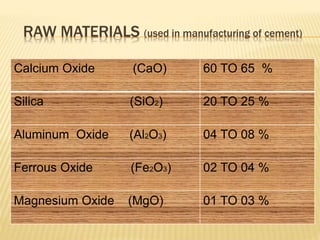
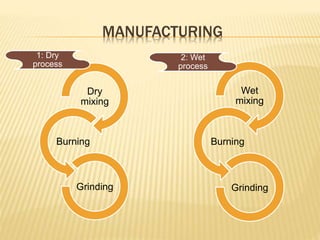
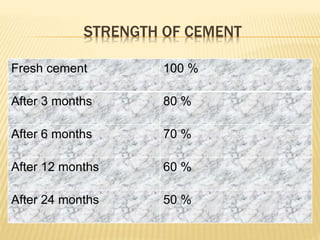
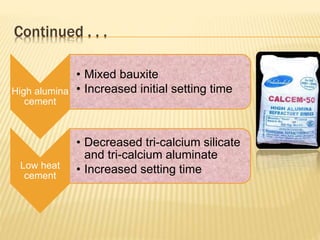
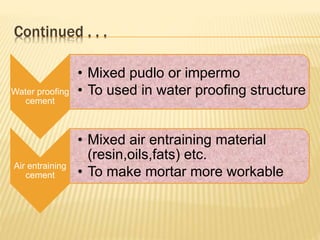
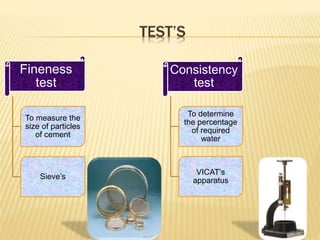
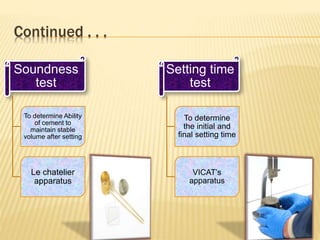
The document discusses cement, including its historical background, composition, manufacturing processes (dry and wet), and various classifications. It highlights the importance of cement in construction, transportation, and civil engineering applications, as well as different types of cement such as rapid hardening, high alumina, and waterproof cement. The document concludes by emphasizing cement's role as a crucial binding material developed by Joseph Aspdin in 1824.