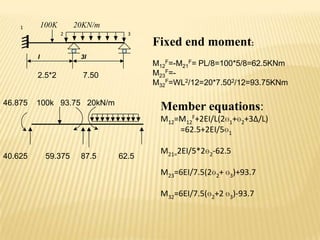
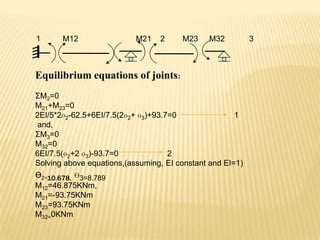
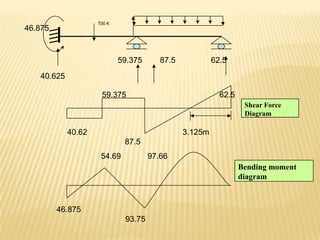
This document provides an overview of a presentation on solving statically indeterminate structures using the slope deflection method. The presentation covers the assumptions, sign convention, fundamental equations, and an example problem of determining support moments in a continuous beam. The slope deflection method represents end moments in terms of deflections. An example problem is worked through to determine the support moments in a continuous beam with three spans by writing member equations from the fundamental equation and applying joint equilibrium equations.






![FUNDAMENTAL SLOPE
DEFLECTION EQUATION:
W
A
ɵA
∆
MAB
ɵB
MB
A
MAB=2EI/L[2ɵA+ɵB+3∆/L]+FMAB
MBA=2EI/L[2ɵB+ɵA+3∆/L]+FMBA
Here
E=modulus of elasticity of the material
I=moment of inertia of the beam,
L=span
FMAB=Fixed end moment at A
FMBA=Fixed end moment at B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slopedeflectiontanni-131209010426-phpapp01/85/solving-statically-indeterminate-structure-by-slope-deflection-method-8-320.jpg)