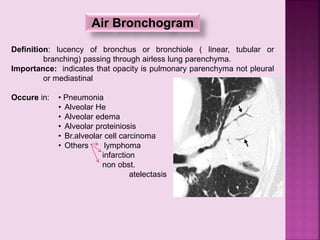
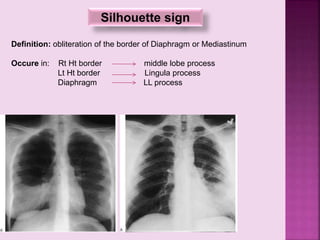
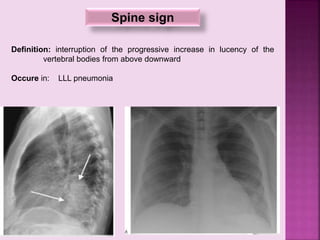
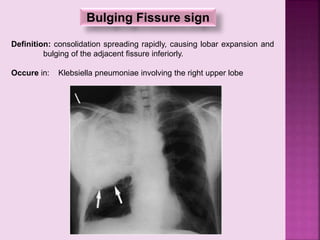
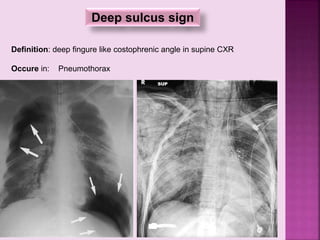
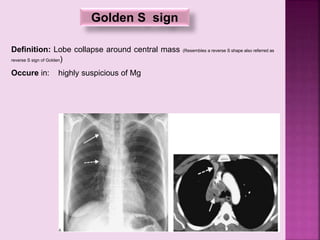
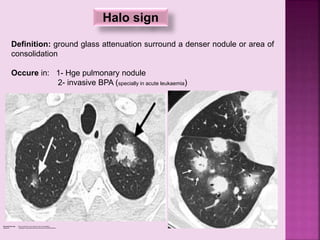
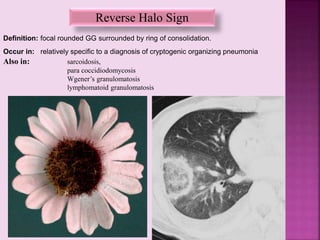
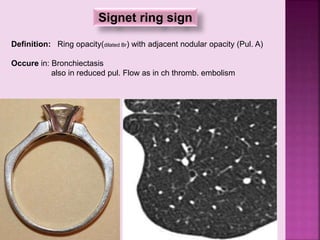
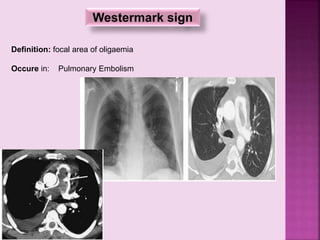
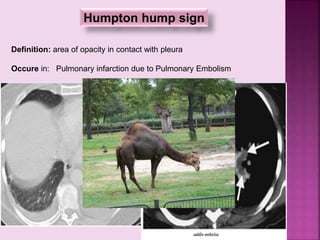
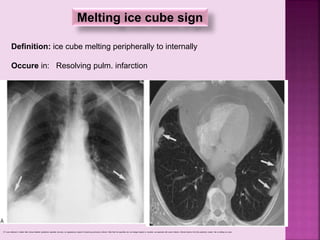
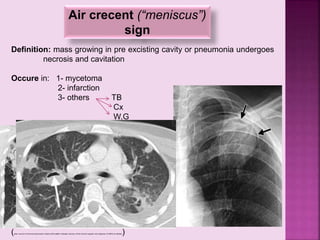
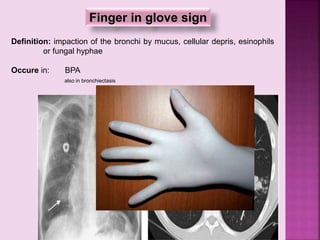
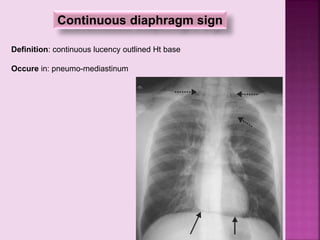
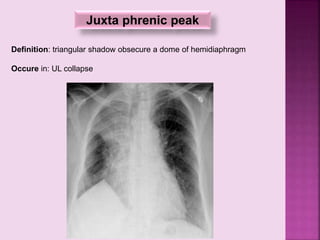
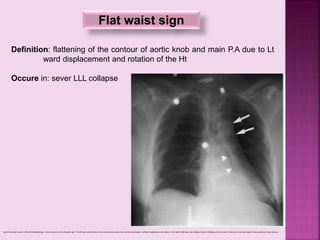
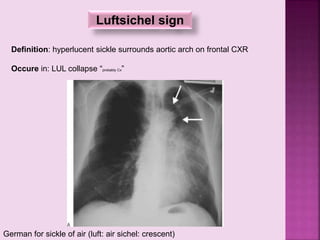
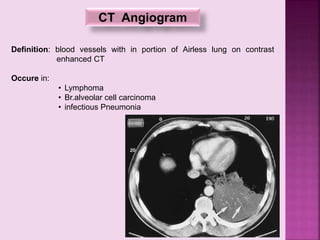
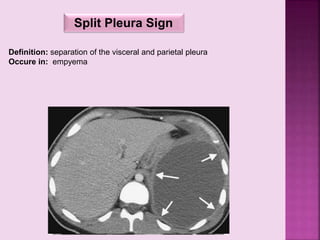
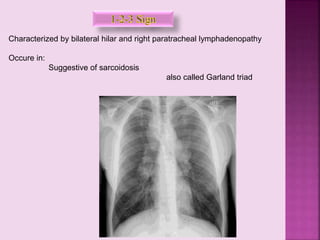
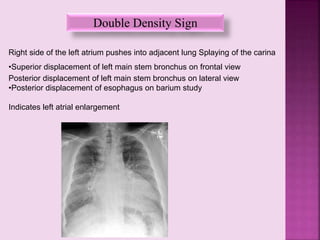
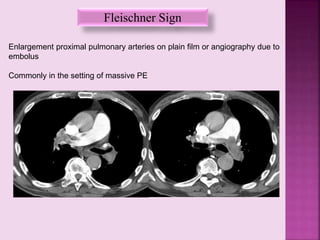
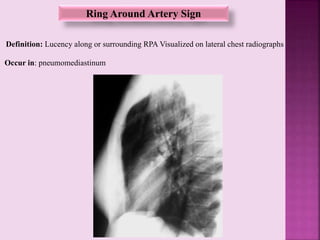
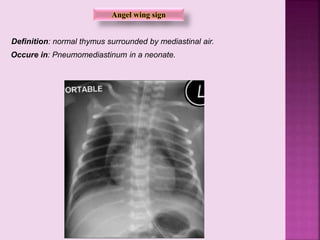
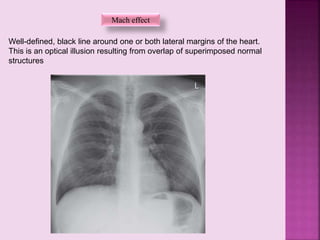
This document defines and describes several radiographic signs seen on chest x-rays. It defines signs such as the air bronchogram, silhouette sign, spine sign, and bulging fissure sign. For each sign, it provides a brief definition and examples of medical conditions in which the sign may occur, such as pneumonia, lung tumors, and pulmonary embolism. The document aims to inform radiologists and doctors about important signs seen on chest x-rays and their potential medical implications.