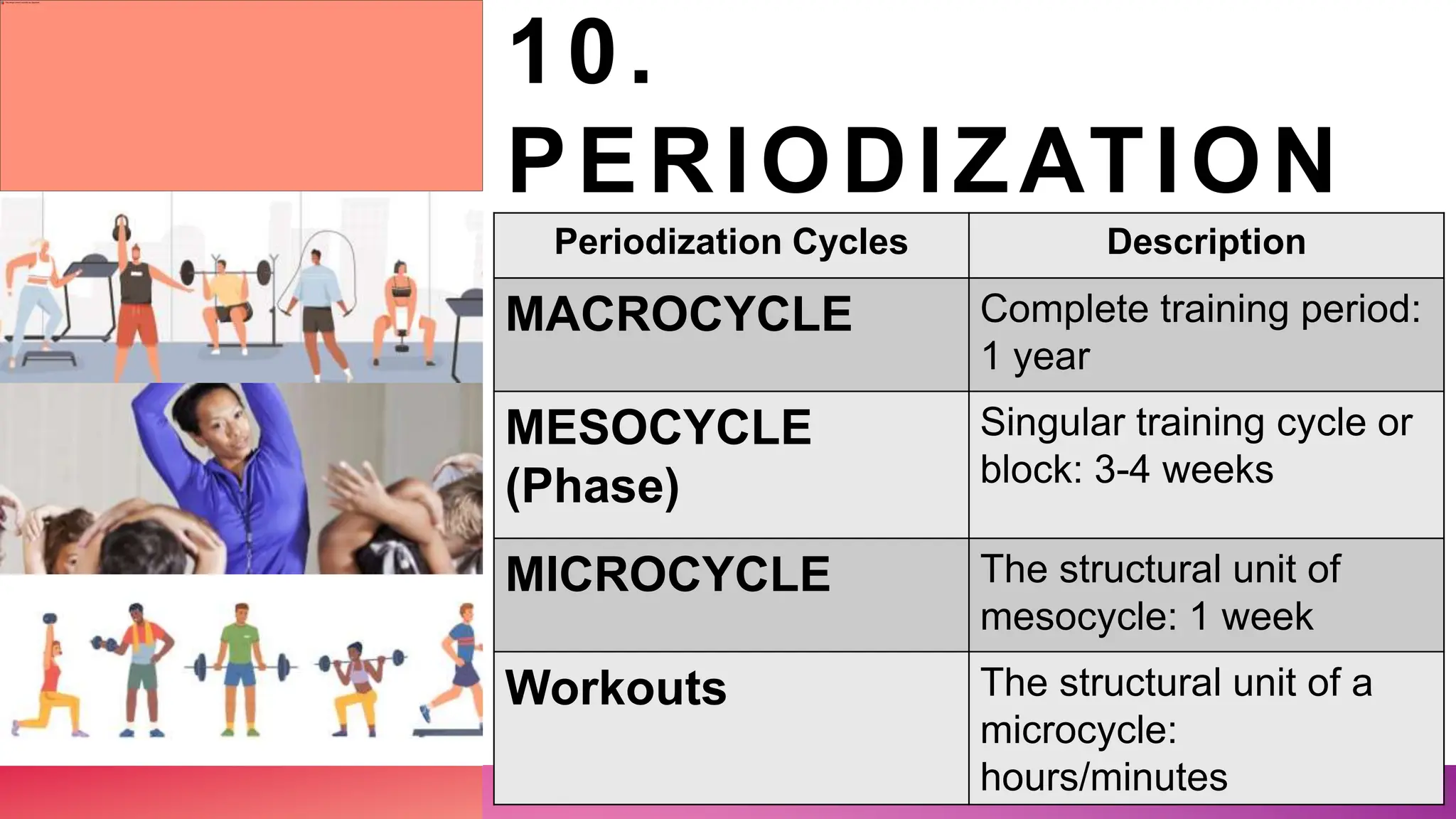
This document outlines 10 principles of exercise: 1) specificity, which means exercise must be tailored to goals, 2) overload to stress the body beyond its normal limits, 3) FITT which refers to frequency, intensity, time and type of training, 4) progression to gradually increase intensity, 5) regression to decrease demands, 6) individualization as exercise should be specific to each person, 7) recovery to allow the body to rest and repair, 8) adaptation as the body programs muscles, 9) variation to prevent plateaus and injury, and 10) periodization to systematically vary training over periods of time.