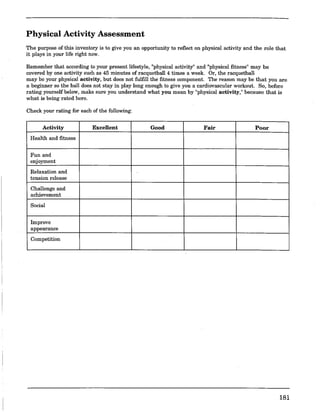
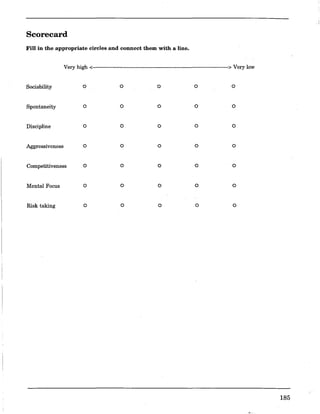
This document provides an overview and guidelines for the Instructional Physical Education 20 and 30 curriculum in Saskatchewan secondary schools. It discusses the aims, goals and perspectives of the physical education program, which includes foundational, activity, and personal-cultural components. It also addresses initiatives like common essential learnings, adaptive dimensions, gender equity, and resource-based learning. The document provides examples of instructional approaches, assessment strategies, activity area guidelines, and planning templates to assist physical education teachers in curriculum delivery.




























































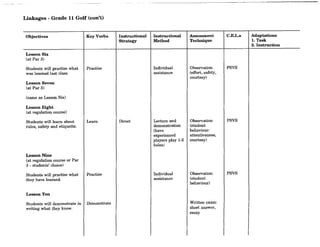
![Instruction Plan
Objectives Instructional Strategies & Methods Assessment Techniques Time- !
lines
Strategies Methods of Methods of Ongoing Student Quizzes and Tests
IOrganization Data Recording Activities
IF'oundational
Indirect Experiential Independent
I
nd Direct Interactive
!Learning Objectives E
1l ~ I
{l • 1l • ~
*
.~ • • S " •
*
S 0
~ • 1l ,!l ,!l ~
a e
!:i $l • :lj • ,!l
J
• • • • ~" ~
"E
" ,!l •
~ • • s
~ <! • E • e
~ 8 -"
.~ • ~
" '13Q • ~ • " ,!l.;: • ~
" • • s
~
~
• ,!l -"
" • r:;
"
0 0
• 0
•
" ~
0
.;:
"' § -" • •
i
•• ] • ~ "' 0
" • • "" '" -li
*
, "" ~ • '" "
l! e 0
~ e •
i "] " ~ gp
" • "" :§ ~"- 13 • ,§ 11 • • " • " "• ,
'"
•
~ ~ • .8 e "l!
.8 2l OiMethods
~ ~ " :; • II • " 0': ~Ii
0
• ~ - • ~ ril -" :E :EQ-'"
"- 0
" " 0
'"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spe111physicaleducationmanual-170113160431/85/Spe-111-physical-education-manual-64-320.jpg)















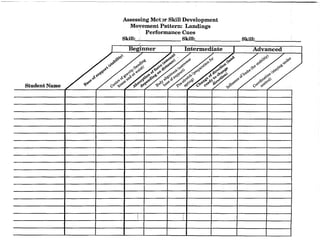
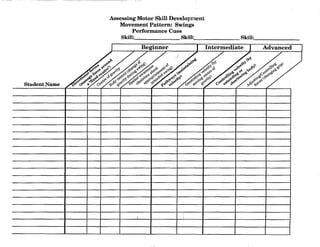
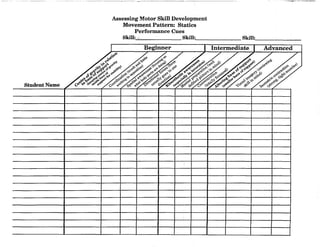
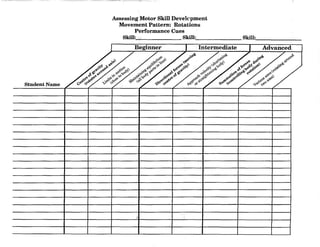











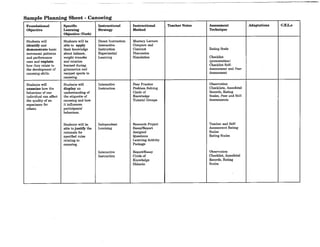
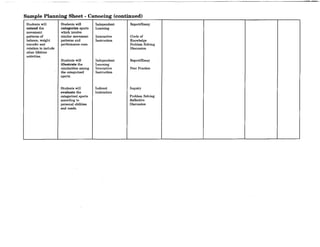
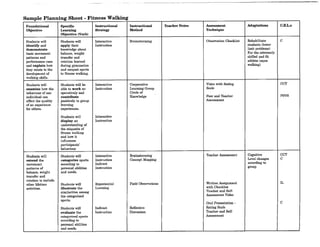
































































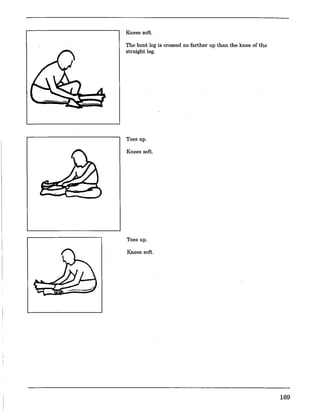

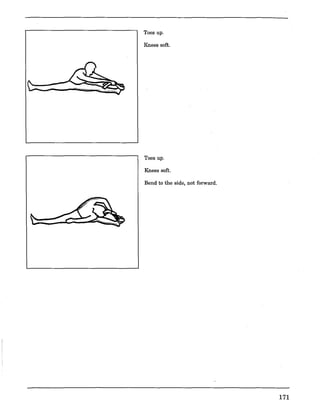








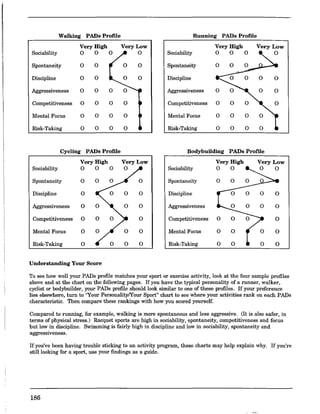
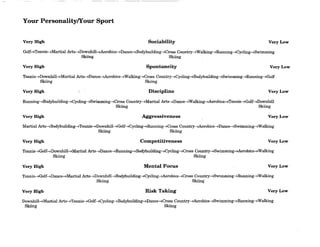



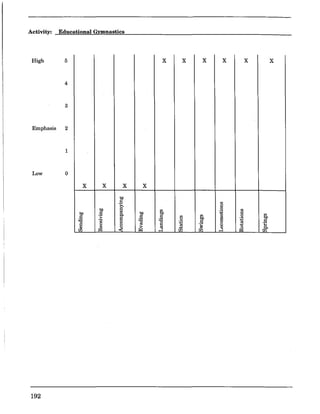
![Charting Movement Patterns
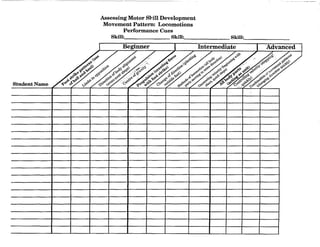
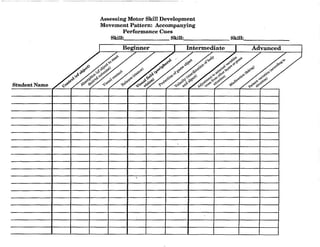
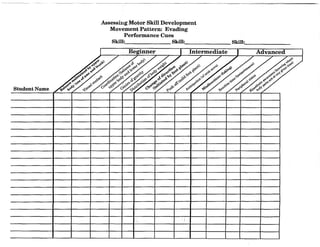
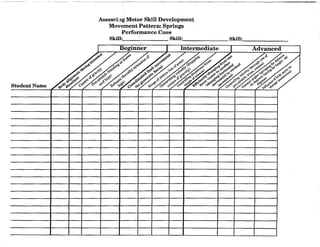
When planning for the activity component, you might want to use this chart to diagram the movement
patterns. This will serve as a check to make sure that your students are receiving a well rounded
exposure to all movement patterns according to the percentages given on page 11 of this document.
Samples appear on the next two pages.
Activity:
High 5
4
3
Emphasis 2
1
Low 0
~
'".~
.::
bJ) § '"
0
'"bJ)
.~
bJ)
~
:0 g
;@ s: .S '" '"
0
'";a <> bJ) s :g bJ)
'$ 0 '1:S :0
.~ 0 .@.:: <> <>
" §
"
<> ...,
" .
~ .;;] rt 00 0
~ ~rn
'""
rn
'""
191](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spe111physicaleducationmanual-170113160431/85/Spe-111-physical-education-manual-199-320.jpg)