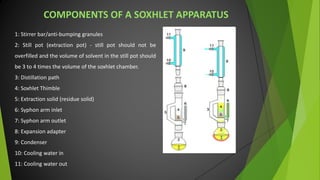
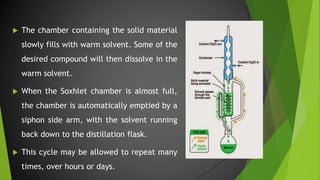
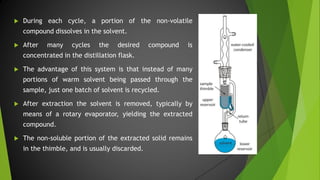
The document discusses the Soxhlet extractor, a laboratory apparatus invented in 1879 designed for the continuous extraction of compounds from solid materials using a solvent. It describes the working mechanism of the extractor, the components involved, and its applications in fields like pharmaceutics, environment, and foodstuffs. While it offers efficient extraction, the process is lengthy and can require specific solvent mixtures for optimal results.