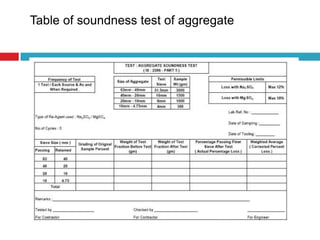
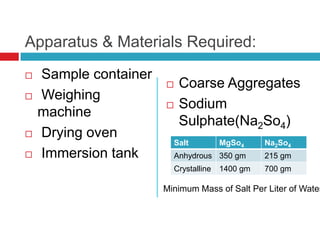
This document describes a test to determine the resistance of aggregates to disintegration from saturated sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate solutions. The soundness test involves immersing coarse aggregate samples in a sodium sulfate solution for 24 hours, then drying and cooling them in cycles over 10 days. The percentage loss is calculated by comparing the initial and final weights, with aggregates showing less than 25% loss considered suitable for use in road pavement due to sufficient resistance to weathering.





![Observation & Calculation:
Percentage loss = *100 %
W0-W1
W0
Where, w0 = initial wt of sample
w1= final retained wt on sample
container after 10 cycles
For example:
Let w0=100 gm
w1= 82 gm
Then, percentage loss = [(100-82)/100] *100 %
= 18 % which is less than 25%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soundnesstest-140710051430-phpapp02/85/Soundness-test-7-320.jpg)