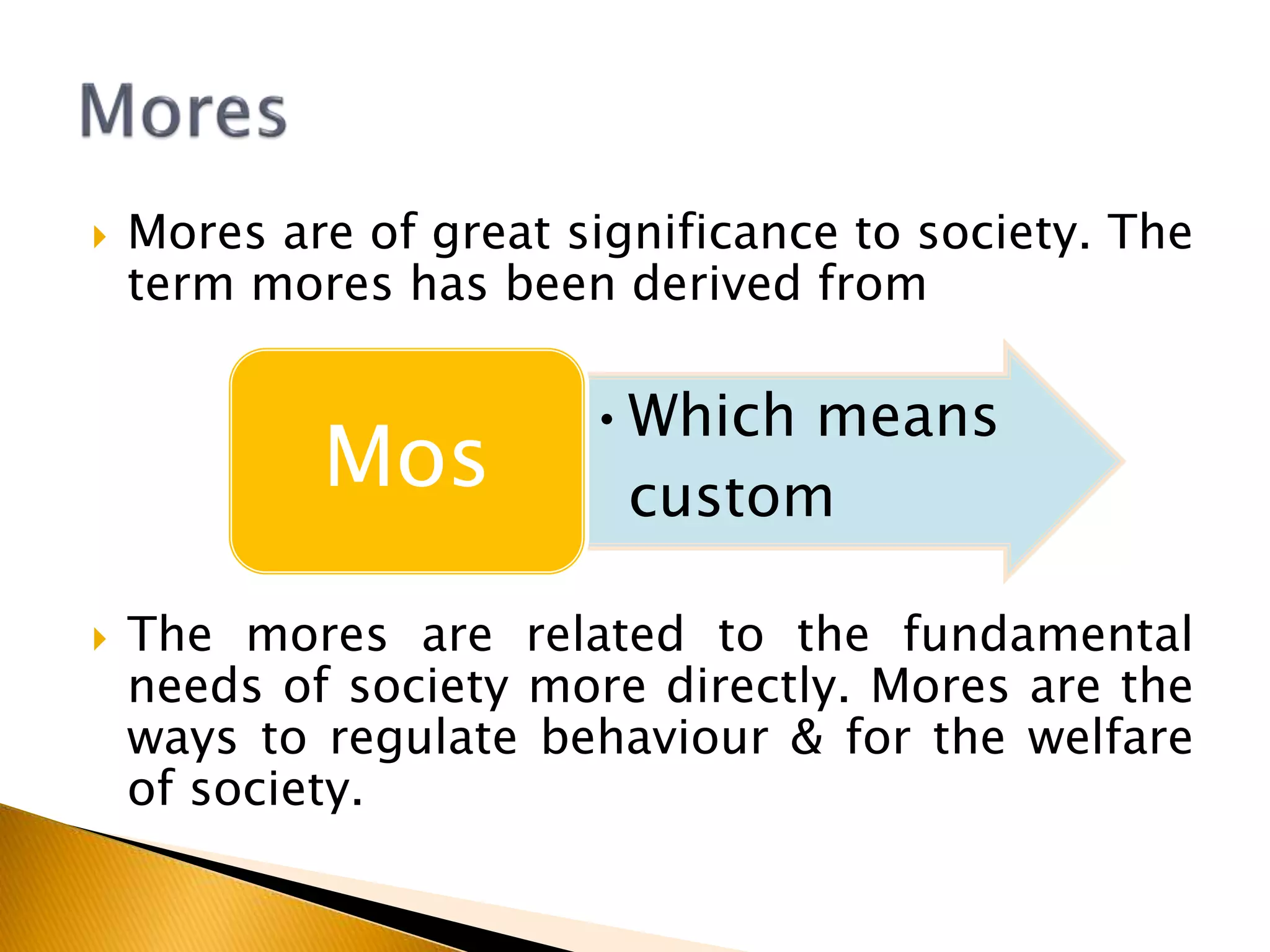
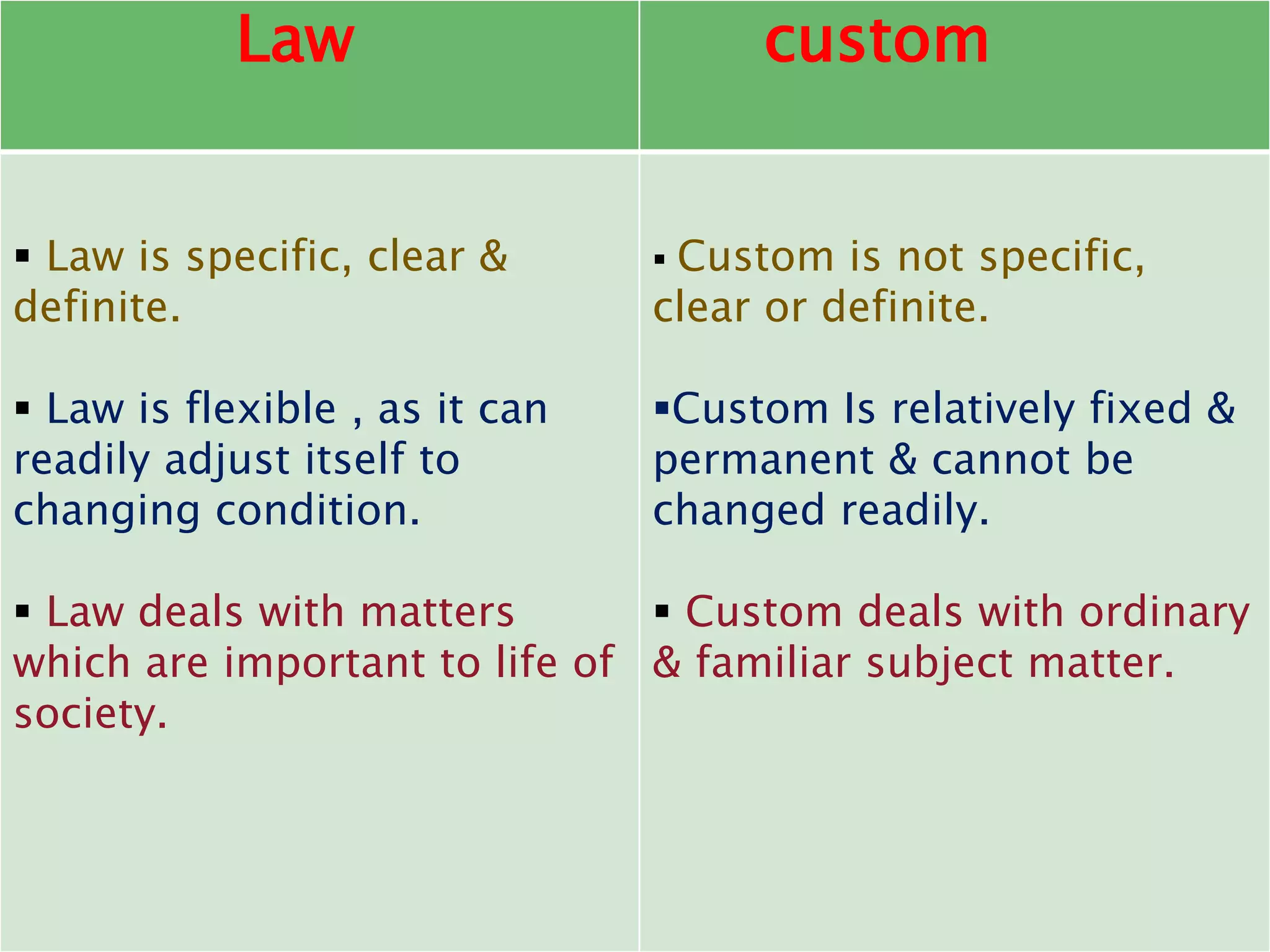
The document discusses the concept of social norms, including their definitions, classifications (folkways, mores, customs, and fashions), and roles in society as standards of behavior that influence interactions and maintain social order. It highlights how these norms are internalized, vary across cultures, and are enforced through social control, emphasizing their significance for individual behavior and societal cohesion. Additionally, the document outlines the role of healthcare professionals, such as nurses, in promoting adherence to these norms and managing social behavior.