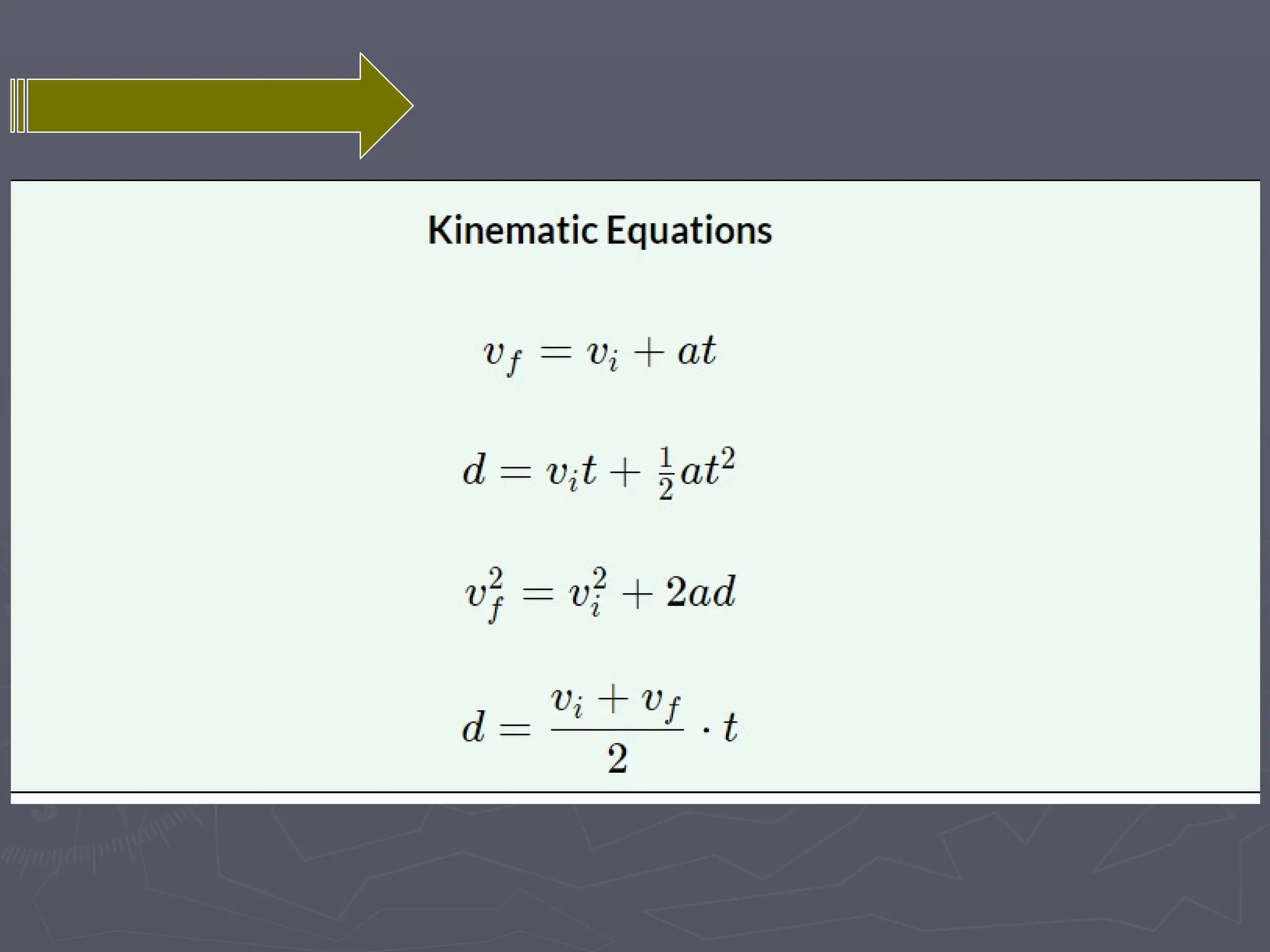
The document discusses the concepts of motion, speed, velocity, and acceleration, explaining their definitions and relationships. It highlights how speed is defined as distance traveled over time, while velocity includes direction, and details various scenarios for calculating both. The document also addresses acceleration as the rate of change of velocity and provides examples of calculating speed, velocity, and acceleration in different contexts.