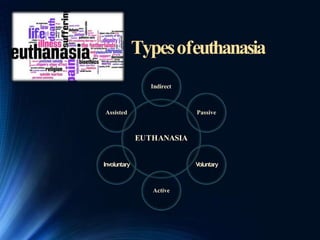
The document discusses euthanasia, defined as the painless killing of a patient suffering from an incurable disease or in irreversible coma, and provides an overview of its types, reasons, and legal status in various regions. It highlights the importance of euthanasia as a matter of personal choice and autonomy while presenting arguments for and against it. Additionally, it outlines different forms of euthanasia including voluntary, non-voluntary, passive, and active euthanasia, emphasizing the moral and ethical considerations surrounding the practice.